TSC22 domain family protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TSC22D3 gene. [5] [6]
TSC22 domain family protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TSC22D3 gene. [5] [6]
The protein encoded by this gene shares significant sequence identity with the murine TSC-22 and Drosophila shs, both of which are leucine zipper proteins, that function as transcriptional regulators. GILZ shows ubiquitous expression across tissues, including thymus, spleen, lung, fat, liver, kidney, heart, and skeletal muscle. [7] [8] The expression of this gene is stimulated by glucocorticoids and interleukin 10, and it appears to play a key role in the anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of this steroid and chemokine. Transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene. [6]
TSC22D3 has been shown to interact with C-Raf, [9] NFKB2 [10] and NFKB1. [10]
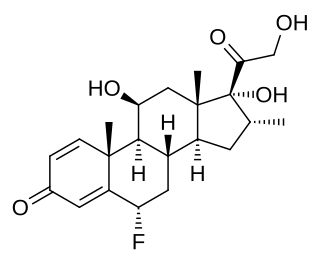
Paramethasone is a fluorinated glucocorticoid with anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant properties.

Activator protein 1 (AP-1) is a transcription factor that regulates gene expression in response to a variety of stimuli, including cytokines, growth factors, stress, and bacterial and viral infections. AP-1 controls a number of cellular processes including differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. The structure of AP-1 is a heterodimer composed of proteins belonging to the c-Fos, c-Jun, ATF and JDP families.

Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NFKB1 gene.

Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p100 subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NFKB2 gene.
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEBPB gene.

Activating transcription factor 4 , also known as ATF4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATF4 gene.

CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), epsilon, also known as CEBPE and CRP1, is a type of ccaat-enhancer-binding protein. CEBPE is its human gene and is pro-apoptotic.

Transcription regulator protein BACH1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BACH1 gene.

Hepatic leukemia factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLF gene.
Transcription factor MafG is a bZip Maf transcription factor protein that in humans is encoded by the MAFG gene.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase 12 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAP3K12 gene.

Transcription factor MafB also known as V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MAFB gene. This gene maps to chromosome 20q11.2-q13.1, consists of a single exon and spans around 3 kb.

Fos-related antigen 2 (FRA2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOSL2 gene.

Transcription regulator protein BACH2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BACH2 gene. It contains a BTB/POZ domain at its N-terminus which forms a disulphide-linked dimer and a bZip_Maf domain at the C-terminus.

Glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRLF1 gene.

Thyrotroph embryonic factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TEF gene.

Golgin-45 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BLZF1 gene.

Basic leucine zipper transcription factor, ATF-like, also known as BATF, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the BATF gene.

Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 18 (TNFRSF18), also known as glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein (GITR) or CD357. GITR is encoded and tnfrsf18 gene at chromosome 4 in mice. GITR is type I transmembrane protein and is described in 4 different isoforms. GITR human orthologue, also called activation-inducible TNFR family receptor (AITR), is encoded by the TNFRSF18 gene at chromosome 1.

Selective glucocorticoid receptor modulators (SEGRMs) and selective glucocorticoid receptor agonists (SEGRAs) formerly known as dissociated glucocorticoid receptor agonists (DIGRAs) are a class of experimental drugs designed to share many of the desirable anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, or anticancer properties of classical glucocorticoid drugs but with fewer side effects such as skin atrophy. Although preclinical evidence on SEGRAMs’ anti-inflammatory effects are culminating, currently, the efficacy of these SEGRAMs on cancer are largely unknown.