Related Research Articles
A syllogism is a kind of logical argument that applies deductive reasoning to arrive at a conclusion based on two propositions that are asserted or assumed to be true.

Gödel, Escher, Bach: an Eternal Golden Braid, also known as GEB, is a 1979 book by Douglas Hofstadter. By exploring common themes in the lives and works of logician Kurt Gödel, artist M. C. Escher, and composer Johann Sebastian Bach, the book expounds concepts fundamental to mathematics, symmetry, and intelligence. Through short stories, illustrations, and analysis, the book discusses how systems can acquire meaningful context despite being made of "meaningless" elements. It also discusses self-reference and formal rules, isomorphism, what it means to communicate, how knowledge can be represented and stored, the methods and limitations of symbolic representation, and even the fundamental notion of "meaning" itself.

Alice's Adventures in Wonderland is an 1865 novel by English author Lewis Carroll. It tells of a young girl named Alice, who falls through a rabbit hole into a subterranean fantasy world populated by peculiar, anthropomorphic creatures. It is considered to be one of the best examples of the literary nonsense genre. The tale plays with logic, giving the story lasting popularity with adults as well as with children.
A Venn diagram is a widely-used diagram style that shows the logical relation between sets, popularized by John Venn in the 1880s. The diagrams are used to teach elementary set theory, and to illustrate simple set relationships in probability, logic, statistics, linguistics and computer science. A Venn diagram uses simple closed curves drawn on a plane to represent sets. Very often, these curves are circles or ellipses.
A logic puzzle is a puzzle deriving from the mathematical field of deduction.

Alice Pleasance Hargreaves, was, in her childhood, an acquaintance and photography subject of Lewis Carroll. One of the stories he told her during a boating trip became the children's classic 1865 novel Alice's Adventures in Wonderland. She shared her name with "Alice", the heroine of the story, but scholars disagree about the extent to which the character was based upon her.
"What the Tortoise Said to Achilles", written by Lewis Carroll in 1895 for the philosophical journal Mind, is a brief allegorical dialogue on the foundations of logic. The title alludes to one of Zeno's paradoxes of motion, in which Achilles could never overtake the tortoise in a race. In Carroll's dialogue, the tortoise challenges Achilles to use the force of logic to make him accept the conclusion of a simple deductive argument. Ultimately, Achilles fails, because the clever tortoise leads him into an infinite regression.

Isaac Watts was an English Christian minister (Congregational), hymn writer, theologian, and logician. He was a prolific and popular hymn writer and is credited with some 750 hymns. He is recognized as the "Godfather of English Hymnody"; many of his hymns remain in use today and have been translated into numerous languages.
In philosophy, term logic, also known as traditional logic, syllogistic logic or Aristotelian logic, is a loose name for an approach to logic that began with Aristotle and was developed further in ancient history mostly by his followers, the peripatetics, but largely fell into decline by the third century CE. Term logic revived in medieval times, first in Islamic logic by Alpharabius in the tenth century, and later in Christian Europe in the twelfth century with the advent of new logic, and remained dominant until the advent of modern predicate logic in the late nineteenth century. This entry is an introduction to the term logic needed to understand philosophy texts written before it was expanded as a formal logic system by predicate logic. Readers lacking a grasp of the basic terminology and ideas of term logic can have difficulty understanding such texts, because their authors typically assumed an acquaintance with term logic.

The Prior Analytics is a work by Aristotle on deductive reasoning, known as his syllogistic, composed around 350 BCE. Being one of the six extant Aristotelian writings on logic and scientific method, it is part of what later Peripatetics called the Organon. Modern work on Aristotle's logic builds on the tradition started in 1951 with the establishment by Jan Łukasiewicz of a revolutionary paradigm. His approach was replaced in the early 1970s in a series of papers by John Corcoran and Timothy Smiley—which inform modern translations of Prior Analytics by Robin Smith in 1989 and Gisela Striker in 2009.
A polysyllogism is a string of any number of propositions forming together a sequence of syllogisms such that the conclusion of each syllogism, together with the next proposition, is a premise for the next, and so on. Each constituent syllogism is called a prosyllogism except the last, because the conclusion of the last syllogism is not a premise for another syllogism.
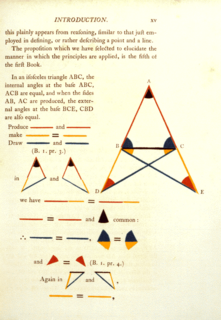
In geometry, the statement that the angles opposite the equal sides of an isosceles triangle are themselves equal is known as the pons asinorum, typically translated as "bridge of asses". This statement is Proposition 5 of Book 1 in Euclid's Elements, and is also known as the isosceles triangle theorem. Its converse is also true: if two angles of a triangle are equal, then the sides opposite them are also equal. The term is also applied to the Pythagorean theorem.

The Topics is the name given to one of Aristotle's six works on logic collectively known as the Organon. The treatise presents the art of dialectic — the invention and discovery of arguments in which the propositions rest upon commonly held opinions or endoxa. Topoi (τόποι) are "places" from which such arguments can be discovered or invented.

An Euler diagram is a diagrammatic means of representing sets and their relationships. They are particularly useful for explaining complex hierarchies and overlapping definitions. They are similar to another set diagramming technique, Venn diagrams. Unlike Venn diagrams, which show all possible relations between different sets, the Euler diagram shows only relevant relationships.

A Carroll diagram, Lewis Carroll's square, biliteral diagram or a two-way table is a diagram used for grouping things in a yes/no fashion. Numbers or objects are either categorised as 'x' or 'not x'. They are named after Lewis Carroll, the pseudonym of Charles Lutwidge Dodgson.
A Tangled Tale is a collection of 10 brief humorous stories by Lewis Carroll, published serially between April 1880 and March 1885 in The Monthly Packet magazine. Arthur B. Frost added illustrations when the series was printed in book form. The stories, or Knots as Carroll calls them, present mathematical problems. In a later issue, Carroll gives the solution to a Knot and discusses readers' answers. The mathematical interpretations of the Knots are not always straightforward. The ribbing of readers answering wrongly – giving their names – was not always well received.

Charles Lutwidge Dodgson, better known by his pen name Lewis Carroll, was an English writer of children's fiction, notably Alice's Adventures in Wonderland and its sequel Through the Looking-Glass. He was noted for his facility with word play, logic, and fantasy. The poems "Jabberwocky" and The Hunting of the Snark are classified in the genre of literary nonsense. He was also a mathematician, photographer, inventor, and Anglican deacon.

Lewis Carroll: A Biography is a 1995 biography of author Lewis Carroll by Morton N. Cohen, first published by Knopf, later by Macmillan. It is generally considered to be the definitive scholarly work on Carroll's life. Cohen's approach is mainly chronological, with some chapters grouped by theme, such as those on Carroll's religion, his love of little girls, and his guilty feelings. Cohen, a Carroll scholar for 30 years, opts to use Dodgson's first name, Charles, throughout the work, because it "seems most appropriate in a book dealing with the intimacy of his life".

Logic is the systematic study of valid rules of inference, i.e. the relations that lead to the acceptance of one proposition on the basis of a set of other propositions (premises). More broadly, logic is the analysis and appraisal of arguments.

How the Snake Lost Its Legs: Curious Tales from the Frontier of Evo-Devo is a 2014 book on evolutionary developmental biology by Lewis I. Held, Jr. The title pays homage to Rudyard Kipling's Just So Stories, but the "tales" are strictly scientific, explaining how a wide range of animal features evolved, in molecular detail. The book has been admired by other biologists as both accurate and accessible.
References
- ↑ "Lewis Carroll's The Game of Logic". The British Library. Retrieved 2021-07-10.
- 1 2 3 Weisstein, Eric W. "Game of Logic". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2021-07-10.