Related Research Articles
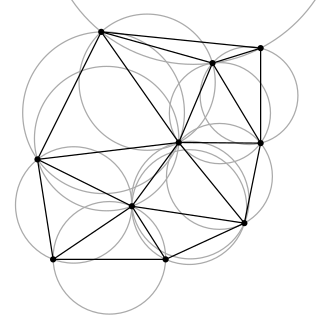
In computational geometry, a Delaunay triangulation or Delone triangulation of a set of points in the plane subdivides their convex hull into triangles whose circumcircles do not contain any of the points. This maximizes the size of the smallest angle in any of the triangles, and tends to avoid sliver triangles.
A fourth-generation programming language (4GL) is a high-level computer programming language that belongs to a class of languages envisioned as an advancement upon third-generation programming languages (3GL). Each of the programming language generations aims to provide a higher level of abstraction of the internal computer hardware details, making the language more programmer-friendly, powerful, and versatile. While the definition of 4GL has changed over time, it can be typified by operating more with large collections of information at once rather than focusing on just bits and bytes. Languages claimed to be 4GL may include support for database management, report generation, mathematical optimization, GUI development, or web development. Some researchers state that 4GLs are a subset of domain-specific languages.

Wolfram Mathematica is a software system with built-in libraries for several areas of technical computing that allows machine learning, statistics, symbolic computation, data manipulation, network analysis, time series analysis, NLP, optimization, plotting functions and various types of data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other programming languages. It was conceived by Stephen Wolfram, and is developed by Wolfram Research of Champaign, Illinois. The Wolfram Language is the programming language used in Mathematica. Mathematica 1.0 was released on June 23, 1988 in Champaign, Illinois and Santa Clara, California.
Computational geometry is a branch of computer science devoted to the study of algorithms which can be stated in terms of geometry. Some purely geometrical problems arise out of the study of computational geometric algorithms, and such problems are also considered to be part of computational geometry. While modern computational geometry is a recent development, it is one of the oldest fields of computing with a history stretching back to antiquity.

In mathematics, a Voronoi diagram is a partition of a plane into regions close to each of a given set of objects. It can be classified also as a tessellation. In the simplest case, these objects are just finitely many points in the plane. For each seed there is a corresponding region, called a Voronoi cell, consisting of all points of the plane closer to that seed than to any other. The Voronoi diagram of a set of points is dual to that set's Delaunay triangulation.
A key generator (key-gen) is a computer program that generates a product licensing key, such as a serial number, necessary to activate for use of a software application. Keygens may be legitimately distributed by software manufacturers for licensing software in commercial environments where software has been licensed in bulk for an entire site or enterprise, or they may be developed and distributed illegitimately in circumstances of copyright infringement or software piracy.
In geometry, a triangulation is a subdivision of a planar object into triangles, and by extension the subdivision of a higher-dimension geometric object into simplices. Triangulations of a three-dimensional volume would involve subdividing it into tetrahedra packed together.

Open Cascade Technology (OCCT), formerly called CAS.CADE, is an open-source software development platform for 3D CAD, CAM, CAE, etc. that is developed and supported by Open Cascade SAS company.

Mesh generation is the practice of creating a mesh, a subdivision of a continuous geometric space into discrete geometric and topological cells. Often these cells form a simplicial complex. Usually the cells partition the geometric input domain. Mesh cells are used as discrete local approximations of the larger domain. Meshes are created by computer algorithms, often with human guidance through a GUI, depending on the complexity of the domain and the type of mesh desired. A typical goal is to create a mesh that accurately captures the input domain geometry, with high-quality (well-shaped) cells, and without so many cells as to make subsequent calculations intractable. The mesh should also be fine in areas that are important for the subsequent calculations.
SALOME is a multi-platform open source (LGPL-2.1-or-later) scientific computing environment, allowing the realization of industrial studies of physics simulations.
The Computational Geometry Algorithms Library (CGAL) is an open source software library of computational geometry algorithms. While primarily written in C++, Scilab bindings and bindings generated with SWIG are also available.
Parallel mesh generation in numerical analysis is a new research area between the boundaries of two scientific computing disciplines: computational geometry and parallel computing. Parallel mesh generation methods decompose the original mesh generation problem into smaller subproblems which are solved (meshed) in parallel using multiple processors or threads. The existing parallel mesh generation methods can be classified in terms of two basic attributes:
- the sequential technique used for meshing the individual subproblems and
- the degree of coupling between the subproblems.
The James H. Wilkinson Prize for Numerical Software is awarded every four years to honor outstanding contributions in the field of numerical software. The award is named to commemorate the outstanding contributions of James H. Wilkinson in the same field.
In mesh generation, Delaunay refinements are algorithms for mesh generation based on the principle of adding Steiner points to the geometry of an input to be meshed, in a way that causes the Delaunay triangulation or constrained Delaunay triangulation of the augmented input to meet the quality requirements of the meshing application. Delaunay refinement methods include methods by Chew and by Ruppert.

The FEniCS Project is a collection of free and open-source software components with the common goal to enable automated solution of differential equations. The components provide scientific computing tools for working with computational meshes, finite-element variational formulations of ordinary and partial differential equations, and numerical linear algebra.
code_saturne is a general-purpose computational fluid dynamics free computer software package. Developed since 1997 at Électricité de France R&D, code_saturne is distributed under the GNU GPL licence. It is based on a co-located finite-volume approach that accepts meshes with any type of cell and any type of grid structure.
Gmsh is a finite-element mesh generator developed by Christophe Geuzaine and Jean-François Remacle. Released under the GNU General Public License, Gmsh is free software.
GetFEM++ is a generic finite element C++ library with interfaces for Python, Matlab and Scilab. It aims at providing finite element methods and elementary matrix computations for solving linear and non-linear problems numerically. Its flexibility in choosing among different finite element approximations and numerical integration methods is one of its distinguishing characteristics.
FEATool Multiphysics is a physics, finite element analysis (FEA), and partial differential equation (PDE) simulation toolbox. FEATool Multiphysics features the ability to model fully coupled heat transfer, fluid dynamics, chemical engineering, structural mechanics, fluid-structure interaction (FSI), electromagnetics, as well as user-defined and custom PDE problems in 1D, 2D (axisymmetry), or 3D, all within a graphical user interface (GUI) or optionally as script files. FEATool has been employed and used in academic research, teaching, and industrial engineering simulation contexts.
References
- ↑ "TetGen Licensing FAQ".
- ↑ Si, Hang (2015). "TetGen, a Delaunay-based Tetrahedral Mesh Generator". ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software. 41 (2): 11:1–11:36. doi:10.1145/2629697. S2CID 10022108.
- ↑ "Wolfram Mathematica: introduction to TetGenLink".
- ↑ "Gmsh:6.1 Choosing the right unstructured algorithm".
- ↑ "TetGen: Release Notes".