Related Research Articles

Hindi cinema, popularly known as Bollywood and formerly as Bombay cinema, refers to the film industry based in Mumbai, engaged in production of motion pictures in Hindi language. The popular term Bollywood is a portmanteau of "Bombay" and "Hollywood". The industry is a part of the larger Indian cinema, which also includes South Indian cinema and other smaller film industries.

Marathi is an Indo-Aryan language predominantly spoken by Marathi people in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the official language of Maharashtra, and an additional official language in the state of Goa used to reply provided the request is received in Marathi. It is one of the 22 scheduled languages of India, with 83 million speakers as of 2011. Marathi ranks 13th in the list of languages with most native speakers in the world. Marathi has the third largest number of native speakers in India, after Hindi and Bengali. The language has some of the oldest literature of all modern Indian languages. The major dialects of Marathi are Standard Marathi and the Varhadi dialect.

Urdu is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan, where it is also an official language alongside English. In India, Urdu is an Eighth Schedule language, the status and cultural heritage of which are recognised by the Constitution of India; and it also has an official status in several Indian states. In Nepal, Urdu is a registered regional dialect and in South Africa it is a protected language in the constitution. It is also spoken as a minority language in Afghanistan and Bangladesh, with no official status.

Hindustani is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in North India, Pakistan and the Deccan and used as the official language of India and Pakistan. Hindustani is a pluricentric language with two standard registers, known as Hindi and Urdu. Thus, it is also called Hindi–Urdu. Colloquial registers of the language fall on a spectrum between these standards. In modern times, a third variety of Hindustani with significant English influences has also appeared which is sometimes called Hinglish or Urdish.
Indian English (IE) is a group of English dialects spoken in the Republic of India and among the Indian diaspora. English is used by the Government of India for communication, and is enshrined in the Constitution of India. English is also an official language in seven states and seven union territories of India, and the additional official language in seven other states and one union territory. Furthermore, English is the sole official language of the Judiciary of India, unless the state governor or legislature mandates the use of a regional language, or if the President of India has given approval for the use of regional languages in courts.
Hinglish is the macaronic hybrid use of South Asian English and the Hindustani language. Its name is a portmanteau of the words Hindi and English. In the context of spoken language, it involves code-switching or translanguaging between these languages whereby they are freely interchanged within a sentence or between sentences.

Deccani is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Deccan region of south-central India and the native language of the Deccani people. The historical form of Deccani sparked the development of Urdu literature during the late-Mughal period. Deccani arose as a lingua franca under the Delhi and Bahmani Sultanates, as trade and migration from the north introduced Hindavi to southern India. It later developed a literary tradition under the patronage of the Deccan Sultanates. Deccani itself came to influence Hindustani, on which Urdu and Hindi are based.
Bombay Hindi, also known as Bambaiya Hindi or Mumbaiya Hindi, is the Hindustani dialect spoken in Mumbai, in the Konkan region of India. Its vocabulary is largely from Hindi–Urdu, additionally, it has the predominant substratum of Marathi-Konkani, which is the official language and is also widely spoken in the Konkan division of Maharashtra. Bombay Hindi also has elements of Gujarati.
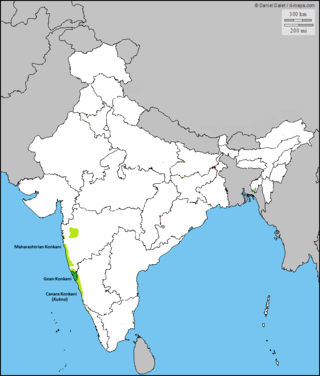
Konkani is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Konkani people, primarily in the Konkan region, along the western coast of India. It is one of the 22 scheduled languages mentioned in the Indian Constitution, and the official language of the Indian state of Goa. It is also spoken in Karnataka, Maharashtra, Kerala, Gujarat as well as Damaon, Diu & Silvassa.

Amol Palekar is an Indian actor, director and producer of Hindi and Marathi cinema.

Laxmikant Berde was an Indian Marathi language film actor who appeared in Marathi and Hindi movies. Known for his highly energetic slapstick performances, Berde started his career as an employee in the production company Mumbai Marathi Sahitya Sangh and then played supporting roles in a few Marathi stage plays. In 1983–84, he first became famous with the Marathi play Tur Tur.
Tapori can refer to:
Shemaroo Entertainment Ltd. is an Indian content creator, aggregator and distributor, specifically in the media and entertainment industry. It was founded by Buddhichand Maroo in 1962 as a book-circulating library under the name Shemaroo. It set up India's first video rental business in 1979. The company went national after it began content distribution in 1987, became aggregators and bought rights to movies for home video.

Marathi Cinema, also known as Marathi Chitrapat, is the segment of Indian cinema, dedicated to the production of motion pictures in the Marathi language widely spoken in the state of Maharashtra. It is based in Mumbai. It is the oldest film industry of India and one of the leaders in filmmaking in the Indian film industry. The first Marathi talkie film was Ayodhyecha Raja, released in 1932, one year after Alam Ara, the first Hindi talkie, was released, before releasing Aayodhyecha Raja. All Marathi films until then were silent films with intertitles.
Varhadi or Varhadi-Nagpuri is a dialect of Marathi spoken in Vidarbha region of Maharashtra and by Marathi people of adjoining parts of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Telangana in India.
IndoWordNet is a linked lexical knowledge base of wordnets of 18 scheduled languages of India, viz., Assamese, Bangla, Bodo, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Malayalam, Meitei (Manipuri), Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Tamil, Telugu and Urdu.
Parsi theatre is a generic term for an influential theatre tradition, staged by Parsis, and theatre companies largely-owned by the Parsi business community, which flourished between 1850 and the 1930s. Plays were primarily in the Hindustani language, as well as Gujarati to an extent. After its beginning in Bombay, it soon developed into various travelling theatre companies, which toured across India, especially north and western India, popularizing proscenium-style theatre in regional languages.

Modern Standard Hindi is mutually intelligible with Urdu, the national and official language of Pakistan. Both are standard registers of the Hindustani language. As a result of linguistic and cultural similarities, Hindi has had notable influences in Pakistan and is taught as an academic subject in some institutions; before the partition of colonial India, Hindi was taught at major universities in the provinces that came to form Pakistan. While Hindi and Urdu both have a predominantly Indic (Indo-Aryan) base, Hindi uses more Sanskrit words in its educated vocabulary while Urdu incorporates more Arabic, Persian, and a few Turkic words for the same. Most poetry, ghazals, qawalis & lyrics use many Urdu words.

Gully rap is an emerging genre of hip-hop music that originated from Mumbai. It has since spread across India. Inspired by American rappers like Tupac, The Notorious B.I.G. and Nas the music discusses the street life in distinct Hindu-Urdu rhythm and cadence. Gully means "narrow lane" in Hindi. DIVINE and Naezy are artists that are considered at the forefront of the genre. It stands in contrast to mainstream desi rap or Bollywood which focus on more superficial aspects of life. By contrast, gully rap has a socio-political emphasis.
References
- 1 2 Mazumdar, R. 2007. Bombay Cinema: An Archive of the City. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press
- ↑ Jeffrey, Craig (14 July 2010). "Timepass: Youth, class, and time among unemployed young men in India". American Ethnologist. 37 (3): 466. doi:10.1111/j.1548-1425.2010.01266.x.
- ↑ Tapori Children's Network - ATD Fourth World