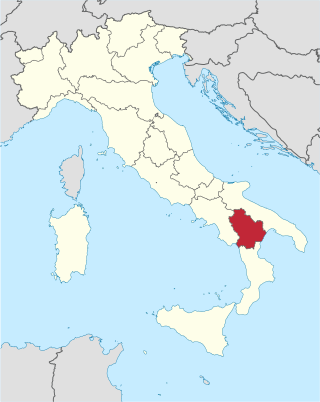
Basilicata, also known by its ancient name Lucania, is an administrative region in Southern Italy, bordering on Campania to the west, Apulia to the north and east, and Calabria to the south. It has two coastlines: a 30-km stretch on the Tyrrhenian Sea between Campania and Calabria, and a longer coastline along the Gulf of Taranto between Calabria and Apulia. The region can be thought of as the "arch" of the "boot" of Italy, with Calabria functioning as the "toe" and Apulia the "heel".

Carlo Gesualdo da Venosa was an Italian nobleman and composer. Though both the Prince of Venosa and Count of Conza, he is better known for writing madrigals and pieces of sacred music that use a chromatic language not heard again until the late 19th century. He is also known for killing his first wife and her aristocratic lover upon finding them in flagrante delicto.

Venosa is a town and comune in the province of Potenza, in the southern Italian region of Basilicata, in the Vulture area. It is bounded by the comuni of Barile, Ginestra, Lavello, Maschito, Montemilone, Palazzo San Gervasio, Rapolla and Spinazzola. It is one of I Borghi più belli d'Italia.

Maschito is a town and comune of the province of Potenza, in the Basilicata region of southern Italy. Like other towns in the Vulture area, Maschito was repopulated by Albanian refugees after the occupation of Albania by the Ottoman Empire.

Sarracenia purpurea, the purple pitcher plant, northern pitcher plant, turtle socks, or side-saddle flower, is a carnivorous plant in the family Sarraceniaceae.

Rapana venosa, common name the veined rapa whelk or Asian rapa whelk, is a species of large predatory sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc or whelk, in the family Muricidae, the rock shells.

Robert Venosa was an American Fantastic Realistic, Visionary painter who resided in Cadaques, Spain and Boulder, Colorado, US. He studied with what are termed the New Masters. His artworks reside in collections around the world.
The Italian Catholic diocese of Venosa, in southern Italy, existed until 1986. In that year it was united into the Diocese of Melfi-Rapolla-Venosa. From 1976 to 1986, Venosa had been a suffragan of the archdiocese of Potenza e Marsico Nuovo.

Disciotis is a genus of fungi in the family Morchellaceae. Members of this family, characterized by their cup- or bowl-shaped apothecia, have a widespread distribution, especially in northern temperate regions.

Rapana is a genus of large predatory sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Muricidae, the rock snails.
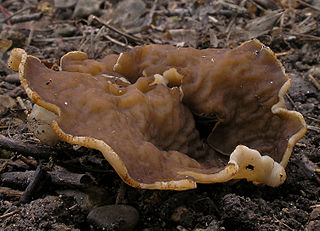
Disciotis venosa, commonly known as the bleach cup, veiny cup fungus, or the cup morel is a species of fungus in the family Morchellaceae. Fruiting from April, they are often difficult to locate because of their nondescript brown color.

Abantis venosa, the veined skipper or veined paradise skipper, is a butterfly of the family Hesperiidae. It is found in Zululand, Eswatini, Transvaal, Zimbabwe, Kenya and Uganda.
Chione is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae containing the single species Chione venosa. It is native to the neotropics, occurring in most of Mexico, and throughout Central America, the Caribbean, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. It is typically a tree growing 10 to 20 meters tall. In harsh habitats, it may be dwarfed and shrubby. It has no known economic use.

The Abbey of Santissima Trinità or Abbey of the Most Holy Trinity, Italian: Abbazia della Santissima Trinità, is a Roman Catholic abbey complex at Venosa, in the Vulture area of the province of Potenza, in the southern Italian region of Basilicata. The architecture of the abbey shows Roman, Lombard, and Norman influences. The complex lies within the Parco Archeologico of Venosa, approximately 1.5 km north-east of the town; it falls under the Roman Catholic Diocese of Melfi-Rapolla-Venosa. It consists of the old church, of uncertain date; the monastery buildings; and the Incompiuta, the unfinished or new church, begun in the last quarter of the eleventh century and never completed. The complex was declared a National Monument by Royal Decree on 20 November 1897. It is no longer a monastery, but is used by the Trinitarian Order.
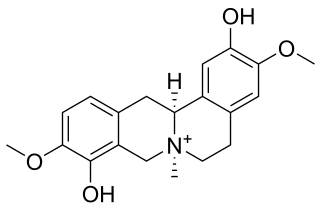
Cyclanoline is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor isolated from Stephania venosa tuber.

Sybra is a genus of beetles in the family Cerambycidae, containing the following species:

Sybra umbratica is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Pascoe in 1865.

Sybra ordinata is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Henry Walter Bates in 1873.
Tommaso da San Cipriano was a Roman Catholic prelate who served as Bishop of Venosa (1519–?).

Fontainea venosa, also commonly known as southern blushwood, veiny fontainea, Queensland fontainea and formerly named as Bahrs scrub fontainea is a rare rainforest shrub or tree of the family Euphorbiaceae. It is found in southeastern Queensland, Australia, extending from Boyne Valley to Cedar Creek and is considered vulnerable due to several contributing threats. The total population size is around 200 plants.














