Chytridiomycota are a division of zoosporic organisms in the kingdom Fungi, informally known as chytrids. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek χυτρίδιον, meaning "little pot", describing the structure containing unreleased zoospores. Chytrids are one of the earliest diverging fungal lineages, and their membership in kingdom Fungi is demonstrated with chitin cell walls, a posterior whiplash flagellum, absorptive nutrition, use of glycogen as an energy storage compound, and synthesis of lysine by the α-amino adipic acid (AAA) pathway.
Under United States law, Biological select agents or toxins (BSATs)—or simply select agents for short—are bio-agents which have been declared by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) or by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) to have the "potential to pose a severe threat to public health and safety". The agents are divided into (1) HHS select agents and toxins affecting humans; (2) USDA select agents and toxins affecting agriculture; and (3) overlap select agents and toxins affecting both.

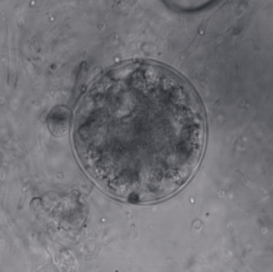
Synchytrium endobioticum is a chytrid fungus that causes the potato wart disease, or black scab. It also infects some other plants of the genus Solanum, though potato is the only cultivated host.

Cercospora is a genus of ascomycete fungi. Most species have no known sexual stage, and when the sexual stage is identified, it is in the genus Mycosphaerella. Most species of this genus cause plant diseases, and form leaf spots. It is a relatively well-studied genus of fungi, but there are countless species not yet described, and there is still much to learn about the best-known members of the genus.
Septoria liquidambaris is a fungal plant pathogen infecting sweetgum trees.
Stigmina liquidambaris is a fungal plant pathogen infecting sweetgum trees.

Succisa pratensis, also known as devil's-bit or devil's-bit scabious, is a flowering plant in the honeysuckle family Caprifoliaceae. It differs from other similar species in that it has four-lobed flowers, whereas small scabious and field scabious have five lobes and hence it has been placed in a separate genus in the same family. It also grows on damper ground.

Desmodium gangeticum is commonly known by the name salparni. It can be found throughout most parts of India and Himalayas.

Marasmius funalis is a species of Marasmiaceae fungus known only from Japan. The species produces small mushrooms with reddish-brown caps up to 6 millimetres (0.24 in) in diameter and dark-brown, threadlike stems of up to 50 millimetres (2.0 in) in length. The species has a number of distinctive microscopic features, including very long cystidia on the stem, visible as bristles. Described in 2002 by Haruki Takahashi, the species grows on dead wood. The closest relative of M. funalis is M. liquidambari, known from Mexico and Papua New Guinea, and it is also similar in appearance to M. hudonii and Setulipes funaliformis, the latter of which was named after M. funalis.

Kathleen Maisey Curtis, Lady Rigg was a New Zealand mycologist and was a founder of plant pathology in New Zealand.

Bintje is a middle-early ripening potato variety bred in the Netherlands by the Frisian schoolmaster K.L. de Vries in 1904 from and marketed for the first time in 1910. The name of the potato, a diminutive of Benedict, was borrowed from one of his former students.

Flora Wambaugh Patterson was an American mycologist, and the first female plant pathologist hired by the United States Department of Agriculture. She ran the US National Fungus Collections for almost thirty years, radically growing the collection and shaping its direction, and supervised or discovered numerous significant fungal diseases.
The National Fungus Collections of the United States is the "world's largest herbarium of dried fungus specimens". It is housed within the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).

Synchytrium is a large genus of plant pathogens within the phylum Chytridiomycota. Species are commonly known as false rust or wart disease. Approximately 200 species are described, and all are obligate parasites of angiosperms, ferns, or mosses. Early species were mistakenly classified among the higher fungi because of their superficial similarity to the rust fungi. Anton de Bary and Mikhail S. Woronin recognized the true nature of these fungi and established the genus to accommodate Synchytrium taraxaci, which grows on dandelions, and S. succisae, which grows on Succisa pratensis. Synchytrium taraxaci is the type of the genus. The genus has been divided into 6 subgenera based on differences in life cycles.

Synchytriaceae is a chytrid fungus family in the division Chytridiomycota. The family was described by German mycologist Joseph Schröter in 1892. The type genus, Synchytrium, contains about 200 species of fungi that are parasitic on flowering plants, ferns, mosses, and algae. Synchytrium endobioticum causes potato wart disease, an economically important disease of cultivated potato.
Stigmina is a genus of fungal plant pathogens in the family Mycosphaerellaceae.
Claude Wilbur Edgerton was an American mycologist. He was born in Woodbine, Iowa, and earned a Bachelor of Science degree from the University of Nebraska in 1903, and a PhD from Cornell University in 1908. After this he was employed at Louisiana State University, initially as a plant pathologist in the Agricultural Research Station, and later as Professor and then Head of Botany, Bacteriology, and Plant Pathology in 1924. Edgerton had this position until his retirement in 1950. He was known for his study of sugarcane diseases; his teaching materials formed the basis of the book Sugarcane and Its Diseases, first published in 1955 after his retirement. Species named in honor of Edgerton include Cryptosporiopsis edgertonii and Synchytrium edgertonii.

Eupterote is a genus of moths in the family Eupterotidae. It was first described by Jacob Hübner in 1820.

Mary Dilys Glynne was a British plant pathologist and mountaineer.











