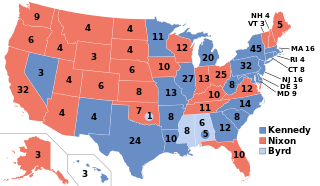
The 1960 United States presidential election was the 44th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 1960. The Democratic ticket of Senator John F. Kennedy and his running mate, Senate Majority Leader Lyndon B. Johnson, narrowly defeated the Republican ticket of incumbent Vice President Richard Nixon and his running mate, U.N. Ambassador Henry Cabot Lodge Jr. This was the first election in which 50 states participated, marking the first participation of Alaska and Hawaii, and the last in which the District of Columbia did not. This made it the only presidential election in which the threshold for victory was 269 electoral votes. It was also the first election in which an incumbent president—in this case, Dwight D. Eisenhower—was ineligible to run for a third term because of the term limits established by the 22nd Amendment.

Eugene Luther Gore Vidal was an American writer and public intellectual known for his acerbic epigrammatic wit. His novels and essays interrogated the social and sexual norms he perceived as driving American life. Vidal was heavily involved in politics, and unsuccessfully sought office twice as a Democratic Party candidate, first in 1960 to the United States House of Representatives, and later in 1982 to the United States Senate.

Thomas Kennerly Wolfe Jr. was an American author and journalist widely known for his association with New Journalism, a style of news writing and journalism developed in the 1960s and 1970s that incorporated literary techniques. Much of Wolfe's work was satirical and centred on the counterculture of the 1960s and issues related to class, social status, and the lifestyles of the economic and intellectual elites of New York City.

Nachem Malech Mailer, known by his pen name Norman Kingsley Mailer, was an American writer and filmmaker. In a career spanning more than six decades, Mailer had 11 best-selling books, at least one in each of the seven decades after World War II.
New Journalism is a style of news writing and journalism, developed in the 1960s and 1970s, that uses literary techniques unconventional at the time. It is characterized by a subjective perspective, a literary style reminiscent of long-form non-fiction. Using extensive imagery, reporters interpolate subjective language within facts whilst immersing themselves in the stories as they reported and wrote them. In traditional journalism, the journalist is "invisible"; facts are meant to be reported objectively.

Arthur Meier Schlesinger Jr. was an American historian, social critic, and public intellectual. The son of the influential historian Arthur M. Schlesinger Sr. and a specialist in American history, much of Schlesinger's work explored the history of 20th-century American liberalism. In particular, his work focused on leaders such as Harry S. Truman, Franklin D. Roosevelt, John F. Kennedy, and Robert F. Kennedy. In the 1952 and 1956 presidential campaigns, he was a primary speechwriter and adviser to the Democratic presidential nominee, Adlai Stevenson II. Schlesinger served as special assistant and "court historian" to President Kennedy from 1961 to 1963. He wrote a detailed account of the Kennedy administration, from the 1960 presidential campaign to the president's state funeral, titled A Thousand Days: John F. Kennedy in the White House, which won the 1966 Pulitzer Prize for Biography or Autobiography.

The Armies of the Night: History as a Novel/The Novel as History is a nonfiction novel recounting the October 1967 March on the Pentagon written by Norman Mailer and published by New American Library in 1968. It won the Pulitzer Prize for General Nonfiction and the National Book Award in category Arts and Letters. Mailer's unique rendition of the nonfiction novel was perhaps his most successful example of new journalism, and received the most critical attention. The book originated as an essay published in Harper's Magazine titled "The Steps of the Pentagon," at the time the longest magazine article ever published, surpassing John Hersey's "Hiroshima" in The New Yorker.

An American Dream is a 1965 novel by American author Norman Mailer. It was published by Dial Press. Mailer wrote it in serialized form for Esquire, consciously attempting to resurrect the methodology used by Charles Dickens and other earlier novelists, with Mailer writing each chapter against monthly deadlines. The book is written in a poetic style heavy with metaphor that creates unique and hypnotising narrative and dialogue. The novel's action takes place over 32 hours in the life of its protagonist Stephen Rojack. Rojack is a decorated war-hero, former congressman, talk-show host, and university professor. He is depicted as the metaphorical embodiment of the American Dream.

The 1960 Democratic National Convention was held in Los Angeles, California, on July 11–15, 1960. It nominated Senator John F. Kennedy of Massachusetts for president and Senate Majority Leader Lyndon B. Johnson of Texas for vice president.
Dwight Macdonald was an American writer, critic, philosopher, and activist. Macdonald was a member of the New York Intellectuals and editor of their leftist magazine Partisan Review for six years. He also contributed to other New York publications including Time, The New Yorker, The New York Review of Books, and Politics, a journal which he founded in 1944.

The White Negro: Superficial Reflections on the Hipster is a 9,000-word essay by Norman Mailer that connects the "psychic havoc" wrought by the Holocaust and atomic bomb to the aftermath of slavery in America in the figuration of the Hipster, or the "white negro". The essay is a call to abandon Eisenhower liberalism and a numbing culture of conformity and psychoanalysis in favor of the rebelliousness, personal violence and emancipating sexuality that Mailer associates with marginalized black culture. The White Negro was first published in the 1957 special issue of Dissent, before being published separately by City Lights. Mailer's essay was controversial upon its release and received a mixed reception, winning praise, for example, from Eldridge Cleaver and criticism from James Baldwin, Ralph Ellison, and Allen Ginsberg. Baldwin, in particular, heavily criticized the work, asserting that it perpetuated the notorious "myth of the sexuality of Negros" and stating that it was beneath Mailer's talents. The work remains his most famous and most reprinted essay and it established Mailer's reputation as a "philosopher of hip".

J. Michael Lennon is an American academic and writer who is the Emeritus Professor of English at Wilkes University and the late Norman Mailer’s archivist and authorized biographer. He published Mailer's official biography Norman Mailer: A Double Life in 2013. He edited Mailer's selected letters in 2014 and the Library of America's two-volume set Norman Mailer: The Sixties in 2018.
Noel Edward Parmentel Jr. was an American writer who was a leading figure on the New York political journalism, literary, and cultural scene during the 20th century. He was known for criticizing political figures on the left and right that he considered "phonies". He was credited with introducing a much-quoted question about Richard Nixon: "Would you buy a used car from this man?" He wrote for publications such as The Nation, National Review and Esquire. Parmentel mentored writers such as John Gregory Dunne and Joan Didion. He collaborated on films with Norman Mailer and Richard Leacock and advised Mailer to run for mayor of New York City in 1969.
Theodore Harold White was an American political journalist and historian, known for his reporting from China during World War II and the Making of the President series.

Miami and the Siege of Chicago: An Informal History of the Republican and Democratic Conventions of 1968 is a non-fiction novel written by Norman Mailer which covers the Republican and Democratic national party political conventions of 1968 and the anti-Vietnam War protests surrounding them. It was published in 1968 by the World Publishing Company.
Bob Gomel is an American photojournalist who created images of 1960s world leaders, athletes, entertainers, and major events. His photographs have appeared on the covers of Life, Sports Illustrated, Newsweek, Fortune, and Forbes, and in Time, The New York Times, and Stern, and in more than 40 books. Gomel's images are held in the collections of the U.S. Library of Congress and the Museum of Fine Arts in Houston.

The Short Fiction of Norman Mailer is a 1967 anthology of short stories by Norman Mailer. It is grouped into eight thematic sections and contains nineteen stories, many appearing in one of Mailer's miscellanies; thirteen were published in periodicals or other anthologies before appearing in this collection. The collection was reprinted in hardcover in 1980 and some of the stories were reprinted in other volumes.

This Norman Mailer bibliography lists major books by and about Mailer, an American novelist, new journalist, essayist, public intellectual, filmmaker, and biographer. Over a fifty-nine-year period, Mailer won two Pulitzer Prizes and had eleven books spend a total of 160 weeks on the New York Times bestseller list. Mailer's output included fiction, non-fiction, poems and essays. Biographer J. Michael Lennon called Mailer the chronicler of the American Century, and a talent whose career has "been at once so brilliant, varied, controversial, improvisational, public, productive, lengthy and misunderstood".

The Faith of Graffiti is a 1974 essay by American novelist and journalist Norman Mailer about New York City's graffiti artists. Mailer's essay appeared in a shorter form in Esquire and as a book with 81 photographs by Jon Naar and design by Mervyn Kurlansky. Through interviews, exploration, and analyses, the essay explores the political and artistic implications of graffiti. The essay was controversial at the time of publication because of its attempt to validate graffiti as an art form by linking it with great artists of the past. Some critics also said Mailer was using the essay as a platform to express his political grievances. Faith grew out of Mailer's existential philosophy of the hip, in which a Hipster is guided by his instincts regardless of consequences or perception, and upholds graffiti as a subversive and healthy check on the status quo. Like several of his other non-fiction narratives, Mailer continued his use of new journalism techniques, adopting a persona, the A-I or "Aesthetic Investigator", to provide both an objective distance from the topic and to engender the text with the creative and critical eye of the novelist.
"In the Red Light: A History of the Republican Convention in 1964" is an essay written by Norman Mailer for Esquire about the Republican National Convention in 1964. Like Mailer's other journalism in the 1960s, "Red Light" uses the subjective techniques of new journalism and assumes a third-person persona to participate in, report on, and comment on the events in California in the summer of 1964. The essay is divided into three sections: the events leading up to the convention, including Goldwater's rise, the events leading up to Goldwater's nomination, and Mailer's view of his acceptance.













