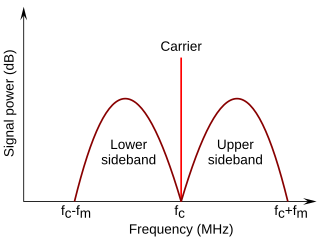
In radio communications, a sideband is a band of frequencies higher than or lower than the carrier frequency, that are the result of the modulation process. The sidebands carry the information transmitted by the radio signal. The sidebands comprise all the spectral components of the modulated signal except the carrier. The signal components above the carrier frequency constitute the upper sideband (USB), and those below the carrier frequency constitute the lower sideband (LSB). All forms of modulation produce sidebands.

Shortwave radio is radio transmission using radio frequencies in the shortwave bands (SW). There is no official definition of the band range, but it always includes all of the high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz ; above the medium frequency band (MF), to the bottom of the VHF band.
International broadcasting consists of radio and television transmissions that purposefully cross international boundaries, often with then intent of allowing expatriates to remain in touch with their countries of origin as well as educate, inform, and influence residents of foreign countries. Content can range from overt propaganda and counterpropaganda to cultural content to news reports that reflect the point of view and concerns of the originating country or that seek to provide alternative information to that otherwise available as well as promote tourism and trade. In the first half of the twentieth century, international broadcasting was used by colonial empires as a means of connecting colonies with the metropole. When operated by governments or entities close to a government, international broadcasting can be a form of soft power. Less frequently, international broadcasting has been undertaken for commercial purposes by private broadcasters.
A numbers station is a shortwave radio station characterized by broadcasts of formatted numbers, which are believed to be addressed to intelligence officers operating in foreign countries. Most identified stations use speech synthesis to vocalize numbers, although digital modes such as phase-shift keying and frequency-shift keying, as well as Morse code transmissions, are not uncommon. Most stations have set time schedules, or schedule patterns; however, some appear to have no discernible pattern and broadcast at random times. Stations may have set frequencies in the high-frequency band.

A radiotelephone, abbreviated RT, is a radio communication system for conducting a conversation; radiotelephony means telephony by radio. It is in contrast to radiotelegraphy, which is radio transmission of telegrams (messages), or television, transmission of moving pictures and sound. The term is related to radio broadcasting, which transmit audio one way to listeners. Radiotelephony refers specifically to two-way radio systems for bidirectional person-to-person voice communication between separated users, such as CB radio or marine radio. In spite of the name, radiotelephony systems are not necessarily connected to or have anything to do with the telephone network, and in some radio services, including GMRS, interconnection is prohibited.

Digital Radio Mondiale is a set of digital audio broadcasting technologies designed to work over the bands currently used for analogue radio broadcasting including AM broadcasting—particularly shortwave—and FM broadcasting. DRM is more spectrally efficient than AM and FM, allowing more stations, at higher quality, into a given amount of bandwidth, using xHE-AAC audio coding format. Various other MPEG-4 codecs and Opus are also compatible, but the standard now specifies xHE-AAC.
CHU is the call sign of a shortwave time signal radio station operated by the Institute for National Measurement Standards of the National Research Council. CHU's signal is used for continuous dissemination of official Canadian government time signals, derived from atomic clocks.
BPM is the call sign of the official short-wave time signal service of the People's Republic of China, operated by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, broadcasting from CAS's National Time Service Center in Pucheng County, Shaanxi at 34°56′55.96″N109°32′34.93″E, roughly 70 km northeast of Lintong, along with NTSC's long-wave time signal BPL on 100 kHz.

WWV is a shortwave radio station, located near Fort Collins, Colorado. It has broadcast a continuous time signal since 1945, and implements United States government frequency standards, with transmitters operating on 2.5, 5, 10, 15, and 20 MHz. WWV is operated by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), under the oversight of its Time and Frequency Division, which is part of NIST's Physical Measurement Laboratory based in Gaithersburg, Maryland.

WWVH is the callsign of the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology's shortwave radio time signal station located at the Barking Sands Missile Range, in Kekaha, on the island of Kauai in the state of Hawaii.

JJY is the call sign of a low frequency time signal radio station located in Japan.

Radio Havana Cuba is the official government-run international broadcasting station of Cuba. It can be heard in many parts of the world, including the United States, on shortwave frequencies. Radio Havana Cuba, along with Radio Rebelde, Cubavision Television, and other Cuban radio and television, broadcasts to North, Central and South America via free-to-air programming from the Hispasat 30W-6 satellite over the Atlantic Ocean and worldwide via Internet streaming.
Letter beacons are radio transmissions of uncertain origin and unknown purpose, consisting of only a single repeating Morse code letter. They have been classified into a number of groups according to transmission code and frequency, and it is supposed that the source for most of them is Russia and began during the Soviet Union.
Amateur radio frequency allocation is done by national telecommunication authorities. Globally, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) oversees how much radio spectrum is set aside for amateur radio transmissions. Individual amateur stations are free to use any frequency within authorized frequency ranges; authorized bands may vary by the class of the station license.

Voice of Korea is the international broadcasting service of North Korea. It broadcasts primarily information in Chinese, Spanish, German, English, French, Russian, Japanese and Arabic. Until 2002 it was known as Radio Pyongyang. The interval signal is identical to that of Korean Central Television.

UVB-76, also known by the nickname "The Buzzer", is a shortwave radio station that broadcasts in Upper Side Band mode on the frequency of 4625 kHz. It broadcasts a short, monotonous, repeating at a rate of approximately 25 tones per minute, 24 hours per day. Sometimes, the buzzer signal is interrupted and a voice transmission in Russian takes place.
The Pip is a shortwave radio station that broadcasts on the frequency 5448 kHz by day, and 3756 kHz during the night. It broadcasts short, repeated beeps at a rate of around 50 per minute, for 24 hours per day. The beep signal is occasionally interrupted by voice messages in Russian. The Pip has been active since 1986, when its distinctive beeping sound was first recorded by listeners, and is a sister station to UVB-76.
BSF is the callsign of the time signal transmitter owned by the National Time and Frequency Standards Laboratory of the Ministry of Economic Affairs (Taiwan), which transmits time information on 77.5 kHz in the longwave range. It was launched on May 1, 1969 and is broadcast from Zhongli District in Taichung using a T-antenna located at 25°0′20″N121°21′54″E.

Swedish Rhapsody was a Polish numbers station, operated by the Ministry of Public Security that used AM broadcasting and operated between the late 1950s and 1998. It was used to send coded messages to intelligence agents in the Western Bloc. It is notorious for its use of what was once believed to be the voice of a young girl speaking in German, only revealed to be that of a special machine used by the East German State Security Service known as the "Sprach-Morse-Generator".












