
The Suez Canal is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The 193.30-kilometre-long (120.11 mi) canal is a key trade route between Europe and Asia.

A transmission tower is a tall structure, usually a lattice tower made of steel that is used to support an overhead power line. In electrical grids, transmission towers carry high-voltage transmission lines that transport bulk electric power from generating stations to electrical substations, from which electricity is delivered to end consumers; moreover, utility poles are used to support lower-voltage sub-transmission and distribution lines that transport electricity from substations to electricity customers.

The HVDC Volgograd–Donbass is a 475 kilometres (295 mi) long bipolar ±400 kV high voltage direct current powerline used for transmitting electric power from Volga Hydroelectric Station at Volgograd in Russia to Donbas in eastern Ukraine and vice versa.
The Mettlen–Lavorgo powerline, also called the Lukmanier powerline, is the 400 kV three-phase alternating current high voltage electric power transmission line over the Lukmanier Pass in Switzerland, from Mettlen substation, next Inwil, about 7-kilometre (4.3 mi) south of Hochdorf, to Lavorgo substation, next Lavorgo, about 5-kilometre (3.1 mi) south of Faido. Trees falling on the line in 2003 caused a major blackout in Italy.

The Pylons of Messina are two free-standing steel towers, the Sicilian one in Torre Faro and the Calabrian one in Villa San Giovanni. They were used from 1955 to 1994 to carry a 220 kilovolt power line across the Strait of Messina, between the Scilla substation in Calabria on the Italian mainland at 38°14′42″N15°40′59″E and the Messina-Santo substation in Sicily at 38°15′57″N15°39′04″E.

The Pylons of Cádiz, also known as the Towers of Cádiz, are two 158 m (518 ft)-tall pylons supporting a double-circuit 132 kV three-phase AC powerline over the bay of Cádiz, Spain, running from Puerto Real Substation to the substation of the former Cádiz Thermal Power Station, situated on the peninsula upon which the city of Cádiz stands.

An overhead line crossing is the crossing of an obstacle—such as a traffic route, a river, a valley or a strait—by an overhead power line. The style of crossing depends on the local conditions and regulations at the time the power line is constructed. Overhead line crossings can sometimes require extensive construction and can also have operational issues. In such cases, those in charge of construction should consider whether a crossing of the obstacle would be better accomplished by an underground or submarine cable.

An overhead power line is a structure used in electric power transmission and distribution to transmit electrical energy along large distances. It consists of one or more conductors suspended by towers or poles. Since the surrounding air provides good cooling, insulation along long passages and allows optical inspection, overhead power lines are generally the lowest-cost method of power transmission for large quantities of electric energy.

The El Ferdan Railway Bridge is a swing bridge that spans the western shipping lane of the Suez Canal near Ismailia, Egypt. It is the longest swing bridge in the world, with a span of 1,100 feet (340 m).

The Ahmed Hamdi Tunnel is a 1.63-kilometre-long (1.01 mi) car tunnel under the Suez Canal at Shallufa. The tunnel is named after Ahmed Hamdi, an Egyptian engineer and general killed in action during the October 1973 War. It has two lanes of traffic, one in each direction, and it connects the Asian Sinai Peninsula to the town of Suez on the African mainland.
The Yangtze River power line crossings are overhead power lines that cross the Yangtze River in China. There are at least three power line crossings on the Yangtze River at Jiangyin, Nanjing, and Wuhu. The towers of the crossing in Jiangyin are among the highest in the world.

The 400 kV Thames Crossing is an overhead power line crossing of the River Thames, between Botany Marshes in Swanscombe, Kent, and West Thurrock, Essex, England. Its towers are the tallest electricity pylons in the UK.

The Suez Canal Bridge, also known as the Egyptian–Japanese Friendship Bridge, Al Salam Bridge, Al Salam Peace Bridge or Mubarak Peace Bridge, is a road bridge crossing the Suez Canal at El-Qantara, whose name means "the peace" in Egyptian Arabic. The bridge links the continents of Africa and Asia.

Aust Severn Powerline Crossing is the longest overhead power line span in the United Kingdom with a length of 1,618 m (5,308 ft).

GKK Etzenricht, an abbreviation of Gleichstromkurzkupplung Etzenricht, meaning Etzenricht HVDC-back-to-back station, was an HVDC back-to-back facility near Etzenricht in the district of Neustadt an der Waldnaab in Bavaria, Germany. It was built on the site of the Etzenricht substation, a 380 kV/220 kV/110 kV-substation, which went into service in 1970 and expanded afterwards several times. The facility was used between 1993 and 1995 for the exchange of power between Germany and the Czech Republic, operated by Bayernwerk AG.

The 275 kV Forth Crossing is an overhead power line crossing of the River Forth in Scotland. The crossing, located next to the Clackmannanshire Bridge and the Kincardine Bridge, has the tallest electricity towers (pylons) in Scotland.
The Saint Lawrence River HVDC Powerline Crossing is the crossing of Hydro-Québec's Quebec-New England HVDC transmission line over the Saint Lawrence River between Grondines and Lotbinière, Quebec, Canada. The crossing is remarkable, for being first implemented as an overhead crossing, and then later replaced by a cable tunnel. Hydro-Québec wanted to complete the transmission line in time, which was only possible with an overhead crossing of Saint Lawrence River. However, due to the negative visual impact of the large towers of the overhead crossing on the local populations of Grondines and Lotbinière, it was decided to build a cable tunnel under the river, although this made the project more expensive.
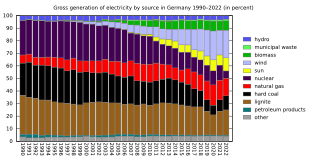
Germany's electrical grid is part of the Synchronous grid of Continental Europe. In 2020, due to COVID-19 conditions and strong winds, Germany produced 484 TW⋅h of electricity of which over 50% was from renewable energy sources, 24% from coal, and 12% from natural gas, this amounting to 36% from fossil fuel. This is the first year renewables represented more than 50% of the total electricity production and a major change from 2018, when a full 38% was from coal, only 40% was from renewable energy sources, and 8% was from natural gas.
The Zhoushan Island Overhead Powerline Tie is a 220 kV three-phase AC interconnection of the power grid of Zhoushan Island with that of the Chinese mainland. It runs over several islands and consists of several long-distance spans, the longest with a length of 2.7 kilometres (1.7 mi) south of Damao Island. This span uses two 370-metre-tall (1,210 ft) pylons, which were the highest electricity pylons in the world, until a 500 kV line to Zhoushan from mainland was completed. The north tower on Damao Island was completed in 2009, and the south tower on Liangmao Island was completed in 2010. These pylons resemble those of the Messina Strait, but are steel-tube lattice structures.
Powerline river crossings comprise both overhead lines and cable tunnels beneath rivers and estuaries. Overhead power lines are supported on towers which are usually significantly taller than overland pylons and are more widely spaced to cross the river in a single span. Tall pylons ensure that the electricity cables which they support provide an adequate safety clearance for river traffic.
















