Related Research Articles

Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced in a specific time period. GDP (nominal) per capita does not, however, reflect differences in the cost of living and the inflation rates of the countries; therefore, using a basis of GDP per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP) is arguably more useful when comparing living standards between nations, while nominal GDP is more useful comparing national economies on the international market.

The economy of Pakistan is the 23rd largest in the world in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP), and 42nd largest in terms of nominal gross domestic product. Pakistan has a population of over 220 million, giving it a nominal GDP per capita of $1,357 in 2019, which ranks 154th in the world and giving it a PPP GDP per capita of 5,839 in 2019, which ranks 132nd in the world for 2019. However, Pakistan's undocumented economy is estimated to be 36% of its overall economy, which is not taken into consideration when calculating per capita income. Pakistan is a developing country and is one of the Next Eleven countries identified by Jim O'Neill in a research paper as having a high potential of becoming, along with the BRICS countries, among the world's largest economies in the 21st century. The economy is semi-industrialized, with centres of growth along the Indus River. Primary export commodities include textiles, leather goods, sports goods, chemicals and carpets/rugs.

The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics and statistics and serves as a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System. The BLS is a governmental statistical agency that collects, processes, analyzes, and disseminates essential statistical data to the American public, the U.S. Congress, other Federal agencies, State and local governments, business, and labor representatives. The BLS also serves as a statistical resource to the United States Department of Labor, and conducts research into how much families need to earn to be able to enjoy a decent standard of living.
An economic indicator is a statistic about an economic activity. Economic indicators allow analysis of economic performance and predictions of future performance. One application of economic indicators is the study of business cycles. Economic indicators include various indices, earnings reports, and economic summaries: for example, the unemployment rate, quits rate, housing starts, consumer price index, consumer leverage ratio, industrial production, bankruptcies, gross domestic product, broadband internet penetration, retail sales, stock market prices, and money supply changes.

The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) of the United States Department of Commerce is a U.S. government agency that provides official macroeconomic and industry statistics, most notably reports about the gross domestic product (GDP) of the United States and its various units—states, cities/towns/townships/villages/counties and metropolitan areas. They also provide information about personal income, corporate profits, and government spending in their National Income and Product Accounts (NIPAs).

The national debt of the United States is the total debt, or unpaid borrowed funds, carried by the federal government of the United States, which is measured as the face value of the currently outstanding Treasury securities that have been issued by the Treasury and other federal government agencies. The terms "national deficit" and "national surplus" usually refer to the federal government budget balance from year to year, not the cumulative amount of debt. A deficit year increases the debt, while a surplus year decreases the debt as more money is received than spent.
Economic data or economic statistics are data describing an actual economy, past or present. These are typically found in time-series form, that is, covering more than one time period or in cross-sectional data in one time period. Data may also be collected from surveys of for example individuals and firms or aggregated to sectors and industries of a single economy or for the international economy. A collection of such data in table form comprises a data set.

In economics, a country's current account records the value of exports and imports of both goods and services. It is one of the three components of its balance of payments, the others being the capital account and the financial account. Current account measures the nation's earnings and spendings abroad and it consists of the balance of trade, net primary income or factor income and net unilateral transfers, that have taken place over a given period of time. The current account balance is one of two major measures of a country's foreign trade. A current account surplus indicates that the value of a country's net foreign assets grew over the period in question, and a current account deficit indicates that it shrank. Both government and private payments are included in the calculation. It is called the current account because goods and services are generally consumed in the current period.
The national income and product accounts (NIPA) are part of the national accounts of the United States. They are produced by the Bureau of Economic Analysis of the Department of Commerce. They are one of the main sources of data on general economic activity in the United States.
The personal consumption expenditure (PCE) measure is the component statistic for consumption in gross domestic product (GDP) collected by the United States Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA). It consists of the actual and imputed expenditures of households and includes data pertaining to durable and non-durable goods and services. It is essentially a measure of goods and services targeted towards individuals and consumed by individuals.
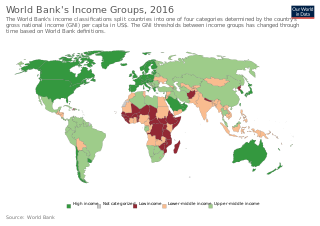
The gross national income (GNI), previously known as gross national product (GNP), is the total domestic and foreign output claimed by residents of a country, consisting of gross domestic product (GDP), plus factor incomes earned by foreign residents, minus income earned in the domestic economy by nonresidents. Comparing GNI to GDP shows the degree to which a nation's GDP represents domestic or international activity. GNI has gradually replaced GNP in international statistics. While being conceptually identical, it is calculated differently. GNI is the basis of calculation of the largest part of contributions to the budget of the European Union. In February 2017, Ireland's GDP became so distorted from the base erosion and profit shifting ("BEPS") tax planning tools of U.S. multinationals, that the Central Bank of Ireland replaced Irish GDP with a new metric, Irish Modified GNI*. In 2017, Irish GDP was 162% of Irish Modified GNI*.
Consumer confidence is an economic indicator that measures the degree of optimism that consumers feel about the overall state of the economy and their personal financial situation. If the consumer has confidence in the immediate and near future economy and his/her personal finance, then the consumer will spend more than save.
In economics, gross output (GO) is the measure of total economic activity in the production of new goods and services in an accounting period. It is a much broader measure of the economy than gross domestic product (GDP), which is limited mainly to final output. As of first-quarter 2019, the Bureau of Economic Analysis estimated gross output in the United States to be $37.2 trillion, compared to $21.1 trillion for GDP.

The Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) is the independent statutory agency of the Australian Government responsible for statistical collection and analysis, and for giving evidence-based advise to federal, state and territory governments. The ABS collects and analyses statistics on economic, population, environmental and social issues, publishing many on their website. The ABS also operates the national Census of Population and Housing that occurs every five years.

Personal income is an individual's total earnings from wages, investment interest, and other sources. The Bureau of Labor Statistics reported a median personal income of $865 weekly for all full-time workers in 2017. The U.S. Census Bureau lists the annual median personal income at $33,706 in 2018.
The China Economic Databases (CED) is a project of the China Studies Center at National Chengchi University, Taiwan. It collects and publishes information on China's economic development to support scholarly research. The CED is available in Chinese and English.

Foreign trade of the United States comprises the international imports and exports of the United States. The country is among the top three global importers and exporters.
The Regional Input–Output Modeling System is a regional economic model developed and maintained by the US Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA).
The Livingston Survey is a biannual survey about the economy of the United States conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia. Begun in 1946, it is the longest continuous record of economists' expectations.
References
- ↑ "Survey of Current Business Online" . Retrieved April 17, 2014.
- 1 2 "Survey of Current Business". FRASER . Retrieved October 16, 2014.
- 1 2 "Survey of Current Business, and related publications by the BEA". Digitization Projects Registry, Federal Depository Library Program . Retrieved April 17, 2014.
- ↑ "Bureau of Economic Analysis: Survey of Current Business". Internet Scout, University of Wisconsin-Madison . Retrieved April 17, 2014.
- ↑ "Survey of Current Business" (PDF). Bureau of Economic Analysis. July 1, 1921. Retrieved April 17, 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Survey of Current Business Online: Archives". Bureau of Economic Analysis . Retrieved April 17, 2014.
- ↑ Andrew D. Reamer. The Origins of the Survey of Current Business. Survey of Current Business, Oct 2020
- 1 2 "Survey of Current Business". Bureau of Economic Analysis . Retrieved April 17, 2014.
- ↑ "Interactive Data". Bureau of Economic Analysis . Retrieved April 17, 2014.
- ↑ "Livingston Survey: Data Sources and Descriptions" (PDF). Retrieved April 17, 2014.