
West Kalimantan is a province of Indonesia. It is one of five Indonesian provinces comprising Kalimantan, the Indonesian part of the island of Borneo. Its capital and largest city is Pontianak. It is bordered by East Kalimantan and Central Kalimantan to the east, the Malaysian state of Sarawak to the north, and the Bangka Belitung Islands to the west and the Java Sea to the south. The province has an area of 147,037 km2, and had a population of 4,395,983 at the 2010 Census and 5,414,390 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 5,623,328, and was projected to rise to 5,695,500 at mid 2024. Ethnic groups include the Dayak, Malay, Chinese, Javanese, Bugis, and Madurese. The borders of West Kalimantan roughly trace the mountain ranges surrounding the vast watershed of the Kapuas River, which drains most of the province. The province shares land borders with Central Kalimantan to the southeast, East Kalimantan to the east, and the Malaysian territory of Sarawak to the north.
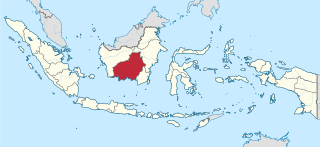
Central Kalimantan is a province of Indonesia. It is one of five provinces in Kalimantan, the Indonesian part of Borneo. It is bordered by West Kalimantan to the west, South Kalimantan and East Kalimantan to the east, Java Sea to the south and is separated narrowly from North Kalimantan and Malaysia by East Kalimantan's Mahakam Ulu Regency. Its provincial capital is Palangka Raya and in 2010 its population was over 2.2 million, while the 2020 Census showed a total of almost 2.67 million; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 2,774,747, and was projected to rise to 2,809,700 at mid 2024.

Pontianak, also known as Khuntien in Hakka, is the capital of the Indonesian province of West Kalimantan, founded first as a trading port on the island of Borneo, occupying an area of 118.21 km2 in the delta of the Kapuas River, at a point where it is joined by its major tributary, the Landak River. The city is on the equator, hence it is widely known as Kota Khatulistiwa. The city center is less than 3 kilometres (2 mi) south of the equator. Pontianak is the 23rd most populous city in Indonesia, and the fourth most populous city on the island of Borneo (Kalimantan) after Samarinda, Balikpapan and (Malaysia's) Kuching; it is now slightly ahead of Banjarmasin. It had a population of 658,685 at the 2020 Census within the city limits, with significant suburbs outside those limits. The official estimate as of mid-2023 was 675,468.

The Kapuas River is a river in the Indonesian part of Borneo island, at the geographic center of Maritime Southeast Asia. At 1,143 kilometers (710 mi) in length, it is the longest river in the island of Borneo and the longest river in Indonesia and one of the world's longest island rivers. It originates in the Müller mountain range at the center of the island and flows west into the South China Sea creating an extended marshy delta. The delta is located west-southwest of Pontianak, the capital of the West Kalimantan province. This Kapuas River should be distinguished from another Kapuas River, which starts on the other side of the same mountain range in central Borneo but flows to the south, merging with the Barito River and discharging into the Java Sea.

Samarinda is the capital city of the Indonesian province of East Kalimantan on the island of Borneo. The city lies on the banks of the Mahakam River with a land area of 718 km2 (277 sq mi). Samarinda was one of Indonesia's top ten Most Liveable Cities in 2022, ranks first on East Kalimantan Human Development Index and it is the most populous city on the entire Borneo island, with a population of 727,500 at the 2010 Census and 827,994 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 861,878. Samarinda is East Kalimantan's largest exporter and fifth-largest importer. The city has the highest number of bank headquarters in East Kalimantan.

Palangka Raya is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of Central Kalimantan. The city is situated between the Kahayan and the Sabangau rivers on the island of Borneo. As of the 2020 census, the city has a population of 293,500; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 305,797. Palangka Raya is the largest city by land area in Indonesia ; however, most of the area is forested including protected forests, nature conservation areas, and Tangkiling Forest.

Syamsudin Noor Airport is an airport serving Banjarmasin in South Kalimantan, Indonesia. It is located in the district of Landasan Ulin, 5 km (3.1 mi) west of Banjarbaru, the capital of South Kalimantan, and about 25 km (16 mi) southeast from the centre of the city of Banjarmasin, the largest city of South Kalimantan. The airport served more than 5.3 million passengers in 2017.

China Road and Bridge Corporation (CRBC), a subsidiary of China Communications Construction Company (CCCC), is a Chinese state-owned construction and engineering firm that focuses on global infrastructure projects such as highways, skyways, railways, bridges, ports, and tunnels. Growing out of the Foreign Aid Office of the Ministry of Communications of China, CRBC and its predecessors have been executing projects since 1958. In 1979, CRBC was formally established and entered the international contracting market. The partner entity, CCCC, was formed through the combination of CRBC and China Harbour Engineering Company Ltd (CHEC) in 2005.

The Kapuas River is a river in the Indonesian part of Borneo island. It originates in the Müller Mountain Range at the center of the island and flows south until merging with the Barito River and discharging into the Java Sea. It should be distinguished from another Kapuas River, which starts on the other side of the same mountain range in central Borneo but flows to the west and empties to the South China Sea.

North Kalimantan is a province of Indonesia. It is located on the northernmost of Kalimantan, the Indonesian part of the island of Borneo. North Kalimantan borders the Malaysian states of Sabah to the north and Sarawak to the west, and by the Indonesian province of East Kalimantan to the south. Tanjung Selor serves as the capital of the province, while Tarakan is the largest city and the financial centre.
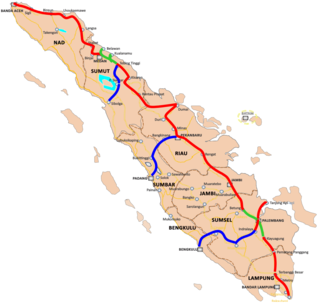
Trans-Sumatra Toll Road is an under-construction tolled expressway stretching across Sumatra Island in Indonesia from the northern tip of Banda Aceh to the southern tip of Bakauheni. This toll road was originally planned to connect to the established toll road system of Java through the now cancelled Sunda Strait Bridge. The toll road is to include supporting corridors connecting the cities of Padang, Bengkulu, and Sibolga on the western coast of the island to the main corridors stretching across the more populated eastern coast. State construction company Hutama Karya has been given a government-granted monopoly to operate the network.

Merah Putih Bridge is a cable stayed bridge located in Ambon city, Maluku, Indonesia. The bridge spans over Ambon Bay in Ambon Island, connecting Rumah Tiga village (Poka) in Sirimau sub-district on the north side, with Hative Kecil/Galala village in Teluk Ambon sub-district on the south side. This bridge is the longest bridge in the eastern region of Indonesia; it is the landmark of the city.

Putussibau is an Indonesian town in Kapuas Hulu Regency, West Kalimantan. It sits on the river Kapuas, with the main part of the town located on the right banks, or north, of the river. Officially an administrative village within North Putussibau District, the urban settlement sprawls outside of the primary boundaries to the opposite bank of the river. Official estimates from Statistics Indonesia places the population of the town proper at 12,459 in 2015.
The Trans-Kalimantan Highway Southern Route, or simply the Trans-Kalimantan Highway, is a 3,901-kilometre (2,424 mi) national road that forms the backbone highway system in Kalimantan, Indonesia. It forms a part of the larger Pan-Borneo Highway network which also combines with highway networks of East Malaysia and Brunei. The combined highway network forms the entire Asian Highway Network Route AH150.

Suroboyo Bridge commonly known as Kenjeran Bridge is a through arch bridge across the coastal area of Eastern Surabaya in Kenjeran Beach, District Kenjeran, Surabaya, East Java, Indonesia. This bridge has a length of 800 meters with a width of 18 meters and a height of 12 meters which is held with 150 stakes. The design of the bridge is built in a circle with a view of the fountain in the center of the bridge.

Bonifasius Belawan Geh, also known popularly as "Mr. Boni", is an Indonesian businessman and politician who is currently serving as the regent of Mahakam Ulu. He is the first elected to the regency since its creation, after the separation of the regency from West Kutai, having previously been led by two acting regents. As regent, he initiated several infrastructure programs in the region, including the first asphalt-sealed road in the regency to alleviate the region's remoteness.

Nusantara, officially Nusantara Capital City, is the future capital of Indonesia, located between Kutai Kartanegara Regency and Penajam North Paser Regency, East Kalimantan, on the island of Borneo. Nusantara is planned to be a special capital region at the provincial level, replacing Jakarta.
The Bali Strait Bridge (Indonesian: Jembatan Selat Bali, JSB, is a proposed road and railway megaproject between the two Indonesian islands of Java and Bali across the Bali Strait. The Bali Strait Bridge is envisioned as a critical infrastructure project connecting the islands of Sumatra, Java, and Bali, providing a continuous and elevated route over both land and sea. The design of the bridge accounts for the challenging conditions of the Bali Strait, known for its high waves and strong currents.

Sei Alalak Bridge is a curved cable-stayed bridge in South Kalimantan province of Indonesia. The bridge, which has length of 850 meters, crossing the Alalak river in Alalak District, Barito Kuala Regency, and connecting the regency through the main Trans-Kalimantan Road towards Banjarmasin city.



















