
Mantidae is one of the largest families in the order of praying mantises, based on the type species Mantis religiosa; however, most genera are tropical or subtropical. Historically, this was the only family in the order, and many references still use the term "mantid" to refer to any mantis. Technically, however, "mantid" refers only to members of the family Mantidae, and not the 14 remaining families of mantises. Some of the most recent classifications have promoted a number of the mantid subfamilies to the rank of family, e.g. Iridopterygidae, Sibyllidae, Tarachodidae, Thespidae, and Toxoderidae, while other classifications have reduced the number of subfamilies without elevating them to higher rank.

Rhombodera is a genus of praying mantises native to Asia and possessing common names such as shield mantis, hood mantis, and leaf mantis because of their extended, leaf-like thoraxes.
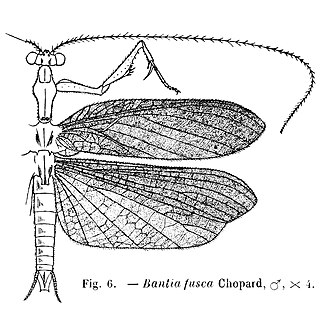
Thespidae is a family of insects in the order Mantodea. Following a major revision of this order in 2019, the old-world subfamilies Haaniinae and Hoplocoryphinae, previously placed here, have been upgraded to family level. Thespidae are mostly Neotropical and few species have reached the Nearctic realm.

Acanthopidae is a family of South American mantises consisting of 16 genera in the order Mantodea. The group was first formally split off as a separate family by the German entomologist Reinhard Ehrmann in 2002. In 2016, five genera were moved from Acanthopidae to the newly created family Acontistidae, but this has not been accepted in most recent classifications.

Angelidae is a family of mantises found in tropical Central and South Americas.

Iridopteryginae is a subfamily of mantises in the family Gonypetidae. There are two tribes, distributed in tropical Asia.

Tropidomantinae is a subfamily of mantises in the new (2019) family Nanomantidae. Within the single tribe Tropidomantini there are six genera, distributed in Asia and the Pacific.

Acontistini is a tribe of neotropical mantises in the superfamily Acanthopoidea, and family Acanthopidae. There are 7 genera and more than 30 described species in Acontistini. In 2016, several genera were moved from Acanthopidae to a newly created family Acontistidae, but this has not been accepted in most recent classifications.

Coptopterygidae is a family of mantises in the order Mantodea. There are at least 2 genera and more than 20 described species in Coptopterygidae.

Photinaidae is a family of mantises in the order Neotropical Mantodea, in the superfamily Acanthopoidea. There are about 11 genera and more than 40 described species in Photinaidae.

Haaniinae is a subfamily of mantises, now placed in the new (2019) family Haaniidae; the species can be found in Asia.
Nanomantini is a tribe of Asian mantises in the new (2019) family Nanomantidae. There are about 6 genera and 10 described species in Nanomantini.

Pseudovates is a genus of praying mantis in the family Mantidae. There are more than 20 described species in the genus Pseudovates, and are found in North, Central, and South America.

The Haaniidae are a new (2019) family of praying mantids, based on the type genus Haania. The first use of "Haaniidae" was by Giglio-Tos and it was revived as part of a major revision of mantid taxonomy; genera in the subfamily Haaniinae havie been moved here from the family Thespidae.

The Hierodulinae are a subfamily of praying mantids, originally used by Brunner von Wattenwyl. It was restored as part of a major revision of mantid taxonomy, and now contains genera previously placed elsewhere in the family Mantidae.

The Nanomantidae are a new (2019) family of praying mantises, based on the type genus Nanomantis. As part of a major revision of mantid taxonomy, genera and tribes have been moved here, substantially replacing the old family Iridopterygidae.

The Deroplatyidae are a new (2019) family of praying mantises, based on the type genus Deroplatys. As part of a major revision of mantis taxonomy, the subfamily Deroplatyinae has been moved here from the previously structured family Mantidae.

Hoplocoryphidae is a newly erected (2019) family of praying mantids, based on the type genus Hoplocorypha. As part of a major revision of mantid taxonomy, genera have been moved here from the subfamily Hoplocoryphinae of the previously polyphyletic family Thespidae. The family Hoplocoryphidae is the only member of superfamily Hoplocoryphoidea. Species in this family have been recorded from tropical Africa.
The Chroicopteridae are a family of praying mantids, based on the type genus Chroicoptera. The name is derived from first use, for subfamily Chroicopterinae, by Giglio-Tos and it has been revived as part of a major revision of mantid taxonomy. Some genera have also been moved here from the tribe Rivetinini, with others placed elsewhere including the subfamily Miomantinae.

Liturgusa is the type genus of praying mantises of the family Liturgusidae. The genus consists of more than twenty species with a Neotropical distribution.
















