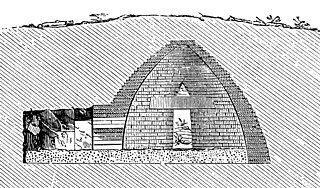
A beehive tomb, also known as a tholos tomb, is a burial structure characterized by its false dome created by corbelling, the superposition of successively smaller rings of mudbricks or, more often, stones. The resulting structure resembles a beehive, hence the traditional English name.

The tomb of Tutankhamun, also known by its tomb number, KV62, is the burial place of Tutankhamun, a pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of ancient Egypt, in the Valley of the Kings. The tomb consists of four chambers and an entrance staircase and corridor. It is smaller and less extensively decorated than other Egyptian royal tombs of its time, and it probably originated as a tomb for a non-royal individual that was adapted for Tutankhamun's use after his premature death. Like other pharaohs, Tutankhamun was buried with a wide variety of funerary objects and personal possessions, such as coffins, furniture, clothing and jewelry, though in the unusually limited space these goods had to be densely packed. Robbers entered the tomb twice in the years immediately following the burial, but Tutankhamun's mummy and most of the burial goods remained intact. The tomb's low position, dug into the floor of the valley, allowed its entrance to be hidden by debris deposited by flooding and tomb construction. Thus, unlike other tombs in the valley, it was not stripped of its valuables during the Third Intermediate Period.

A gallery grave is a form of megalithic tomb built primarily during the Neolithic Age in Europe in which the main gallery of the tomb is entered without first passing through an antechamber or hallway. There are at least four major types of gallery grave, and they may be covered with an earthen mound or rock mound.

The Thracian Tomb of Svestari is 2.5 kilometers (1.6 mi) southwest of the village of Sveshtari, Razgrad Province, which is 42 kilometers (26 mi) northeast of Razgrad, in northeast Bulgaria. The tomb is probably the grave of Dromichaetes who was a king of the Getae on both sides of the lower Danube around 300 BCE, and his wife, the daughter of King Lysimachus who was a general and diadochus of Alexander the Great. The tomb is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

The Thracian Tomb of Kazanlak is a vaulted-brickwork "beehive" (tholos) tomb that is located near the town of Kazanlak in central Bulgaria.

Denghoog is a Neolithic passage grave dating from around 3000 BC on the northern edge of Wenningstedt-Braderup on the German island of Sylt. The name Denghoog derives from the Söl'ring Deng (Thing) and Hoog (Hill).

Maglizh is a town in Stara Zagora Province, South-central Bulgaria. It is the administrative centre of the homonymous Maglizh Municipality. As of December 2009, the town has a population of 3,426 inhabitants.

Seuthes III was a king of Odrysia, a part of Thrace, during the late 4th century BC.
The Lohra tomb was a megalithic monument outside Lohra near Marburg in north central Hesse, Germany. It is one of the lesser known among its type in Central Europe. It dates to the late Neolithic, probably just after 3000 BC. It belongs to the gallery graves of the Wartberg culture, but is unique among them because of its rich ceramic assemblage.

The Illyrian Tombs of Selca e Poshtme are located near the town of Pogradec in Albania near the village of Selcë e Poshtme. On the right bank of the river Shkumbin at an elevation of 1040 m above sea level, lie the remains of the ancient city of Pelion and the accompanying necropolis. The Roman Via Egnatia led past it towards Thessaloniki. Though there are traces of human activity in Neolithic times, the settlement proper dates to the Iron Age through to the Illyrian urban period, and reached its height under settlement by the Illyrian tribe of Enchele in the later Iron Age and was also occupied in the Roman period as traces of a municipal building show. From the 4th to 1st centuries BC the city was the royal residence of Illyrian kings and therefore, also probably an important political and economic centre. In 1996, Albania included the Royal tombs of Selca e Poshtme in the UNESCO World heritage list of proposals.

The Aleksandrovo tomb is a Thracian burial mound and tomb excavated near Aleksandrovo, Haskovo Province, South-Eastern Bulgaria, dated to c. 4th century BCE.

The Tomb of Seuthes III is located near Kazanlak, Bulgaria. Seuthes III was the King of the Odrysian Kingdom of Thrace from c. 331 to c. 300 BC and founder of the nearby Thracian city of Seuthopolis.

The Ostrusha mound is a Thracian burial tumulus near the Bulgarian town of Shipka. It was constructed in the middle of the 4th century BCE. The stone structures under the more than 18 meters high mound form one of the biggest representative tomb-cult complexes with 6 rooms on an area of 100 square meters. It was professionally excavated in 1993.

The Thracian tomb at Shushmanets is a mound located in the Valley of the Thracian Rulers. It was built as a temple in the 4th century BC and later used as a tomb.

The Thracian tomb "Helvetia" mound near Shipka, Bulgaria, was built in the middle of the 4th century BC.

The Thracian tomb Griffins, found in Bulgaria, has a façade decorated with plastic columns and with a pediment above them. The pediment`s ends are semi-palmettes, the lower leaves of which are elongated and look like heads of griffins. The temple was built in the 5th century BC. There is a corridor made from river stones, floored with earth. The façade, the antechamber and the circular chamber are built of granite blocks. The entrances to the antechamber and the dome chamber had been closed by stone doors which were found broken during the research of the facility. The antechamber is of rectangular shape and has a double-pitched roof. The round chamber is covered with fine-made dome. The floors of both rooms are made of plastered granite slabs. Opposite the entrance of the circular chamber is situated a ritual stone bed with decorations. On a stone block in front of the bed were found gold paws. A funeral took place in the temple in the 4th century BC. The corridor was filled with river stones and soil. It was robbed in antiquity.

The Valley of the Thracian Rulers is a name which was made popular by the archaeologist Georgi Kitov and describes the extremely high concentration and variety of monuments of the Thracian culture in the Kazanlak Valley in Bulgaria. It is believed that there are over 1500 tumuli in the region, with only 300 being researched so far.

The Roman Tomb of Silistra is an Ancient Roman burial tomb in the town of Silistra in northeastern Bulgaria. Dating to the mid-4th century AD, the Roman Tomb is the best-preserved architectural monument of the Ancient Roman city of Durostorum. The tomb is considered "one of the most investigated and most discussed monuments of the late antique art in Bulgaria" and the Balkans, owing in large part to the quality and extent of its interior frescoes.

In the middle of the 19th century, an important Macedonian tomb, now known as Tomb A, was discovered near the Greek village of Korinos, at the site of ancient Pydna. In 1991 a second, smaller grave was discovered and excavated.

The Mogilan mound or Mogilanska mound is a burial mound in the center of Vratsa, Bulgaria.



















