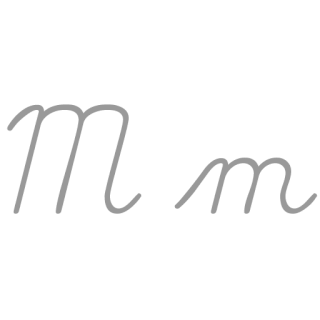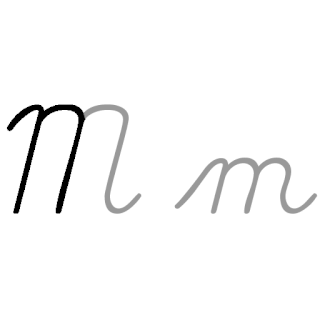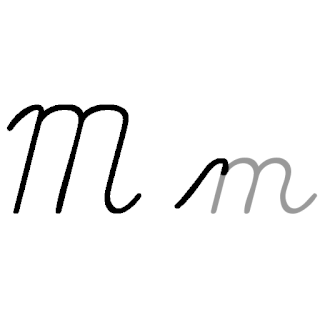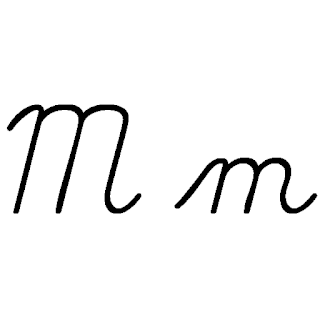January is the first month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian calendars and is also the first of seven months to have a length of 31 days. The first day of the month is known as New Year's Day. It is, on average, the coldest month of the year within most of the Northern Hemisphere and the warmest month of the year within most of the Southern Hemisphere. In the Southern hemisphere, January is the seasonal equivalent of July in the Northern hemisphere and vice versa.

A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestral language or parental language, called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in historical linguistics, which makes use of a metaphor comparing languages to people in a biological family tree, or in a subsequent modification, to species in a phylogenetic tree of evolutionary taxonomy. Linguists therefore describe the daughter languages within a language family as being genetically related.
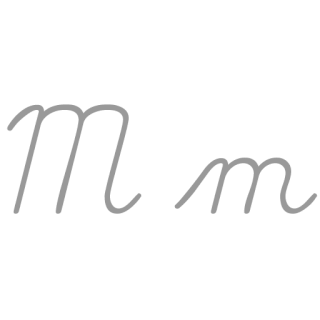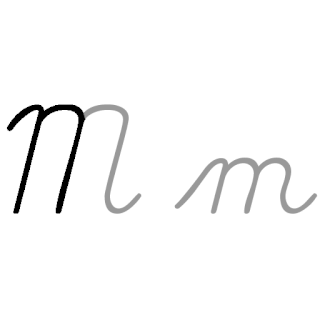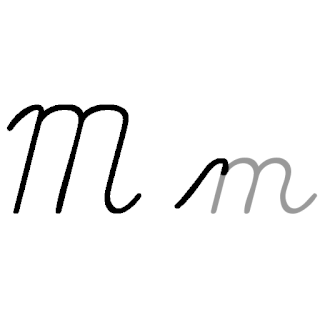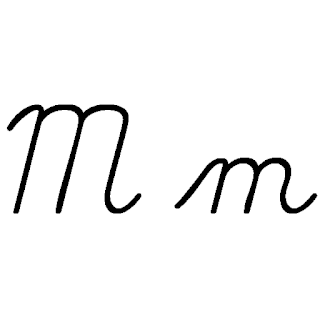
M, or m, is the thirteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is em, plural ems.

A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate causes of phenomena, and usually frame their understanding in mathematical terms. Physicists work across a wide range of research fields, spanning all length scales: from sub-atomic and particle physics, through biological physics, to cosmological length scales encompassing the universe as a whole. The field generally includes two types of physicists: experimental physicists who specialize in the observation of natural phenomena and the development and analysis of experiments, and theoretical physicists who specialize in mathematical modeling of physical systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. Physicists can apply their knowledge towards solving practical problems or to developing new technologies.
An online encyclopedia, also called an Internet encyclopedia, or a digital encyclopedia, is an encyclopedia accessible through the internet. Examples include Wikipedia and Encyclopædia Britannica.

The rabbit is the fourth in the twelve-year cycle of animals that appear in the Chinese zodiac related to the Chinese calendar. The Year of the Rabbit is associated with the Earthly Branch symbol 卯.

Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration, is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Over time, however, some people experience a gradual worsening of vision that may affect one or both eyes. While it does not result in complete blindness, loss of central vision can make it hard to recognize faces, drive, read, or perform other activities of daily life. Visual hallucinations may also occur.

Most generally, in the lineal kinship system used in the English-speaking world, a cousin is a type of familial relationship in which two relatives are two or more familial generations away from their most recent common ancestor. Commonly, "cousin" refers to a first cousin – a relative of the same generation whose most recent common ancestor with the subject is a grandparent.

L, or l, is the twelfth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is el, plural els.

Proposition 218 is an adopted initiative constitutional amendment which revolutionized local and regional government finance and taxation in California. Named the "Right to Vote on Taxes Act," it was sponsored by the Howard Jarvis Taxpayers Association as a constitutional follow-up to the landmark property tax reduction initiative constitutional amendment, Proposition 13, approved in 1978. Proposition 218 was approved and adopted by California voters during the November 5, 1996, statewide general election.

The Blastobasidae are a family of moths in the superfamily Gelechioidea. Its species can be found almost anywhere in the world, though in some places they are not native but introduced by humans. In some arrangements, these moths are included in the case-bearer family (Coleophoridae) as subfamily Blastobasinae. The Symmocidae are sometimes included in the Blastobasidae as subfamily or tribe.

Blastobasis is the type genus of the gelechioid moth family Blastobasidae; in some arrangements these are placed in the case-bearer family (Coleophoridae) as a subfamily. Within the Blastobasidae, the subfamily Blastobasinae has been established to distinguish the Blastobasis lineage from the group around Holcocera, but the delimitation is not yet well-resolved.
Tecmerium is a genus of moths in the family Blastobasidae.

Australasia is a region that comprises Australia, New Zealand and some neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologically, where the term covers several slightly different, but related regions.

Holcocera irroratella is a moth in the family Blastobasidae. It is found in South Africa and Gambia.
Tecmerium anthophaga is a moth in the family Blastobasidae. It is found in France, Portugal and Spain, as well as on Corsica and Sardinia.
Tecmerium perplexum is a moth in the family Blastobasidae. It is found in Hungary, Slovakia, Greece, Turkey and on Cyprus.
Tecmerium rosmarinella is a moth in the family Blastobasidae. It is found in France.
Tecmerium spermophagia is a moth in the family Blastobasidae. It is found in Portugal and Spain.