
The history of the Falkland Islands goes back at least five hundred years, with active exploration and colonisation only taking place in the 18th century. Nonetheless, the Falkland Islands have been a matter of controversy, as they have been claimed by the French, British, Spaniards and Argentines at various points.

Stanley is the capital city of the Falkland Islands. It is located on the island of East Falkland, on a north-facing slope in one of the wettest parts of the islands. At the 2016 census, the city had a population of 2,460. The entire population of the Falkland Islands was 3,398 on Census Day on 9 October 2016.

The Falkland Islands wolf, also known as the warrah and occasionally as the Falkland Islands dog, Falkland Islands fox, warrah fox, or Antarctic wolf, was the only native land mammal of the Falkland Islands. This endemic canid became extinct in 1876, the first known canid to have become extinct in historical times.

Weddell Island is one of the Falkland Islands in the South Atlantic, lying off the southwest extremity of West Falkland. It is situated 1,545 km (960 mi) west-northwest of South Georgia Island, 1,165 km (724 mi) north of Livingston Island, 606 km (377 mi) northeast of Cape Horn, 358 km (222 mi) northeast of Isla de los Estados, and 510 km (320 mi) east of the Atlantic entrance to Magellan Strait.
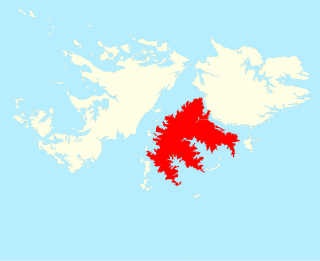
Lafonia is a peninsula forming the southern part of East Falkland, the largest of the Falkland Islands.

The Falkland Sound is a sea strait in the Falkland Islands. Running southwest-northeast, it separates West and East Falkland.

Government House in Stanley has been the home of the Falkland Islands' Governors since the mid-19th century. The official residence was built in 1845.

The Falkland Islands is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about 300 mi (480 km) east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about 752 mi (1,210 km) from Cape Dubouzet at the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, at a latitude of about 52°S. The archipelago, with an area of 4,700 sq mi (12,000 km2), comprises East Falkland, West Falkland, and 776 smaller islands. As a British overseas territory, the Falklands have internal self-governance, but the United Kingdom takes responsibility for their defence and foreign affairs. The capital and largest settlement is Stanley on East Falkland.
Cape Bougainville is the second-most northerly point on East Falkland, Falkland Islands, after Cape Dolphin, and is the second-most northerly point of the two main islands, East and West Falkland. Many of the smaller islands, such as the Jason Islands, are further north.

The peso was a promissory note which was issued on the Falklands Islands by Luis Vernet from around 1828 until the collapse of his settlement in August 1833. Vernet, who was appointed Governor by the United Provinces of Rio de la Plata in 1829, paid workers on the islands in these promissory notes.

Long Island is the largest island in Berkeley Sound, Falkland Islands.

Penguin News is the only newspaper produced in the Falkland Islands. It is published every Friday and provides news and features about the islands.

Race Point is the point on the north side of Smylie Channel forming the south extremity of Weddell Island in the Falkland Islands. The point is located at 51°59′22″S61°00′00″W, which is 26.7 km south-southwest of Swan Point, 3.5 km west-northwest of neighbouring Dyke Island, 1.8 km north of West Island and 4 km north-northeast of Orford Hill, West Falkland.

Swan Point is the point on the southwest side of the entrance to Queen Charlotte Bay, forming the northeast extremity of Weddell Island in the Falkland Islands.

French Harbour is the 500 m wide bay indenting for 3.1 km the west coast of Weddell Island in the Falkland Islands. It is entered 5.5 km north of Weddell Point, and centred at 51°51′03″S61°06′50″W.

Quaker Harbour is the irregularly shaped bay indenting for 3.7 km the north coast of Weddell Island in the Falkland Islands. It is centred at 51°49′00″S61°04′35″W, and has its head fed by Pitt Creek. The bay takes its name from nearby Quaker Island.

Loop Head is the point on the east side of the entrance to Chatham Harbour in Weddell Island, Falkland Islands. It is located at 51°45′48″S60°53′49″W, which is 2.4 kilometres (1.5 mi) west of Swan Point and 5.5 kilometres (3.4 mi) east-northeast of Beacon Point.

New Year Cove is the 1.7 km wide bay indenting for 2.45 km the southeast coast of Weddell Island in the Falkland Islands. It is entered north of Hadassah Point and south of Circum Point and centred at 51°56′30″S60°54′30″W.

Smylie Channel is the 1.4 kilometres (0.76 nmi) wide and 16 kilometres (8.6 nmi) long sea passage in the Falkland Islands between Weddell Island to the north and West Falkland and Dyke Island to the south. It is centred at 51°59′04″S61°03′48″W.











