
In organic chemistry, allenes are organic compounds in which one carbon atom has double bonds with each of its two adjacent carbon atoms. Allenes are classified as cumulated dienes. The parent compound of this class is propadiene, which is itself also called allene. A group of the structure R2C=C=CR− is called allenyl, while a substituent attached to an allene is referred to as an allenic substituent. In analogy to allylic and propargylic, a substituent attached to a saturated carbon α to an allene is referred to as an allenylic substituent. While allenes have two consecutive ('cumulated') double bonds, compounds with three or more cumulated double bonds are called cumulenes.

The Pauson–Khand (PK) reaction is a chemical reaction, described as a [2+2+1] cycloaddition. In it, an alkyne, an alkene and carbon monoxide combine into a α,β-cyclopentenone in the presence of a metal-carbonyl catalyst.

Lawesson's reagent (LR) is a chemical compound used in organic synthesis as a thiation agent. Lawesson's reagent was first made popular by Sven-Olov Lawesson, who did not, however, invent it. Lawesson's reagent was first made in 1956 during a systematic study of the reactions of arenes with P4S10.
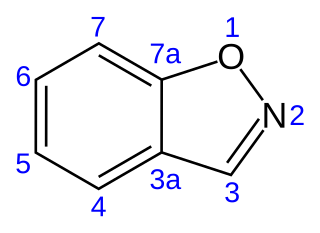
1,2-Benzisoxazole is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula C7H5NO containing a benzene-fused isoxazole ring structure. The compound itself has no common applications; however, functionalized benzisoxazoles and benzisoxazoyls have a variety of uses, including pharmaceutical drugs such as some antipsychotics (including risperidone, paliperidone, ocaperidone, and iloperidone) and the anticonvulsant zonisamide.
The Étard reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the direct oxidation of an aromatic or heterocyclic bound methyl group to an aldehyde using chromyl chloride. For example, toluene can be oxidized to benzaldehyde.
Pivalic acid is a carboxylic acid with a molecular formula of (CH3)3CCO2H. This colourless, odiferous organic compound is solid at room temperature. Two abbreviations for pivalic acid are t-BuC(O)OH and PivOH. The pivalyl or pivaloyl group is abbreviated t-BuC(O).

Tripotassium phosphate, also called tribasic potassium phosphate is a water-soluble salt with the chemical formula K3PO4.(H2O)x (x = 0, 3, 7, 9). Tripotassium phosphate is basic.
The Fukuyama coupling is a coupling reaction taking place between a thioester and an organozinc halide in the presence of a palladium catalyst. The reaction product is a ketone. This reaction was discovered by Tohru Fukuyama et al. in 1998.

The Achmatowicz reaction, also known as the Achmatowicz rearrangement, is an organic synthesis in which a furan is converted to a dihydropyran. In the original publication by the Polish Chemist Osman Achmatowicz Jr. in 1971 furfuryl alcohol is reacted with bromine in methanol to 2,5-dimethoxy-2,5-dihydrofuran which rearranges to the dihydropyran with dilute sulfuric acid. Additional reaction steps, alcohol protection with methyl orthoformate and boron trifluoride) and then ketone reduction with sodium borohydride produce an intermediate from which many monosaccharides can be synthesised.

Michael E. Jung is a Professor of Chemistry in the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry at the University of California at Los Angeles.

The Birch reduction is an organic reaction that is used to convert arenes to 1,4-cyclohexadienes. The reaction is named after the Australian chemist Arthur Birch and involves the organic reduction of aromatic rings in an amine solvent with an alkali metal and a proton source. Unlike catalytic hydrogenation, Birch reduction does not reduce the aromatic ring all the way to a cyclohexane.
Desulfonylation reactions are chemical reactions leading to the removal of a sulfonyl group from organic compounds. As the sulfonyl functional group is electron-withdrawing, methods for cleaving the sulfur–carbon bonds of sulfones are typically reductive in nature. Olefination or replacement with hydrogen may be accomplished using reductive desulfonylation methods.
Ethyl decadienoate, also known as pear ester, is an organic chemical compound used in flavors and perfumery for its pear-like taste and odor.

Trichloroacetonitrile is an organic compound with the formula CCl3CN. It is a colourless liquid, although commercial samples often are brownish. It is used commercially as a precursor to the fungicide etridiazole. It is prepared by dehydration of trichloroacetamide. As a bifunctional compound, trichloroacetonitrile can react at both the trichloromethyl and the nitrile group. The electron-withdrawing effect of the trichloromethyl group activates the nitrile group for nucleophilic additions. The high reactivity makes trichloroacetonitrile a versatile reagent, but also causes its susceptibility towards hydrolysis.

Debbie C. Crans is a Professor of Organic, Inorganic and Biological Chemistry and of Cell and Molecular Biology at Colorado State University, where she also is a Professor Laureate of the College of Natural Sciences. Crans specializes in the fundamental chemistry and biochemistry of drugs, with particular focus on vanadium and other transition metal ions as metals in medicine and investigation of their mechanisms of toxicity.
Susan Elizabeth Gibson is a British research chemist, Professor and Chair in Chemistry and Director of the Graduate School at Imperial College London. Gibson is an expert in chemical synthesis and catalysis.

The Journal of Magnetic Resonance (JMR) is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal that publishes original research in the field of magnetic resonance, including nuclear magnetic resonance, electron paramagnetic resonance, magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic resonance spectroscopy and nuclear quadrupole resonance. Since 2021, its editor-in-chief has been Tatyana Polenova of the University of Delaware. According to the Journal Citation Reports, it has an impact factor of 2.624. Authors can pay a fee to have their articles published as open access.
In organic chemistry, the Davis oxidation or Davis' oxaziridine oxidation refers to oxidations involving the use of the Davis reagent or other similar oxaziridine reagents. This reaction mainly refers to the generation of α-hydroxy carbonyl compounds (acyloins) from ketones or esters. The reaction is carried out in a basic environment to generate the corresponding enolate from the ketone or ester. This reaction has been shown to work for amides.
The Blum–Ittah aziridine synthesis, also known as the Blum–Ittah-Shahak aziridine synthesis or simply the Blum aziridine synthesis is a name reaction of organic chemistry, for the generation of aziridines from oxiranes.

Nikolay Zefirov - was a Russian chemist known for his research in Organic chemistry and Medicinal chemistry and the development of new synthetic methods.












