Thracian may refer to:
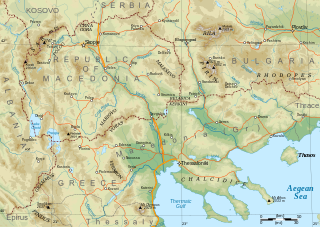
Macedonia is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time; however, it came to be defined as the modern geographical region by the mid-19th century. Today the region is considered to include parts of six Balkan countries: all of North Macedonia, large parts of Greece and Bulgaria, and smaller parts of Albania, Serbia, and Kosovo. It covers approximately 67,000 square kilometres (25,869 sq mi) and has a population of around five million. Greek Macedonia comprises about half of Macedonia's area and population.
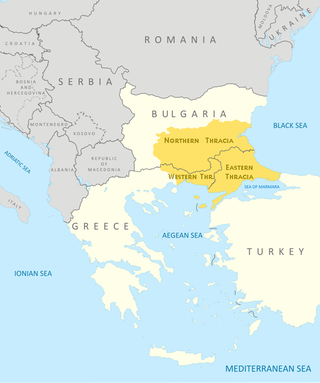
Thrace is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea to the east, it comprises present-day southeastern Bulgaria, northeastern Greece, and the European part of Turkey, roughly the Roman Province of Thrace. Lands also inhabited by ancient Thracians extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania and to the west into Macedonia.

The Dacians were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often considered a subgroup of the Thracians. This area includes mainly the present-day countries of Romania and Moldova, as well as parts of Ukraine, Eastern Serbia, Northern Bulgaria, Slovakia, Hungary and Southern Poland. The Dacians and the related Getae spoke the Dacian language, which has a debated relationship with the neighbouring Thracian language and may be a subgroup of it. Dacians were somewhat culturally influenced by the neighbouring Scythians and by the Celtic invaders of the 4th century BC.

The Thracians were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe and north-western Anatolia in antiquity. They primarily resided on the territories of modern-day Bulgaria, Romania, northern Greece and north-western Turkey.

The Rhodopes are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at 2,191 meters (7,188 ft). The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge.
Dacian is an extinct language generally believed to be a member of the Indo-European language family that was spoken in the ancient region of Dacia.
The Thracian language is an extinct and poorly attested language, spoken in ancient times in Southeast Europe by the Thracians. The linguistic affinities of the Thracian language are poorly understood, but it is generally agreed that it was an Indo-European language.

In antiquity, Paeonia or Paionia was the land and kingdom of the Paeonians or Paionians.

Western Thrace or West Thrace also known as Greek Thrace or Aegean Thrace, is a geographic and historical region of Greece, between the Nestos and Evros rivers in the northeast of the country; East Thrace, which lies east of the river Evros, forms the European part of Turkey, and the area to the north, in Bulgaria, is known as Northern Thrace.

The Getae or Gets were a Thracian-related tribe that once inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube, in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania. Although it is believed that the Getae were related to their westward neighbours, the Dacians, several scholars, especially in the Romanian historiography, posit that the Getae and the Dacians were the same people.
Thracology is the scientific study of Ancient Thrace and Thracian antiquities and is a regional and thematic branch of the larger disciplines of ancient history and archaeology. A practitioner of the discipline is a Thracologist. Thracology investigates the range of ancient Thracian culture from 1000 BC up to the end of Roman rule in the 4th–7th centuries AD. It is believed 'modern' Thracology started with the work of Wilhelm Tomaschek in the late 19th century.

The term Thraco-Roman describes the Romanized culture of Thracians under the rule of the Roman Empire.
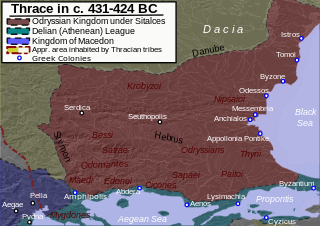
The Thracians were a group of Indo-European tribes inhabiting a large area in Central and Southeastern Europe, centred in modern Bulgaria. They were bordered by the Scythians to the north, the Celts and the Illyrians to the west, the Greeks to the south, and the Black Sea to the east.

East Thrace or eastern Thrace, also known as Turkish Thrace or European Turkey, is the part of Turkey that is geographically a part of Southeast Europe. It accounts for 3.03% of Turkey's land area and 15% of its population. The largest city is Istanbul, which straddles the Bosporus between Europe and Asia. East Thrace is of historic importance as it is next to a major sea trade corridor and constitutes what remains of the once-vast Ottoman region of Rumelia. It is currently also of specific geostrategic importance because the sea corridor, which includes two narrow straits, provides access to the Mediterranean Sea from the Black Sea for the navies of five countries: Russia, Ukraine, Romania, Bulgaria, and Georgia. The region also serves as a future connector of existing Turkish, Bulgarian, and Greek high-speed rail networks. Due to the guest worker agreement with Turkey and Germany, some Turks in Germany originally come from Eastern Thrace, mostly from the Kırklareli Province.

Thracians or Thracian Bulgarians are a regional, ethnographic group of ethnic Bulgarians, inhabiting or native to Thrace. Today, the larger part of this population is concentrated in Northern Thrace, but much is spread across the whole of Bulgaria and the diaspora.

Skudra was a province (satrapy) of the Persian Achaemenid Empire in Europe between 510s BC and 479 BC. Its name is attested in Persian and Egyptian inscriptions (an Egyptian record of c. 498–497 BC, and a list on the tomb of Darius the Great at Naqsh-e Rustam, c. 486 BC. It is believed to have comprised the lands now known as Thrace and Macedon.
Thraco-Macedonian is a conventional name in the study of ancient history to describe the political geography of Macedonia (region) in antiquity. It may refer to:
Thrace is a geographic region in the eastern Balkans, today divided between Bulgaria, Greece and Turkey.
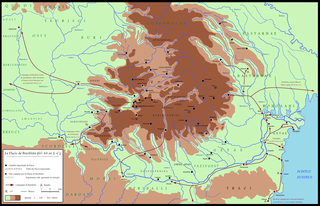
Dava was a Geto-Dacian name for a city, town or fortress. Generally, the name indicated a tribal center or an important settlement, usually fortified. Some of the Dacian settlements and the fortresses employed the Murus Dacicus traditional construction technique.