Related Research Articles

Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, caucho, or caoutchouc, as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia are three of the leading rubber producers.

Vulcanization is a range of processes for hardening rubbers. The term originally referred exclusively to the treatment of natural rubber with sulfur, which remains the most common practice. It has also grown to include the hardening of other (synthetic) rubbers via various means. Examples include silicone rubber via room temperature vulcanizing and chloroprene rubber (neoprene) using metal oxides.

Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a poor barrier to oxygen and water vapour and has a relatively low melting point. Polystyrene is one of the most widely used plastics, the scale of its production being several million tonnes per year. Polystyrene can be naturally transparent, but can be colored with colorants. Uses include protective packaging, containers, lids, bottles, trays, tumblers, disposable cutlery, in the making of models, and as an alternative material for phonograph records.

Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) (chemical formula (C8H8)x·(C4H6)y·(C3H3N)z ) is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately 105 °C (221 °F). ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point.
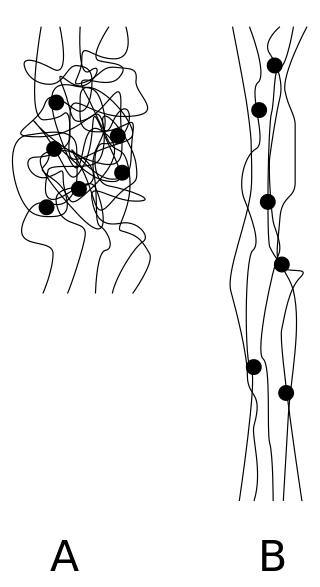
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus (E) and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of elastic polymer, is often used interchangeably with rubber, although the latter is preferred when referring to vulcanisates. Each of the monomers which link to form the polymer is usually a compound of several elements among carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and silicon. Elastomers are amorphous polymers maintained above their glass transition temperature, so that considerable molecular reconformation is feasible without breaking of covalent bonds. At ambient temperatures, such rubbers are thus relatively compliant and deformable. Their primary uses are for seals, adhesives and molded flexible parts. Application areas for different types of rubber are manifold and cover segments as diverse as tires, soles for shoes, and damping and insulating elements.
Accelerants are substances that can bond, mix or disturb another substance and cause an increase in the speed of a natural, or artificial chemical process. Accelerants play a major role in chemistry—most chemical reactions can be hastened with an accelerant. Accelerants alter a chemical bond, speed up a chemical process, or bring organisms back to homeostasis. Accelerants are not necessarily catalysts as they may be consumed by the process.

Microcellular plastics, otherwise known as microcellular foam, is a form of manufactured plastic fabricated to contain billions of tiny bubbles less than 50 microns wide. It is formed by dissolving gas under high pressure into various polymers, relying on the phenomenon of thermodynamic instability to cause the uniform arrangement of the gas bubbles, otherwise known as nucleation. Its main purpose was to reduce material usage while maintaining valuable mechanical properties. the density of the finished product is determined by the gas used. Depending on the gas, the foam's density can be between 5% and 99% of the pre-processed plastic. Design parameters, focused on the foam's final form and the molding process afterward, include the type of die or mold to be used, as well as the dimensions of the bubbles, or cells, that classify the material as a foam. Since the cells' size is close to the wavelength of light, to the casual observer the foam retains the appearance of a solid, light-colored plastic.
Nitrile rubber, also known as nitrile butadiene rubber, NBR, Buna-N, and acrylonitrile butadiene rubber, is a synthetic rubber derived from acrylonitrile (ACN) and butadiene. Trade names include Perbunan, Nipol, Krynac and Europrene. This rubber is unusual in being resistant to oil, fuel, and other chemicals.

Foam rubber refers to rubber that has been manufactured with a foaming agent to create an air-filled matrix structure. Commercial foam rubbers are generally made of synthetic rubber, natural latex or polyurethane. Latex foam rubber, used in mattresses, is well known for its endurance. Polyurethane is a thermosetting polymer that comes from combination of Methyl di-isocyanate and polyethylene and some other chemical additives.

Pneumatic tires are manufactured according to relatively standardized processes and machinery, in around 455 tire factories in the world. With over 1 billion tires manufactured worldwide annually, the tire industry is a major consumer of natural rubber. Tire factories start with bulk raw materials such as synthetic rubber, carbon black, and chemicals and produce numerous specialized components that are assembled and cured.

Foam latex or latex foam rubber is a lightweight form of latex containing bubbles known as cells, created from liquid latex. The foam is generally created though the Dunlop or Talalay process in which a liquid latex is foamed and then cured in a mold to extract the foam.
Gum base is the non-nutritive, non-digestible, water-insoluble masticatory delivery system used to carry sweeteners, flavors, and any other substances in chewing gum and bubble gum. It provides all the basic textural and masticatory properties of gum.
Rubber Technology is the subject dealing with the transformation of rubbers or elastomers into useful products, such as automobile tires, rubber mats and, exercise rubber stretching bands. The materials includes latex, natural rubber, synthetic rubber and other polymeric materials, such as thermoplastic elastomers. Rubber processed through such methods are components of a wide range of items.
A blowing agent is a substance which is capable of producing a cellular structure via a foaming process in a variety of materials that undergo hardening or phase transition, such as polymers, plastics, and metals. They are typically applied when the blown material is in a liquid stage. The cellular structure in a matrix reduces density, increasing thermal and acoustic insulation, while increasing relative stiffness of the original polymer.
Polymer engineering is generally an engineering field that designs, analyses, and modifies polymer materials. Polymer engineering covers aspects of the petrochemical industry, polymerization, structure and characterization of polymers, properties of polymers, compounding and processing of polymers and description of major polymers, structure property relations and applications.

A mattress pad, mattress topper, or underpad is designed to lie atop a mattress. Made from a variety of materials such as wool, cotton, memory foam, feather or latex, its function is to provide an extra layer of comfort, especially when the existing mattress is worn or uncomfortable.

Latex is an emulsion of polymer microparticles in water. Latexes are found in nature, but synthetic latexes are common as well.
Resin casting is a method of plastic casting where a mold is filled with a liquid synthetic resin, which then hardens. It is primarily used for small-scale production like industrial prototypes and dentistry. It can be done by amateur hobbyists with little initial investment, and is used in the production of collectible toys, models and figures, as well as small-scale jewellery production.
RTV silicone is a type of silicone rubber that cures at room temperature. It is available as a one-component product, or mixed from two-components. Manufacturers provide it in a range of hardnesses from very soft to medium—usually from 15 to 40 Shore A. RTV silicones can be cured with a catalyst consisting of either platinum or a tin compound such as dibutyltin dilaurate. Applications include low-temperature over-molding, making molds for reproducing, and lens applications for some optically clear grades. It is also used widely in the automotive industry as an adhesive/sealant, for example to create gaskets in-place.

The Charles Goodyear Medal is the highest honor conferred by the American Chemical Society, Rubber Division. Established in 1941, the award is named after Charles Goodyear, the discoverer of vulcanization, and consists of a gold medal, a framed certificate and prize money. The medal honors individuals for "outstanding invention, innovation, or development which has resulted in a significant change or contribution to the nature of the rubber industry". Awardees give a lecture at an ACS Rubber Division meeting, and publish a review of their work in the society's scientific journal Rubber Chemistry and Technology.
References
- ↑ "Mattress Terms". Mattress1st.com. Retrieved 11 February 2012.
- ↑ "Dunlopillo :: Company / Company History". Dunlopillo.gr. Retrieved 12 February 2012.