The Global 200 is the list of ecoregions identified by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), the global conservation organization, as priorities for conservation. According to WWF, an ecoregion is defined as a "relatively large unit of land or water containing a characteristic set of natural communities that share a large majority of their species dynamics, and environmental conditions". For example, based on their levels of endemism, Madagascar gets multiple listings, ancient Lake Baikal gets one, and the North American Great Lakes get none.
The Philippine archipelago is one of the world's great reservoirs of biodiversity and endemism. The archipelago includes over 7000 islands, and a total land area of 300,780 km².

The Irrawaddy freshwater swamp forests ecoregion covers the freshwater portion of the delta of the Irrawaddy River, set back an average of 70 km from the Bay of Bengal by the saltwater mangroves. To the north is a rainforest belt with less inundated land. The region is extremely fertile due to the river-borne silt, but nearly-total conversion to agriculture has degraded the ecology. There are no fully protected areas in this ecoregion.

The Eastern Java–Bali montane rain forests ecoregion covers the higher altitude mountain rainforests on the eastern side of the island of Java, and most of the center of the island of Bali in Indonesia. The region has a number of active volcanoes, but is under pressure from growing human populations pushing into higher elevations and more marginal land. With elevations rising from sea level to 3,426 metres (11,240 ft), and precipitation varying between rainforest and drier forest levels, the area has many different forest types – evergreen, deciduous and semi-alpine.

The Eastern Java-Bali rain forests ecoregion covers the lowland areas of the eastern half of the island of Java, and the island of Bali, in Indonesia. This ecoregion is distinct from the Eastern Java-Bali montane rain forests, which exists at higher elevations where mountain forest habitat dominates. Very little of the natural lowland rainforest remains in its pre-human settlement state.

The Sumatran lowland rain forests ecoregion covers the lowland forests running the length of the island of Sumatra in Indonesia. The region is one of exceptionally high biodiversity, similar to Borneo and New Guinea islands. Many endangered mammals species are present, and over 450 species of birds have been found in the region. In recent years, illegal logging and human encroachment have put great strain on this ecoregion.

The Sumatran montane rain forests ecoregion covers the mountainous elevations of the Barisan Mountains Range that runs the length of the southwestern side of the island of Sumatra in Indonesia. The ecoregion is almost completely surrounded by the lower elevation Sumatran lowland rain forests. The area is one of very high biodiversity - because of the relative isolation, and variety of forest types, there are 7 endemic species of mammals and eight endemic species of birds.

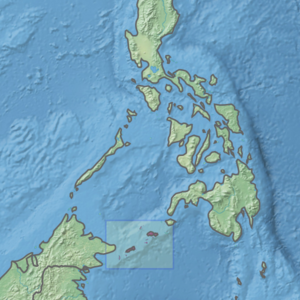
The Mindanao montane rain forests ecoregion covers the montane forests - the zone between the lowland forest and the treeline - in the mountains on the island of Mindanao in the Philippines. Because the ecoregion covers only elevations above 1,000 metres (3,300 ft), it exists in seven discontinuous patches surrounded by lowland rainforest. Biodiversity is high, both because of the isolation of separate mountain ranges that have led to species variation within the island, and because of the altitude zonation. Because most of the surrounding lowland forest has been cleared for human use, the montane regions have become an important refuge for rare and endemic species.

The Greater Negros–Panay rain forests ecoregion covers the central Visayan Islands in the Philippines, including the islands of Panay, Negros, Cebu, Masbate, Sibuyan, Ticao, Guimaras, Romblon, Tablas, Siquijor, and Bohol, but excludes Leyte and Samar. During the last ice age, these were all on the same island. The lack of a land bridge to Asia during the ice age kept most Asian megafauna, including elephants and tigers, from reaching the Philippines and the Visayan Islands, which hosts many unique and endemic species with some exclusive only to an island.

The Mindanao–Eastern Visayas rain forests ecoregion covers the lowland rain forests of the island of Mindanao and of the easternmost of the Visayas Islands in the Philippines. Although 63% of this ecoregion is covered with closed broadleaf evergreen forest or open forest, much of this has been disturbed in the past by human activity, and many of the rare species of the area have been relegated to the isolated areas or higher elevations.

The Mindoro rain forests ecoregion covers the island of Mindoro, which lies between the island of Luzon and the Palawan Archipelago in the Philippines. The island has been subject to heavy commercial logging, with the only original forests remaining on the high ridge of the central mountain range. Logging has been reduced long enough on the east side of the mountains to support a regrown forest and a number of endemic species.

The Sumatran peat swamp forests ecoregion covers the low-lying peat swamp forests along the northeast coast of the island of Sumatra in Indonesia. As is typical for peat swamp forests, this ecoregion lies between a thin strip of saltwater-affected mangroves on the coast, and freshwater swamps and lowland rainforest forest on better drained soils further inland. Because the peat soil has relatively low nutrient levels, this ecoregion has been less used for agriculture, but burning and clearance has degraded half of the forest.

The Palawan rain forests ecoregion covers the Palawan Island Archipelago, centered on Palawan Island, the sixth largest island in the Philippines. The islands act as an ecological bridge between Borneo and the main islands of the Philippines, even though there were channels between the islands through the last ice age when sea levels were low. Biodiversity is high in the islands, with many endemic species, and with many genera shared with Borneo to the south. Pressure from logging is a concern for the forests of this region.

The Southwest Borneo freshwater swamp forests ecoregion covers a number disconnected patches of freshwater swamp forest along the southwestern coasts of Borneo. The swamps are generally set back a few kilometers or two from the sea by the saltwater-affected Sunda Shelf mangroves The relatively fertile, flat soil has led to much of this ecoregion being converted to agriculture.

The Isthmian–Pacific moist forests ecoregion covers the lowland tropical evergreen forests on the Pacific side of the central mountains of southern Costa Rica and western Panama. As the meeting zone between North and South American floral communities, the area is one of very high biodiversity. Much of the rainforest has, however, been cleared for subsistence agriculture and cattle grazing.

The Bocas del Toro-San Bastimentos Island-San Blas mangroves ecoregion covers the mangrove habitats along the Caribbean Sea coast of Costa Rica and across the northern coast of Panama. An offshore reef and barrier islands of the region help protect the mangroves from destructive waves. The ecoregion has a high number of endangered and threatened species, including the loggerhead sea turtle, green sea turtle, and hawk's bill sea turtle.

The Lesser Antilles mangroves ecoregion covers the salt-water habitats along the coasts of the islands on the divide between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. the included islands stretch from Anguilla in the north to the island of Grenada in the south. The species diversity of these small islands is less than that of the larger islands of the Greater Antilles with to the west, but endemism is high due to the relative isolation of the different islands.

The Rio Negro-Rio San Sun mangroves ecoregion covers a series of small of discontinuous mangrove forests on the Caribbean Sea coast of Costa Rica, from a small portion inside the border with Nicaragua in the west to the border with Panama in the east. The coast on this stretch is a flat, alluvial plain, and mangroves are only a small part of a diverse patchwork of local habitats including swamps, mixed rainforests, coastal lagoons, sea grass beds, and sandy beaches. Much of the territory is "blackwater river" in character - slow-moving channels in wooded swamps with water stained by decayed matter. These mangroves are periodically damaged by hurricanes, such as in 1988 from Hurricane Joan, but are able to regenerate.

The Trinidad and Tobago moist forests ecoregion covers most of Trinidad Island and Tobago Island near the coast of South America where the southeastern Caribbean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean. Small portions of the islands around river estuaries and coastal lowlands are mangroves or dry forests. Species diversity is very high, in particular for plants and birds. Tobago, being much smaller, has fewer species.