Related Research Articles
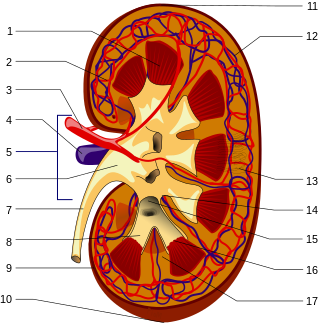
Nephrology is a specialty of adult internal medicine and pediatric medicine that concerns the study of the kidneys, specifically normal kidney function and kidney disease, the preservation of kidney health, and the treatment of kidney disease, from diet and medication to renal replacement therapy. The word “renal” is an adjective meaning “relating to the kidneys”, and its roots are French or late Latin. Whereas according to some opinions, "renal" and "nephro" should be replaced with "kidney" in scientific writings such as "kidney medicine" or "kidney replacement therapy", other experts have advocated preserving the use of renal and nephro as appropriate including in "nephrology" and "renal replacement therapy", respectively.

In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". Prominent examples include celiac disease, post-infectious IBS, diabetes mellitus type 1, Henoch–Schönlein purpura (HSP) sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjögren syndrome, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Graves' disease, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, Addison's disease, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), ankylosing spondylitis, polymyositis (PM), dermatomyositis (DM), and multiple sclerosis (MS). Autoimmune diseases are very often treated with steroids.
The ankle jerk reflex, also known as the Achilles reflex, occurs when the Achilles tendon is tapped while the foot is dorsiflexed. It is a type of stretch reflex that tests the function of the gastrocnemius muscle and the nerve that supplies it. A positive result would be the jerking of the foot towards its plantar surface. Being a deep tendon reflex, it is monosynaptic. It is also a stretch reflex. These are monosynaptic spinal segmental reflexes. When they are intact, integrity of the following is confirmed: cutaneous innervation, motor supply, and cortical input to the corresponding spinal segment.
Encephalopathy means any disorder or disease of the brain, especially chronic degenerative conditions. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but rather to a syndrome of overall brain dysfunction; this syndrome has many possible organic and inorganic causes.

Castlemandisease (CD) describes a group of rare lymphoproliferative disorders that involve enlarged lymph nodes, and a broad range of inflammatory symptoms and laboratory abnormalities. Whether Castleman disease should be considered an autoimmune disease, cancer, or infectious disease is currently unknown.

Infective endocarditis is an infection of the inner surface of the heart, usually the valves. Signs and symptoms may include fever, small areas of bleeding into the skin, heart murmur, feeling tired, and low red blood cell count. Complications may include backward blood flow in the heart, heart failure – the heart struggling to pump a sufficient amount of blood to meet the body's needs, abnormal electrical conduction in the heart, stroke, and kidney failure.

Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both cancer and serious medical issues.
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affect the patient's immune system. Examples of these extrinsic factors include HIV infection and environmental factors, such as nutrition. Immunocompromisation may also be due to genetic diseases/flaws such as SCID.

Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine is an American textbook of internal medicine. First published in 1950, it is in its 21st edition and comes in two volumes. Although it is aimed at all members of the medical profession, it is mainly used by internists and junior doctors in this field, as well as medical students. It is widely regarded as one of the most authoritative books on internal medicine and has been described as the "most recognized book in all of medicine."
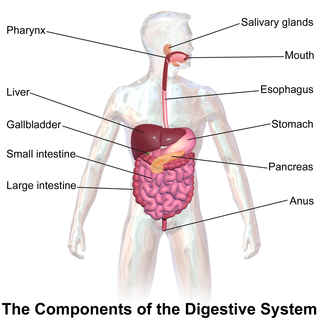
Gastrointestinal diseases refer to diseases involving the gastrointestinal tract, namely the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum, and the accessory organs of digestion, the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.

A chylothorax is an abnormal accumulation of chyle, a type of lipid-rich lymph, in the space surrounding the lung. The lymphatics of the digestive system normally returns lipids absorbed from the small bowel via the thoracic duct, which ascends behind the esophagus to drain into the left brachiocephalic vein. If normal thoracic duct drainage is disrupted, either due to obstruction or rupture, chyle can leak and accumulate within the negative-pressured pleural space. In people on a normal diet, this fluid collection can sometimes be identified by its turbid, milky white appearance, since chyle contains emulsified triglycerides.

Megacolon is an abnormal dilation of the colon. This leads to hypertrophy of the colon. The dilation is often accompanied by a paralysis of the peristaltic movements of the bowel. In more extreme cases, the feces consolidate into hard masses inside the colon, called fecalomas, which can require surgery to be removed.

A pericardial effusion is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardial cavity. The pericardium is a two-part membrane surrounding the heart: the outer fibrous connective membrane and an inner two-layered serous membrane. The two layers of the serous membrane enclose the pericardial cavity between them. This pericardial space contains a small amount of pericardial fluid. The fluid is normally 15-50 mL in volume. The pericardium, specifically the pericardial fluid provides lubrication, maintains the anatomic position of the heart in the chest, and also serves as a barrier to protect the heart from infection and inflammation in adjacent tissues and organs.
An oral medicine or stomatology doctor/dentist has received additional specialized training and experience in the diagnosis and management of oral mucosal abnormalities including oral cancer, salivary gland disorders, temporomandibular disorders and facial pain, taste and smell disorders; and recognition of the oral manifestations of systemic and infectious diseases. It lies at the interface between medicine and dentistry. An oral medicine doctor is trained to diagnose and manage patients with disorders of the orofacial region, essentially as a "physician of the mouth".

Kyphoscoliosis describes an abnormal curvature of the spine in both the coronal and sagittal planes. It is a combination of kyphosis and scoliosis. This musculoskeletal disorder often leads to other issues in patients, such as under-ventilation of lungs, pulmonary hypertension, difficulty in performing day-to-day activities, psychological issues emanating from anxiety about acceptance among peers, especially in young patients. It can also be seen in syringomyelia, Friedreich's ataxia, spina bifida, kyphoscoliotic Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (kEDS), and Duchenne muscular dystrophy due to asymmetric weakening of the paraspinal muscles.

Reproductive medicine is a branch of medicine concerning the male and female reproductive systems. It encompasses a variety of reproductive conditions, their prevention and assessment, as well as their subsequent treatment and prognosis.

Ptosis, also known as blepharoptosis, is a drooping or falling of the upper eyelid. This condition is sometimes called "lazy eye," but that term normally refers to the condition amblyopia. If severe enough and left untreated, the drooping eyelid can cause other conditions, such as amblyopia or astigmatism, so it is especially important to treat the disorder in children before it can interfere with vision development.
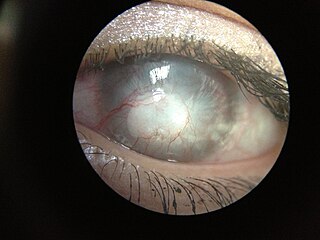
Corneal neovascularization (CNV) is the in-growth of new blood vessels from the pericorneal plexus into avascular corneal tissue as a result of oxygen deprivation. Maintaining avascularity of the corneal stroma is an important aspect of corneal pathophysiology as it is required for corneal transparency and optimal vision. A decrease in corneal transparency causes visual acuity deterioration. Corneal tissue is avascular in nature and the presence of vascularization, which can be deep or superficial, is always pathologically related.
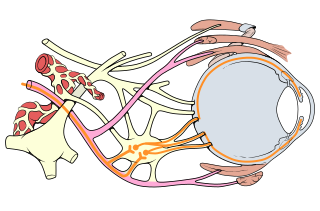
Oculomotor nerve palsy or oculomotor neuropathy is an eye condition resulting from damage to the third cranial nerve or a branch thereof. As the name suggests, the oculomotor nerve supplies the majority of the muscles controlling eye movements. Damage to this nerve will result in an inability to move the eye normally. The nerve also supplies the upper eyelid muscle and is accompanied by parasympathetic fibers innervating the muscles responsible for pupil constriction. The limitations of eye movement resulting from the condition are generally so severe that patients are often unable to maintain normal eye alignment when gazing straight ahead, leading to strabismus and, as a consequence, double vision (diplopia).
References
- ↑ sBMJ
- ↑ Oral diagnosis - the clinician's guide, W. Birnbaum, S. M. Dunne
- ↑ The New Aird's Companion in Surgical Studies (3rd edn). K. Burnand, A. Young, J. Lucas.
- ↑ Surgical Talk: Revision In Surgery, A. Goldberg, G. Stansby
- ↑ Medicine and Surgery: a concise textbook, G. Kendall, K.Y. Shiu, S. L. Johnston
- ↑ Thinking Medicine: Structure Your Knowledge for Success in Medical Exams, C. Koppel, A. Naparus
- ↑ FOX Broadcasting Company: House Archived 2012-05-23 at the Wayback Machine