
Nvidia Corporation is an American multinational technology company, incorporated in Delaware and based in Santa Clara, California. It is a software and fabless company which designs graphics processing units (GPUs), application programming interfaces (APIs) for data science and high-performance computing as well as system on a chip units (SoCs) for the mobile computing and automotive market. Nvidia is a dominant supplier of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware and software. Its professional line of GPUs are used in workstations for applications in such fields as architecture, engineering and construction, media and entertainment, automotive, scientific research, and manufacturing design.

In computing, overclocking is the practice of increasing the clock rate of a computer to exceed that certified by the manufacturer. Commonly, operating voltage is also increased to maintain a component's operational stability at accelerated speeds. Semiconductor devices operated at higher frequencies and voltages increase power consumption and heat. An overclocked device may be unreliable or fail completely if the additional heat load is not removed or power delivery components cannot meet increased power demands. Many device warranties state that overclocking or over-specification voids any warranty, but some manufacturers allow overclocking as long as it is done (relatively) safely.

The GeForce 6 series is Nvidia's sixth generation of GeForce graphic processing units. Launched on April 14, 2004, the GeForce 6 family introduced PureVideo post-processing for video, SLI technology, and Shader Model 3.0 support.
The R420 GPU, developed by ATI Technologies, was the company's basis for its 3rd-generation DirectX 9.0/OpenGL 2.0-capable graphics cards. Used first on the Radeon X800, the R420 was produced on a 0.13 micrometer low-K photolithography process and used GDDR-3 memory. The chip was designed for AGP graphics cards.
Microsoft Virtual Server was a virtualization solution that facilitated the creation of virtual machines on the Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows Server 2003 operating systems. Originally developed by Connectix, it was acquired by Microsoft prior to release. Virtual PC is Microsoft's related desktop virtualization software package.

Super PI is a computer program that calculates pi to a specified number of digits after the decimal point—up to a maximum of 32 million. It uses Gauss–Legendre algorithm and is a Windows port of the program used by Yasumasa Kanada in 1995 to compute pi to 232 digits.

The Radeon R100 is the first generation of Radeon graphics chips from ATI Technologies. The line features 3D acceleration based upon Direct3D 7.0 and OpenGL 1.3, and all but the entry-level versions offloading host geometry calculations to a hardware transform and lighting (T&L) engine, a major improvement in features and performance compared to the preceding Rage design. The processors also include 2D GUI acceleration, video acceleration, and multiple display outputs. "R100" refers to the development codename of the initially released GPU of the generation. It is the basis for a variety of other succeeding products.
UNIGINE is a proprietary cross-platform game engine developed by UNIGINE Company used in simulators, virtual reality systems, serious games and visualization. It supports OpenGL 4, Vulkan and DirectX 12.

The GeForce 8 series is the eighth generation of Nvidia's GeForce line of graphics processing units. The third major GPU architecture developed by Nvidia, Tesla represents the company's first unified shader architecture.
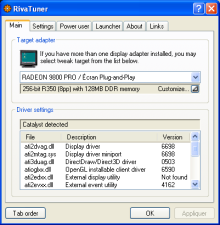
RivaTuner is a freeware overclocking and hardware monitoring program that was first developed by Alexey Nicolaychuk in 1997 for the Nvidia video cards. It was a pioneering application that influenced the design of subsequent freeware graphics card overclocking and monitoring utilities. It supports Nvidia GPUs from the Riva TNT to the GeForce 700 Series, and has limited support for the ATI/AMD Radeon series of video cards from the Radeon 8500 and above.

Haswell is the codename for a processor microarchitecture developed by Intel as the "fourth-generation core" successor to the Ivy Bridge. Intel officially announced CPUs based on this microarchitecture on June 4, 2013, at Computex Taipei 2013, while a working Haswell chip was demonstrated at the 2011 Intel Developer Forum. With Haswell, which uses a 22 nm process, Intel also introduced low-power processors designed for convertible or "hybrid" ultrabooks, designated by the "U" suffix.
The R200 is the second generation of GPUs used in Radeon graphics cards and developed by ATI Technologies. This GPU features 3D acceleration based upon Microsoft Direct3D 8.1 and OpenGL 1.3, a major improvement in features and performance compared to the preceding Radeon R100 design. The GPU also includes 2D GUI acceleration, video acceleration, and multiple display outputs. "R200" refers to the development codename of the initially released GPU of the generation. It is the basis for a variety of other succeeding products.

The GeForce 900 series is a family of graphics processing units developed by Nvidia, succeeding the GeForce 700 series and serving as the high-end introduction to the Maxwell microarchitecture, named after James Clerk Maxwell. They are produced with TSMC's 28 nm process.
NvidiaShadowPlay is a hardware-accelerated screen recording utility available as part of Nvidia's GeForce Experience software for GeForce GPUs. Launched in 2013, it can be configured to record a continuous buffer, allowing the user to save the video retroactively. ShadowPlay is supported for any Nvidia GTX 600 series card or higher.

Kepler is the codename for a GPU microarchitecture developed by Nvidia, first introduced at retail in April 2012, as the successor to the Fermi microarchitecture. Kepler was Nvidia's first microarchitecture to focus on energy efficiency. Most GeForce 600 series, most GeForce 700 series, and some GeForce 800M series GPUs were based on Kepler, all manufactured in 28 nm. Kepler also found use in the GK20A, the GPU component of the Tegra K1 SoC, as well as in the Quadro Kxxx series, the Quadro NVS 510, and Nvidia Tesla computing modules. Kepler was followed by the Maxwell microarchitecture and used alongside Maxwell in the GeForce 700 series and GeForce 800M series.

The Shield Tablet, later relaunched as the Shield Tablet K1, is a gaming tablet, developed by Nvidia and released on July 29, 2014. It was Nvidia's second portable gaming device that uses Android. Compared to the Shield Portable, the controller is not permanently connected to the screen, rather it can be purchased separately. Up to four controllers can be wirelessly connected at the same time. While the Shield tablet features an 8-inch 1920×1200 pixel display, it can output 4K resolution signal to a television via HDMI.
Geekbench is a proprietary and freemium cross-platform utility for benchmarking the central processing unit (CPU) and graphics processing unit (GPU) of computers, laptops, tablets, and phones.
Heaven Benchmark is benchmarking software based on the UNIGINE Engine. The benchmark was developed and published by UNIGINE Company in 2009. The main purpose of software is performance and stability testing for GPUs. Users can choose a workload preset, Basic or Extreme, or set the parameters by custom. The benchmark 3D scene is a steampunk-style city on flying islands in the middle of the clouds. The scene is GPU-intensive because of tessellation used for all the surfaces, dynamic sky with volumetric clouds and day-night cycle, real-time global illumination, and screen-space ambient occlusion.

The Radeon RX 6000 series is a series of graphics processing units developed by AMD, based on their RDNA 2 architecture. It was announced on October 28, 2020 and is the successor to the Radeon RX 5000 series. It consists of the entry-level RX 6400, mid-range RX 6500 XT, high-end RX 6600, RX 6600 XT, RX 6650 XT, RX 6700, RX 6700 XT, upper high-end RX 6750 XT, RX 6800, RX 6800 XT, and enthusiast RX 6900 XT and RX 6950 XT for desktop computers; and the RX 6600M, RX 6700M, and RX 6800M for laptops. A sub-series for mobile, Radeon RX 6000S, was announced in CES 2022, targeting thin and light laptop designs.

The GeForce 40 series is a family of graphics processing units developed by Nvidia, succeeding the GeForce 30 series. The series was announced on September 20, 2022, at the GPU Technology Conference (GTC) 2022 event; the RTX 4090 was released on October 12, 2022, the 16GB RTX 4080 was released on November 16, 2022. An RTX 4080 12GB was announced in September 2022, but following some controversy in the media, was "unlaunched" by Nvidia. On January 5, 2023, that model would be released as the RTX 4070 Ti. The RTX 4070 was then released on April 13, 2023. The RTX 4060 Ti was released on May 24, 2023, and the RTX 4060 on June 29, 2023. An RTX 4060 Ti 16GB followed on July 18, 2023. Further models of this generation of desktop and mobile GPUs are to release later in 2023. On January 8, 2024, Nvidia released RTX 4070 SUPER, RTX 4070 Ti SUPER and RTX 4080 SUPER video cards at higher specs and lower prices than their original counterparts. In the same vein the production of the RTX 4080 and RTX 4070 Ti have stopped due to the SUPER Series, but the 4070 will remain.











