
Spurr is the lava-flooded remains of a lunar impact crater. It was named after American geologist Josiah Edward Spurr. It is located in the midst of the Palus Putredinis plain, to the southeast of the crater Archimedes. Only the southern half of the rim protrudes significantly through the lunar mare material, while the northern section of the wall has a resemblance to a ghost crater rim.

Brackett is a small lunar impact crater that lies near the southeast edge of Mare Serenitatis. The crater is named after American physicist Frederick Sumner Brackett. The crater has been covered by lava flow, leaving only a ring-shaped trace in the surrounding lunar mare. This crater is best observed under oblique illumination, as it is otherwise difficult to find. The southern rim is almost contacting a rille system named the Rimae Plinius.

Caventou is a tiny lunar impact crater located in the western part of the Mare Imbrium. It is a circular, cup-shaped formation surrounded by the lunar mare. It was named after French chemist Joseph B. Caventou in 1976. Prior to that, it had the designation La Hire D, being associated with the mountain Mons La Hire to the southeast.

Deseilligny is a small lunar impact crater in the southern part of the Mare Serenitatis. It was named after French selenographer Jules Deseilligny. It is located to the east-southeast of the crater Bessel. Deseilligny is a bowl-shaped crater with a low rim. It is otherwise undistinguished.

Fahrenheit is a tiny lunar impact crater located in the southeast part of the Mare Crisium. This area of the surface is nearly devoid of impact features of interest. To the east are the Dorsa Harker wrinkle ridges, and beyond them is Promontorium Agarum at the edge of the mare. The landing site of the Soviet Luna 24 probe is located about 15 kilometers to the southeast.

Boethius is a small lunar impact crater located on the east edge of Mare Undarum near the eastern lunar limb. To the southwest is the dark, lava-flooded crater Dubyago.
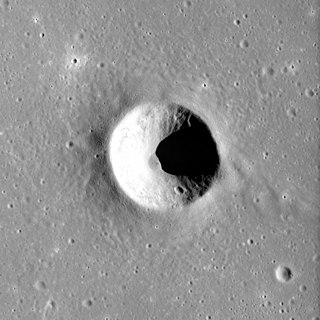
Kuiper is a small lunar impact crater in a relatively featureless part of the Mare Cognitum. It is a circular, cup-shaped feature with only some minor wear. It was named after Dutch-American astronomer Gerard Kuiper in 1976. Kuiper was the Project Scientist for the Ranger program. This crater was previously identified as Bonpland E. The lava-flooded crater Bonpland lies to the east at the edge of the Mare Cognitum.

Beketov is a small lunar impact crater that lies in the northern reaches of the Mare Tranquillitatis. It is named after Russian chemist Nikolay Beketov. To the south is the ghost crater Jansen R. Northeast of Beketov, along the edge of the mare, is the crater Vitruvius. Beketov was previously designated Jansen C before being named by the IAU. The flooded crater Jansen itself lies to the south.

Cajal is a small lunar impact crater on the northern part of the Mare Tranquilitatis. It was named after the Spanish doctor and Nobel laureate Santiago Ramón y Cajal. It is a circular, cup-shaped formation that lies southeast of the lava-inundated crater Jansen. Cajal was formerly designated Jansen F. Also to the northwest is a system of wrinkle ridges designated the Dorsa Barlow.

Auzout is a lunar impact crater that is located to the southeast of the Mare Crisium, near the eastern limb of the Moon. It is named after French astronomer Adrien Auzout."Auzout (crater)". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program. Attached to the southern rim is the smaller crater van Albada. To the east-northeast is the large Condorcet. This crater is not especially notable, although it does possess a central mountain. This crater is designated 'Azout' in some sources.

Bonpland is the remains of a lunar impact crater that is attached to the walled plain Fra Mauro to the north and Parry to the east. The intersection of their rims forms a three-pointed mountainous rise. To the southeast is the small crater Tolansky. Bonpland lies on the eastern edge of Mare Cognitum. It is named after Aimé Bonpland, a French explorer and botanist.
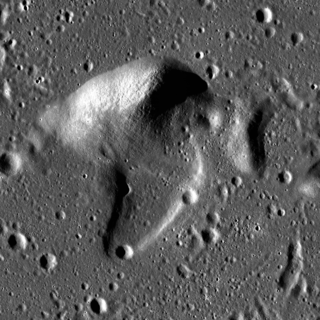
Fedorov is a lunar geologic feature located in the western Mare Imbrium named after Russian rocket scientist Aleksandr Petrovich Fedorov. It lies east-northeast of the crater Diophantus, and southeast of Delisle. About 20 kilometers to the south-southeast is the slightly larger formation of Artsimovich.

Auwers is a small lunar impact crater located in the Montes Haemus mountain range at the south edge of Mare Serenitatis. It is named after German astronomer Arthur Auwers. It lies southeast of the crater Menelaus. The irregular rim of Auwers has a gap at the north-northwest edge, which allowed lava flows to reach the crater floor and flood the interior.
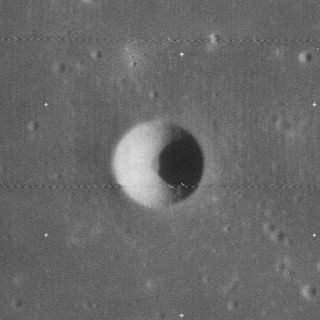
Lucian is a tiny lunar impact crater that is located in the northeastern part of the Mare Tranquillitatis. It was named in 1973 after 2nd century Greek writer Lucian of Samosata. The nearest named craters are Lyell to the east-southeast, Theophrastus to the northeast and Gardner to the north-northeast. A little farther to the north is Maraldi crater. Lucian was previously designated Maraldi B.

Lyell is a lunar impact crater that lies along the eastern edge of the Mare Tranquillitatis, at the northern arm of the bay designated Sinus Concordiae. It was named after Scottish geologist Charles Lyell. To the north along the edge of the lunar mare is the crater Franz. The region of terrain to the east of Lyell is named Palus Somni.

Condorcet is a lunar impact crater that is located in the eastern part of the Moon's near side, to the southeast of the Mare Crisium. It was named after French mathematician Marquis de Condorcet. To the northeast of Condorcet are the craters Hansen and Alhazen.
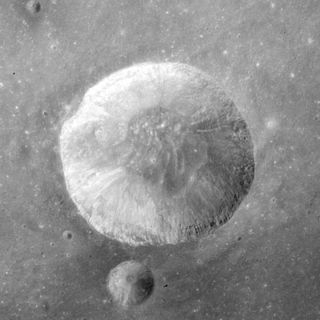
Carmichael is a lunar impact crater that is located along the eastern edge of the Sinus Amoris, in the northeastern quadrant of the Moon's near side. Its diameter is 20 km. It was named after American psychologist Leonard Carmichael. It lies within a couple of crater diameters south-southwest of the smaller crater Hill. Further to the east-northeast is the prominent crater Macrobius. Carmichael was designated Macrobius A before being given its current name by the IAU.

Gardner is a small lunar impact crater in the northeast part of the Moon. It was named after an American physicist Irvine Clifton Gardner in 1976. It lies due east of the crater Vitruvius, in a section of rough terrain north of the Mare Tranquillitatis. Gardner was previously designated Vitruvius A before being given its present name by the IAU. To the northeast of Gardner is the larger crater Maraldi.

Fabbroni is a small lunar impact crater that lies along the northern edge of the Mare Tranquillitatis, at the eastern edge of the gap where the lunar mare joins Mare Serenitatis to the north. To the southeast is the crater Vitruvius.
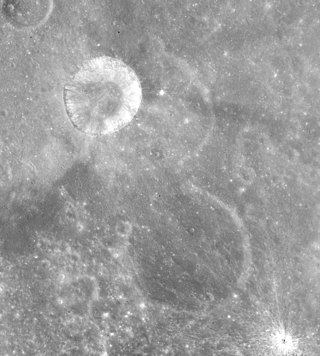
Hume is a small lunar impact crater that lies along the eastern limb of the Moon, along the southeast edge of Mare Smythii. It is located just on the far side of the Moon, but it is often brought into sight from Earth due to libration. Hume lies just to the west-northwest of the much larger Hirayama, and to the northeast of the flooded crater Swasey.





















