
Mehndi is a form of temporary skin decoration using a paste created with henna. In the West, mehndi is commonly known as henna tattoo, although it is not a permanent tattoo.

Bromus is a large genus of grasses, classified in its own tribe Bromeae. They are commonly known as bromes, brome grasses, cheat grasses or chess grasses. Estimates in the scientific literature of the number of species have ranged from 100 to 400, but plant taxonomists currently recognize around 160–170 species.

The water deer is a small deer species native to Korea and China. Its prominent tusks, similar to those of musk deer, have led to both subspecies being colloquially named vampire deer in English-speaking areas to which they have been imported. It was first described to the Western world by Robert Swinhoe in 1870.

Andira inermis is a nitrogen-fixing tree with medicinal properties native to the area from southern Mexico through Central America to northern South America ; it has been introduced to the Caribbean, the Antilles, Florida, and Africa and is often pollinated by bees. The tree has many names due to its wide distribution and multiple uses: it is also known as the almendro macho, almendro de río or river almond (Honduras), bastard cabbage tree, cabbage angelin, cabbage bark, cabbage tree, carne asada, guacamayo (Honduras), Jamaica cabbage tree, harino (Panama), moca, partridge wood, worm bark, or yellow cabbage tree.

Nepenthes dubia is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to the Indonesian island of Sumatra, where it grows at an altitude of 1600–2700 m above sea level. The specific epithet dubia is the Latin word for "doubtful".

Nepenthes inermis is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to the Indonesian island of Sumatra. The specific epithet inermis is Latin for "unarmed" and refers to the upper pitchers of this species, which are unique in that they completely lack a peristome.

Navanax inermis, common name the California aglaja, is a large species of predatory sea slug, a marine opisthobranch gastropod mollusk in the family Aglajidae. Navanax is not a nudibranch, even though it somewhat resembles one; it belongs to a more ancient lineage of opisthobranchs called the cephalaspideans or head shield slugs and snails.

Stomatosuchus is an extinct stomatosuchid neosuchian from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) of Egypt. Much of what is known about Stomatosuchus has been inferred from the related genus Laganosuchus.

Nepenthes × pyriformis is a natural hybrid involving N. inermis and N. talangensis. It is known only from Mount Talang in Sumatra, to which N. talangensis is endemic. Nepenthes talangensis was only described as a distinct species in 1994. Prior to this it was placed within N. bongso and some of the older literature identifies this hybrid as N. bongso × N. inermis.
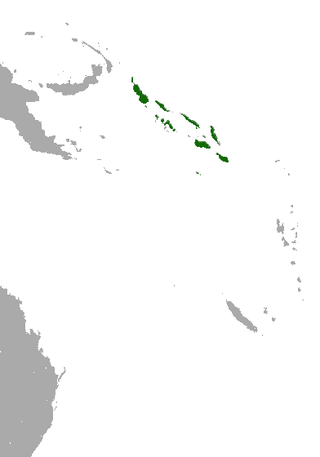
The Solomon's naked-backed fruit bat is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. It is endemic to the Solomon Islands.

The marbled grouper, donkey fish, mutton hamlet, rockhind and sicklefish grouper, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is a predatory reef fish which is found in the Western Atlantic Ocean.

The highlands punaré is a caviomorph rodent of South America from the spiny rat family. It is endemic to gallery forest, savanna and rocky outcrop habitats in Bahia State within the Caatinga ecoregion of eastern Brazil at elevations from 260 m to 1030 m. It sometimes nests and often takes refuge in crevices in rock formations, as means of both predator avoidance and moderating temperature extremes. The species tolerates a degree of habitat disturbance. Although hunted, it is considered common throughout its range. Its karyotype has 2n = 26 and FN = 48.

Bromus inermis is a species of the true grass family (Poaceae). This rhizomatous grass is native to Europe and considered invasive in North America.

Sebastes inermis, the Japanese red seaperch or dark-banded rockfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the family Scorpaenidae. It is found in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. This species is known as mebaru in Japan and as bollak (볼락) in Korea.

Sepiella inermis is a species of cuttlefish in the family Sepiidae. It is indigenous to the Indo-Pacific region. In this region, S. inermis is an economically important species, and is sold and eaten.

Sybra is a genus of beetles in the family Cerambycidae, containing the following species:

Sybra umbratica is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Pascoe in 1865.
Sybra uenoi is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Hayashi in 1956. It is known from Japan.

Sybra ordinata is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Henry Walter Bates in 1873.

















