
A lathe is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece about an axis of rotation to perform various operations such as cutting, sanding, knurling, drilling, deformation, facing, threading and turning, with tools that are applied to the workpiece to create an object with symmetry about that axis.

Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals in order to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term, it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on every scale: from huge ships, buildings, and bridges, down to precise engine parts and delicate jewelry.

Machining is a manufacturing process where a desired shape or part is created using the controlled removal of material, most often metal, from a larger piece of raw material by cutting. Machining is a form of subtractive manufacturing, which utilizes machine tools, in contrast to additive manufacturing, which uses controlled addition of material.

Drilling is a cutting process where a drill bit is spun to cut a hole of circular cross-section in solid materials. The drill bit is usually a rotary cutting tool, often multi-point. The bit is pressed against the work-piece and rotated at rates from hundreds to thousands of revolutions per minute. This forces the cutting edge against the work-piece, cutting off chips (swarf) from the hole as it is drilled.
A reamer is a type of rotary cutting tool used in metalworking. Precision reamers are designed to enlarge the size of a previously formed hole by a small amount but with a high degree of accuracy to leave smooth sides. There are also non-precision reamers which are used for more basic enlargement of holes or for removing burrs. The process of enlarging the hole is called reaming. There are many different types of reamer and they may be designed for use as a hand tool or in a machine tool, such as a milling machine or drill press.

Woodturning is the craft of using a wood lathe with hand-held tools to cut a shape that is symmetrical around the axis of rotation. Like the potter's wheel, the wood lathe is a mechanism that can generate a variety of forms. The operator is known as a turner, and the skills needed to use the tools were traditionally known as turnery. In pre-industrial England, these skills were sufficiently difficult to be known as "the mysteries of the turners' guild." The skills to use the tools by hand, without a fixed point of contact with the wood, distinguish woodturning and the wood lathe from the machinist's lathe, or metal-working lathe.

The phrase speeds and feeds or feeds and speeds refers to two separate velocities in machine tool practice, cutting speed and feed rate. They are often considered as a pair because of their combined effect on the cutting process. Each, however, can also be considered and analyzed in its own right.

A collet is a segmented sleeve, band or collar. One of the two radial surfaces of a collet is usually tapered and the other is cylindrical. The term collet commonly refers to a type of chuck that uses collets to hold either a workpiece or a tool but has other mechanical applications.

In machining, a tool bit is a non-rotary cutting tool used in metal lathes, shapers, and planers. Such cutters are also often referred to by the set-phrase name of single-point cutting tool, as distinguished from other cutting tools such as a saw or water jet cutter. The cutting edge is ground to suit a particular machining operation and may be resharpened or reshaped as needed. The ground tool bit is held rigidly by a tool holder while it is cutting.
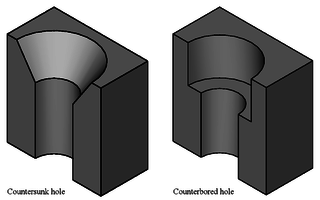
In manufacturing, a countersink is a conical hole cut into a manufactured object, or the cutter used to cut such a hole. A common use is to allow the head of a countersunk bolt, screw or rivet, when placed in the hole, to sit flush with or below the surface of the surrounding material. A countersink may also be used to remove the burr left from a drilling or tapping operation, thereby improving the finish of the product and removing any hazardous sharp edges.

Turning is a machining process in which a cutting tool, typically a non-rotary tool bit, describes a helix toolpath by moving more or less linearly while the workpiece rotates.
Milling cutters are cutting tools typically used in milling machines or machining centres to perform milling operations. They remove material by their movement within the machine or directly from the cutter's shape.

A lathe center, often shortened to center, is a tool that has been ground to a point to accurately position a workpiece on an axis. They usually have an included angle of 60°, but in heavy machining situations an angle of 75° is used.

In machining, a metal lathe or metalworking lathe is a large class of lathes designed for precisely machining relatively hard materials. They were originally designed to machine metals; however, with the advent of plastics and other materials, and with their inherent versatility, they are used in a wide range of applications, and a broad range of materials. In machining jargon, where the larger context is already understood, they are usually simply called lathes, or else referred to by more-specific subtype names. These rigid machine tools remove material from a rotating workpiece via the movements of various cutting tools, such as tool bits and drill bits.

A tipped tool is any cutting tool in which the cutting edge consists of a separate piece of material that is brazed, welded, or clamped onto a body made of another material. In the types in which the cutter portion is an indexable part clamped by a screw, the cutters are called inserts. Tipped tools allow each part of the tool, the shank and the cutter(s), to be made of the material with the best properties for its job. Common materials for the cutters include cemented carbide, polycrystalline diamond, and cubic boron nitride. Tools that are commonly tipped include milling cutters, tool bits, router bits, and saw blades.

Grinding is a type of abrasive machining process which uses a grinding wheel as cutting tool.

In machine tools, a spindle is a rotating axis of the machine, which often has a shaft at its heart. The shaft itself is called a spindle, but also, in shop-floor practice, the word often is used metonymically to refer to the entire rotary unit, including not only the shaft itself, but its bearings and anything attached to it. Spindles are electrically or pneumatically powered and come in various sizes. They are versatile in terms of material it can work with. Materials that spindles work with include embroidery, foam, glass, wood, etc.
In manufacturing, threading is the process of creating a screw thread. More screw threads are produced each year than any other machine element. There are many methods of generating threads, including subtractive methods ; deformative or transformative methods ; additive methods ; or combinations thereof.
In metalworking and woodworking, an automatic lathe is a lathe with an automatically controlled cutting process. Automatic lathes were first developed in the 1870s and were mechanically controlled. From the advent of NC and CNC in the 1950s, the term automatic lathe has generally been used for only mechanically controlled lathes, although some manufacturers market Swiss-type CNC lathes as 'automatic'.

Milling is the process of machining using rotary cutters to remove material by advancing a cutter into a workpiece. This may be done by varying directions on one or several axes, cutter head speed, and pressure. Milling covers a wide variety of different operations and machines, on scales from small individual parts to large, heavy-duty gang milling operations. It is one of the most commonly used processes for machining custom parts to precise tolerances.

















