
An oil platform, oil rig, offshore platform, or oil and/or gas production platform is a large structure with facilities to extract, and process petroleum and natural gas that lie in rock formations beneath the seabed. Many oil platforms will also contain facilities to accommodate their workforce, although it is also common for there to be a separate accommodation platform bridge linked to the production platform. Most commonly, oil platforms engage in activities on the continental shelf, though they can also be used in lakes, inshore waters, and inland seas. Depending on the circumstances, the platform may be fixed to the ocean floor, consist of an artificial island, or float. In some arrangements the main facility may have storage facilities for the processed oil. Remote subsea wells may also be connected to a platform by flow lines and by umbilical connections. These sub-sea solutions may consist of one or more subsea wells or of one or more manifold centres for multiple wells.

Offshore construction is the installation of structures and facilities in a marine environment, usually for the production and transmission of electricity, oil, gas and other resources. It is also called maritime engineering.

A floating production storage and offloading (FPSO) unit is a floating vessel used by the offshore oil and gas industry for the production and processing of hydrocarbons, and for the storage of oil. An FPSO vessel is designed to receive hydrocarbons produced by itself or from nearby platforms or subsea template, process them, and store oil until it can be offloaded onto a tanker or, less frequently, transported through a pipeline. FPSOs are preferred in frontier offshore regions as they are easy to install, and do not require a local pipeline infrastructure to export oil. FPSOs can be a conversion of an oil tanker or can be a vessel built specially for the application. A vessel used only to store oil is referred to as a floating storage and offloading (FSO) vessel.
Marine architecture is the design of architectural and engineering structures which support coastal design, near-shore and off-shore or deep-water planning for many projects such as shipyards, ship transport, coastal management or other marine and/or hydroscape activities. These structures include harbors, lighthouses, marinas, oil platforms, offshore drillings, accommodation platforms and offshore wind farms, floating engineering structures and building architectures or civil seascape developments. Floating structures in deep water may use suction caisson for anchoring.

Offshore drilling is a mechanical process where a wellbore is drilled below the seabed. It is typically carried out in order to explore for and subsequently extract petroleum that lies in rock formations beneath the seabed. Most commonly, the term is used to describe drilling activities on the continental shelf, though the term can also be applied to drilling in lakes, inshore waters and inland seas.
Subsea is fully submerged ocean equipment, operations or applications, especially when some distance offshore, in deep ocean waters, or on the seabed. The term is frequently used in connection with oceanography, marine or ocean engineering, ocean exploration, remotely operated vehicle (ROVs) autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), submarine communications or power cables, seafloor mineral mining, oil and gas, and offshore wind power.
"Offshore", when used in relation to hydrocarbons, refers to operations undertaken at, or under the, sea in association with an oil, natural gas or condensate field that is under the seabed, or to activities carried out in relation to such a field. Offshore is part of the upstream sector of the oil and gas industry.

A fixed platform is a type of offshore platform used for the extraction of petroleum or gas. These platforms are built on concrete and/or steel legs anchored directly onto the seabed, supporting a deck with space for drilling rigs, production facilities and crew quarters. Such platforms are, by virtue of their immobility, designed for very long-term use. Various types of structure are used, steel jacket, concrete caisson, floating steel and even floating concrete. Steel jackets are vertical sections made of tubular steel members, and are usually piled into the seabed. Concrete caisson structures, pioneered by the Condeep concept, often have in-built oil storage in tanks below the sea surface and these tanks were often used as a flotation capability, allowing them to be built close to shore and then floated to their final position where they are sunk to the seabed. Fixed platforms are economically feasible for installation in water depths up to about 500 feet ; for deeper depths a floating production system, or a subsea pipeline to land or to shallower water depths for processing, would usually be considered.
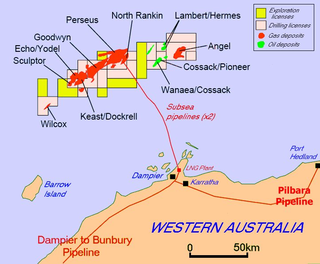
The North West Shelf Venture, situated in the north-west of Western Australia, is Australia's largest resource development project. It involves the extraction of petroleum at offshore production platforms, onshore processing and export of liquefied natural gas, and production of natural gas for industrial, commercial and domestic use within the state.

Grup Servicii Petroliere is a Romanian company providing offshore integrated services for oil and gas industry. The company, established in 2004, is a member of UPETROM Group.

A pipelaying ship is a maritime vessel used in the construction of subsea infrastructure. It serves to connect oil production platforms with refineries on shore. To accomplish this goal a typical pipelaying vessel carries a heavy lift crane, used to install pumps and valves, and equipment to lay pipe between subsea structures.
The Magnus oilfield is a large oilfield in the United Kingdom's zone of North Sea. It is located 160 kilometres (99 mi) north-east of the Shetland Islands. The field is located mainly in Block 211/12a. Resources are estimated to total 1.54 billion barrels of oil, of which 869 million barrels are recoverable reserves.
Roncador oil field is a large oil and gas field located in the Campos Basin, 125 km (78 mi) off the coast of Brazil, northeast from Rio de Janeiro. It covers a 111 km2 (43 sq mi) area and reaches depths between 1,500 and 1,900 metres.

Suction caissons are a form of fixed platform anchor in the form of an open bottomed tube embedded in the sediment and sealed at the top while in use so that lifting forces generate a pressure differential that holds the caisson down. They have a number of advantages over conventional offshore foundations, mainly being quicker to install than deep foundation piles and being easier to remove during decommissioning. Suction caissons are now used extensively worldwide for anchoring large offshore installations, like oil platforms, offshore drillings and accommodation platforms to the seafloor at great depths. In recent years, suction caissons have also seen usage for offshore wind turbines in shallower waters.

Offshore geotechnical engineering is a sub-field of geotechnical engineering. It is concerned with foundation design, construction, maintenance and decommissioning for human-made structures in the sea. Oil platforms, artificial islands and submarine pipelines are examples of such structures. The seabed has to be able to withstand the weight of these structures and the applied loads. Geohazards must also be taken into account. The need for offshore developments stems from a gradual depletion of hydrocarbon reserves onshore or near the coastlines, as new fields are being developed at greater distances offshore and in deeper water, with a corresponding adaptation of the offshore site investigations. Today, there are more than 7,000 offshore platforms operating at a water depth up to and exceeding 2000 m. A typical field development extends over tens of square kilometers, and may comprise several fixed structures, infield flowlines with an export pipeline either to the shoreline or connected to a regional trunkline.
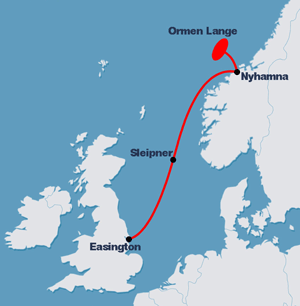
A submarine pipeline is a pipeline that is laid on the seabed or below it inside a trench. In some cases, the pipeline is mostly on-land but in places it crosses water expanses, such as small seas, straits and rivers. Submarine pipelines are used primarily to carry oil or gas, but transportation of water is also important. A distinction is sometimes made between a flowline and a pipeline. The former is an intrafield pipeline, in the sense that it is used to connect subsea wellheads, manifolds and the platform within a particular development field. The latter, sometimes referred to as an export pipeline, is used to bring the resource to shore. Sizeable pipeline construction projects need to take into account many factors, such as the offshore ecology, geohazards and environmental loading – they are often undertaken by multidisciplinary, international teams.
DeepOcean is an Oslo, Norway - based company which provides subsea services to the global offshore industries such as Inspection Maintenance and Repair (IMR), Subsea Construction, Cable Lay, and Subsea Trenching. Its 1,100 employees project manage and operate a fleet of Vessels, ROV's and subsea Trenchers.

GE Oil & Gas was the division of General Electric that owned its investments in the petroleum industry. In July 2017, this division was merged with Baker Hughes.
Gannet is an oil and gas field located in the United Kingdom's continental shelf in the North Sea. It is 180 km (110 mi) east of Aberdeen, and the water depth at the Gannet offshore installation is 95 m (312 ft). The field is located in Blocks 22/21, 22/25, 22/26 and 21/30. It is half-owned by Royal Dutch Shell (50%) and partly by ExxonMobil (50%) and has been operated by Shell UK Ltd since ‘first oil’ in November 1993. The Gannet A installation is the host platform for subsea tiebacks designated Gannet B to G. Like most Shell fields in the central and northern North Sea the field is named after a sea bird the gannet.
Ocean development refers to the establishing of human activities at sea and use of the ocean, as well as its governance.













