A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber.
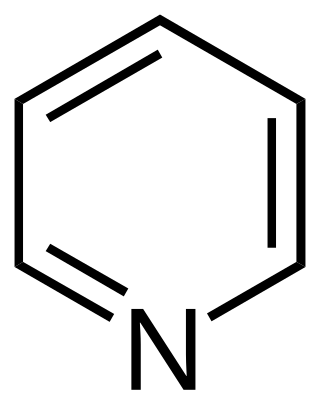
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles.

Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical study.

Indigo dye is an organic compound with a distinctive blue color. Indigo is a natural dye extracted from the leaves of some plants of the Indigofera genus, in particular Indigofera tinctoria; dye-bearing Indigofera plants were commonly grown and used throughout the world, in Asia in particular, as an important crop, with the production of indigo dyestuff economically important due to the historical rarity of other blue dyestuffs.
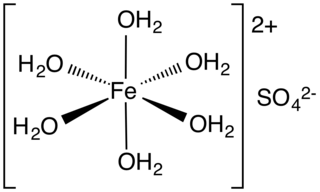
Iron(II) sulfate (British English: iron(II) sulphate) or ferrous sulfate denotes a range of salts with the formula Fe SO4·xH2O. These compounds exist most commonly as the heptahydrate (x = 7) but several values for x are known. The hydrated form is used medically to treat or prevent iron deficiency, and also for industrial applications. Known since ancient times as copperas and as green vitriol (vitriol is an archaic name for sulfate), the blue-green heptahydrate (hydrate with 7 molecules of water) is the most common form of this material. All the iron(II) sulfates dissolve in water to give the same aquo complex [Fe(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry and is paramagnetic. The name copperas dates from times when the copper(II) sulfate was known as blue copperas, and perhaps in analogy, iron(II) and zinc sulfate were known respectively as green and white copperas.

Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans.

Sodium thiosulfate is an inorganic compound with the formula Na2S2O3·(H2O)(x) .Typically it is available as the white or colorless pentahydrate, It is a white solid that dissolves well in water. The compound is a reducing agent and a ligand, and these properties underpin its applications.

In organic chemistry, sulfonic acid refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula R−S(=O)2−OH, where R is an organic alkyl or aryl group and the S(=O)2(OH) group a sulfonyl hydroxide. As a substituent, it is known as a sulfo group. A sulfonic acid can be thought of as sulfuric acid with one hydroxyl group replaced by an organic substituent. The parent compound is the parent sulfonic acid, HS(=O)2(OH), a tautomer of sulfurous acid, S(=O)(OH)2. Salts or esters of sulfonic acids are called sulfonates.
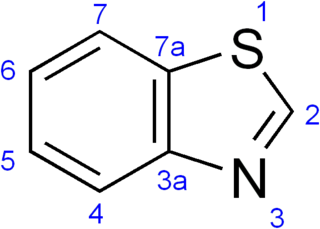
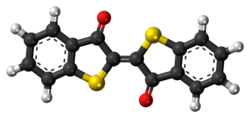
Benzothiazole is an aromatic heterocyclic compound with the chemical formula C
7H
5NS. It is colorless, slightly viscous liquid. Although the parent compound, benzothiazole is not widely used, many of its derivatives are found in commercial products or in nature. Firefly luciferin can be considered a derivative of benzothiazole.

Sodium dithionite is a white crystalline powder with a sulfurous odor. Although it is stable in dry air, it decomposes in hot water and in acid solutions.
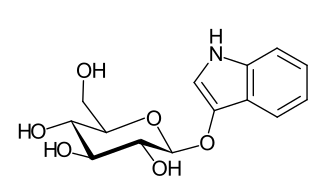
Indican is a colourless organic compound, soluble in water, naturally occurring in Indigofera plants. It is a precursor of indigo dye.

A leuco dye is a dye which can switch between two chemical forms, one of which is colorless. Reversible transformations can be caused by heat, light or pH, resulting in examples of thermochromism, photochromism and halochromism respectively. Irreversible transformations typically involve reduction or oxidation. The colorless form is sometimes referred to as the leuco form.
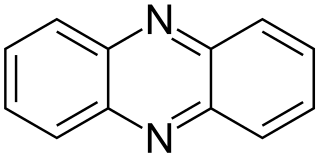
Phenazine is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4)2N2. It is a dibenzo annulated pyrazine, and the parent substance of many dyestuffs, such as the toluylene red, indulines, and safranines (and the closely related eurhodines). Phenazine crystallizes in yellow needles, which are only sparingly soluble in alcohol. Sulfuric acid dissolves it, forming a deep-red solution.

Disulfur dichloride is the inorganic compound of sulfur and chlorine with the formula S2Cl2. It is an amber oily liquid.

Paul Friedländer was a German chemist best known for his research on derivates of indigo and isolation of Tyrian purple from Murex brandaris.
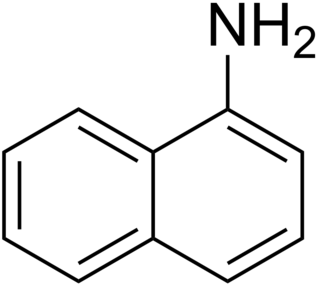
1-Naphthylamine is an aromatic amine derived from naphthalene. It can cause bladder cancer. It crystallizes in colorless needles which melt at 50 °C. It possesses a disagreeable odor, sublimes readily, and turns brown on exposure to air. It is the precursor to a variety of dyes.

Henry Edward Schunck, also known as Edward von Schunck, was a British chemist who did much work with dyes.
Triarylmethane dyes are synthetic organic compounds containing triphenylmethane backbones. As dyes, these compounds are intensely colored. They are produced industrially as dyes.

2-Nitrobenzaldehyde is an organic aromatic compound containing a nitro group ortho to formyl. 2-Nitrobenzaldehyde once was produced as an intermediate in the synthesis of the popular dye Indigo.

Natural dyes are dyes or colorants derived from plants, invertebrates, or minerals. The majority of natural dyes are vegetable dyes from plant sources—roots, berries, bark, leaves, and wood—and other biological sources such as fungi.