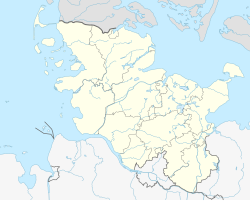
Schleswig-Holstein is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig. Its capital city is Kiel; other notable cities are Lübeck and Flensburg.
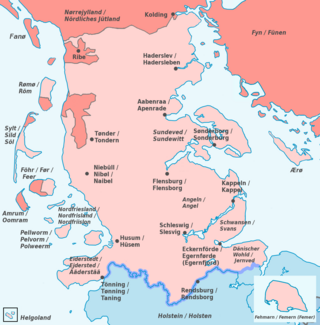
The Duchy of Schleswig was a duchy in Southern Jutland covering the area between about 60 km north and 70 km (45 mi) south of the current border between Germany and Denmark. The territory has been divided between the two countries since 1920, with Northern Schleswig in Denmark and Southern Schleswig in Germany. The region is also called Sleswick in English.

Schleswig is a town in the northeastern part of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is the capital of the Kreis (district) Schleswig-Flensburg. It has a population of about 27,000, the main industries being leather and food processing. It takes its name from the Schlei, an inlet of the Baltic sea at the end of which it sits, and vik or vig which means "bay" in Old Norse and Danish. Schleswig or Slesvig therefore means "bay of the Schlei".
Rendsburg-Eckernförde is a district in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is bounded by the city of Kiel, the district of Plön, the city of Neumünster, the districts of Segeberg, Steinburg, Dithmarschen and Schleswig-Flensburg, and the Baltic Sea.
Ostholstein is a district in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Stormarn, Segeberg and Plön, the Baltic Sea and the city of Lübeck.
Segeberg is a district in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Pinneberg, Steinburg and Rendsburg-Eckernförde, the city of Neumünster, the districts of Plön, Ostholstein and Stormarn, and the city state of Hamburg.

Holstein is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of Germany.

Glücksburg is a small town northeast of Flensburg in the district Schleswig-Flensburg, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany and is the northernmost town in Germany.

The history of Schleswig-Holstein consists of the corpus of facts since the pre-history times until the modern establishing of the Schleswig-Holstein state.

The House of Glücksburg, shortened from House of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg, is a collateral branch of the German House of Oldenburg, members of which have reigned at various times in Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Iceland, several northern German states, Greece, and the United Kingdom.

The House of Oldenburg is a German dynasty with links to Denmark since the 15th century. It has had branches that rule or have ruled in Denmark, Iceland, Greece, Norway, Russia, Sweden, the United Kingdom, Schleswig, Holstein, and Oldenburg. The current Queen of Denmark, King of Norway and King of the United Kingdom are all patrilineal descendants of the Glücksburg branch of this house.

The First Schleswig War was a military conflict in southern Denmark and northern Germany rooted in the Schleswig-Holstein Question, contesting the issue of who should control the Duchies of Schleswig, Holstein and Lauenburg. Ultimately, the Danish side proved victorious with the diplomatic support of the great powers.

The Second Schleswig War also sometimes known as the Dano-Prussian War or Prusso-Danish War was the second military conflict over the Schleswig-Holstein Question of the nineteenth century. The war began on 1 February 1864, when Prussian and Austrian forces crossed the border into the Danish fief Schleswig. Denmark fought the Kingdom of Prussia and the Austrian Empire.
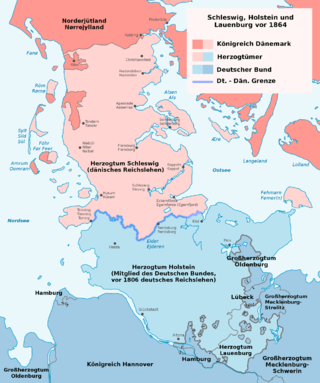
The Schleswig–Holstein question was a complex set of diplomatic and other issues arising in the 19th century from the relations of two duchies, Schleswig and Holstein, to the Danish crown, to the German Confederation, and to each other. The British statesman Lord Palmerston is reported to have said: "Only three people have ever really understood the Schleswig-Holstein business – the Prince Consort, who is dead – a German professor, who has gone mad – and I, who have forgotten all about it."

SMS Schleswig-Holstein was the last of the five pre-dreadnought Deutschland-class battleships built by the German Kaiserliche Marine. The ship, named for the province of Schleswig-Holstein, was laid down in the Germaniawerft dockyard in Kiel in August 1905 and commissioned into the fleet nearly three years later. The ships of her class were already outdated by the time they entered service, being inferior in size, armor, firepower and speed to the new generation of dreadnought battleships.

The Province of Schleswig-Holstein was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1868 to 1946.

The Duchy of Holstein was the northernmost state of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the present German state of Schleswig-Holstein. It originated when King Christian I of Denmark had his County of Holstein-Rendsburg elevated to a duchy by Emperor Frederick III in 1474. Members of the Danish House of Oldenburg ruled Holstein – jointly with the Duchy of Schleswig – for its entire existence.

The Oberliga Schleswig-Holstein, formerly referred to as Schleswig-Holstein-Liga, is the fifth tier of the German football league system and the highest league in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. It is one of fourteen Oberligas in German football.
The Politics of Schleswig-Holstein takes place within a framework of a federal parliamentary representative democratic republic, where the Federal Government of Germany exercises sovereign rights with certain powers reserved to the states of Germany including Schleswig-Holstein. The state has a multi-party system.