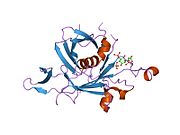
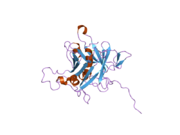
Proprotein convertase 1, also known as prohormone convertase, prohormone convertase 3, or neuroendocrine convertase 1 and often abbreviated as PC1/3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCSK1 gene. PCSK1 and PCSK2 differentially cleave proopiomelanocortin and they act together to process proinsulin and proglucagon in pancreatic islets.

Agouti-signaling protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ASIP gene. It is responsible for the distribution of melanin pigment in mammals. Agouti interacts with the melanocortin 1 receptor to determine whether the melanocyte produces phaeomelanin, or eumelanin. This interaction is responsible for making distinct light and dark bands in the hairs of animals such as the agouti, which the gene is named after. In other species such as horses, agouti signalling is responsible for determining which parts of the body will be red or black. Mice with wildtype agouti will be grey, with each hair being partly yellow and partly black. Loss of function mutations in mice and other species cause black fur coloration, while mutations causing expression throughout the whole body in mice cause yellow fur and obesity.
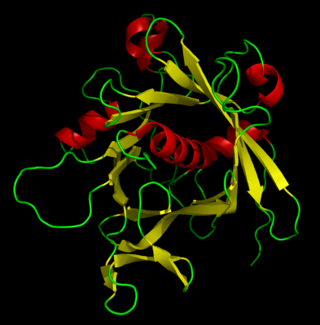
The tubby protein is encoded by the TUB gene. It is an upstream cell signaling protein common to multicellular eukaryotes. The first tubby gene was identified in mice, and proteins that are homologous to tubby are known as "tubby-like proteins" (TULPs). They share a common and characteristic tertiary structure that consists of a beta barrel packed around an alpha helix in the central pore. The gene derives its name from its role in metabolism; mice with a mutated tubby gene develop delayed-onset obesity, sensorineural hearing loss, and retinal degeneration.

Achaete-scute homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ASCL1 gene. Because it was discovered subsequent to studies on its homolog in Drosophila, the Achaete-scute complex, it was originally named MASH-1 for mammalian achaete scute homolog-1.

Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PPARGC1B gene.

Tribbles homolog 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRIB3 gene.

Transcription initiation factor TFIID subunit 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAF8 gene.

Tubby-related protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TULP1 gene.

Chorion-specific transcription factor GCMa is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the GCM1 gene.

DnaJ homolog subfamily A member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAJA2 gene.

Early placenta insulin-like peptide is a protein that in humans is encoded by the INSL4 gene.

Repressor of RNA polymerase III transcription MAF1 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MAF1 gene.

Striated muscle preferentially expressed protein kinase, in the human is encoded by the SPEG gene, a member of the myosin light chain kinase protein family. SPEG is involved in the development of the muscle cell cytoskeleton, and the expression of this gene has important roles in the development of skeletal muscles, and their maintenance and function. Mutations are associated with centronuclear myopathies a group of congenital disorders where the cell nuclei are abnormally centrally placed.

Zinc finger protein 143 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF143 gene.

Homeobox protein SIX4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SIX4 gene.

Teashirt homolog 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TSHZ3 gene. In mice, it is a necessary part of the neural circuitry that controls breathing. The gene is also a homolog of the Drosophila melanogaster teashirt gene, which encodes a zinc finger transcription factor important for development of the trunk.

39S ribosomal protein L17, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MRPL17 gene.

Kruppel-like factor 7 (ubiquitous), also known as KLF7, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the KLF7 gene.

Neuralized-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NEURL gene.

Iroquois-class homeodomain protein IRX-3, also known as Iroquois homeobox protein 3, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IRX3 gene.