Related Research Articles

Charles Edward Ives was an American modernist composer, one of the first American composers of international renown. His music was largely ignored during his early career, and many of his works went unperformed for many years. Later in life, the quality of his music was publicly recognized through the efforts of contemporaries like Henry Cowell and Lou Harrison, and he came to be regarded as an "American original". He was also among the first composers to engage in a systematic program of experimental music, with musical techniques including polytonality, polyrhythm, tone clusters, aleatory elements, and quarter tones. His experimentation foreshadowed many musical innovations that were later more widely adopted during the 20th century. Hence, he is often regarded as the leading American composer of art music of the 20th century.

Henry Dixon Cowell was an American composer, writer, pianist, publisher and teacher. Earning a reputation as an extremely controversial performer and eccentric composer, Cowell became a leading figure of American avant-garde music for the first half of the 20th century — his writings and music serving as a great influence to similar artists at the time, including Lou Harrison, George Antheil, and John Cage, among others. He is considered one of America's most important and influential composers.

The Tides of Manaunaun is a short piano piece in B♭ minor by American composer Henry Cowell (1897–1965). It premiered publicly in 1917, serving as a prelude to a theatrical production, The Building of Banba. The Tides of Manaunaun is the best known of Cowell's many tone cluster pieces.

Virgil Thomson was an American composer and critic. He was instrumental in the development of the "American Sound" in classical music. He has been described as a modernist, a neoromantic, a neoclassicist, and a composer of "an Olympian blend of humanity and detachment" whose "expressive voice was always carefully muted" until his late opera Lord Byron which, in contrast to all his previous work, exhibited an emotional content that rises to "moments of real passion".

Lou Silver Harrison was an American composer, music critic, music theorist, painter, and creator of unique musical instruments. Harrison initially wrote in a dissonant, ultramodernist style similar to his former teacher and contemporary, Henry Cowell, but later moved toward incorporating elements of non-Western cultures into his work. Notable examples include a number of pieces written for Javanese style gamelan instruments, inspired after studying with noted gamelan musician Kanjeng Notoprojo in Indonesia. Harrison would create his own musical ensembles and instruments with his partner, William Colvig, who are now both considered founders of the American gamelan movement and world music; along with composers Harry Partch and Claude Vivier, and ethnomusicologist Colin McPhee.

Henry Dreyfuss Brant was a Canadian-born American composer. An expert orchestrator with a flair for experimentation, many of Brant's works featured spatialization techniques.
A tone cluster is a musical chord comprising at least three adjacent tones in a scale. Prototypical tone clusters are based on the chromatic scale and are separated by semitones. For instance, three adjacent piano keys struck simultaneously produce a tone cluster. Variants of the tone cluster include chords comprising adjacent tones separated diatonically, pentatonically, or microtonally. On the piano, such clusters often involve the simultaneous striking of neighboring white or black keys.

The Piano Sonata No. 2, Concord, Mass., 1840–60 is a piano sonata by Charles Ives. It is one of the composer's best-known and most highly regarded pieces. A typical performance of the piece lasts around 45 minutes.

String piano is a term coined by American composer-theorist Henry Cowell (1897–1965) to collectively describe those pianistic extended techniques in which sound is produced by direct manipulation of the strings, instead of or in addition to striking the piano's keys. Pioneered by Cowell in the 1920s, such techniques are now often called upon in the works of avant-garde classical music composers.

A Symphony: New England Holidays, also known as A New England Holiday Symphony or simply a Holiday Symphony, is a composition for orchestra written by Charles Ives. It took Ives from 1897 to 1913 to complete all four movements. The four movements in order are:
Construction is the title of several pieces by American composer John Cage, all scored for unorthodox percussion instruments. The pieces were composed in 1939–42 while Cage was working at the Cornish School of the Arts in Seattle, Washington, and touring the West Coast with a percussion ensemble he and Lou Harrison had founded. The series comprises three Constructions. A piece titled Fourth Construction, mentioned in several sources, is apparently either an unfinished work from 1942 or, more likely, an early title of the work we now know as Imaginary Landscape No. 2 .

Imaginary Landscape No. 1 is a composition for records of constant and variable frequency, large chinese cymbal and string piano by American composer John Cage and the first in the series of Imaginary Landscapes. It was composed in 1939.

Out of Doors is a set of five piano solo pieces, Sz. 81, BB 89, written by Béla Bartók in 1926. Out of Doors is among the very few instrumental compositions by Bartók with programmatic titles.

Clarissa Belnap Dixon was an American bohemian, anarchist philosopher, labor activist, feminist and poet who lived at various times in Iowa, New York City, Kansas, and California. She was the mother of avant-garde composer Henry Cowell.

The Banshee (1925) is a piano composition by American composer Henry Cowell (1897–1965). It was the first piano piece ever written to be performed entirely free of the keyboard, using only manual manipulation of the strings within the instrument to produce sound via the flesh and nails of the finger.

Henry Cowell wrote his Piano Concerto in 1928.

American composer Henry Cowell wrote one of his first surviving piano pieces, Dynamic Motion, in 1916. It is known as one of the first pieces in the history of music to utilize violent tone clusters for the keyboard. It requires the performer to use various limbs to play massive secundal chords, and calls for keys to be held down without sounding to extend its dissonant cluster overtones via sympathetic resonance. Some of the clusters outlined in this piece are those written for fists, palms, and forearms. The piece is also noted for its extended use of tuplets, featuring triplets, quintuplets, and sextuplets in the melody line.

Henry Cowell's 1938 work Rhythmicana is a suite of piano pieces centered on polyrhythms and dissonant counterpoint. It is known for its unusual time signatures, with the first two movements being in 1
1 time, and the third movement having the polymeter of 3
4 in the right hand and 5
4 in the left.
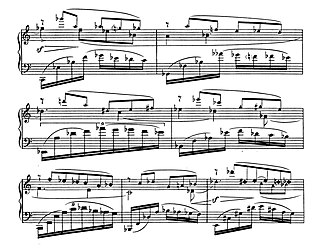
Henry Cowell's 1920 work Fabric, HC 307, is a short piano piece meant to be an exercise in a form of experimental rhythmic notation he had been developing at the time.
Henry Cowell wrote his Variations for Orchestra, HC 833, in 1956.
References
Citations
- ↑ Sachs (2012), p. 146
- ↑ The New York Times , November 14, 1926[ full citation needed ]
Sources
- Sachs, Joel (2012). Henry Cowell: A Man Made of Music. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-510895-8
