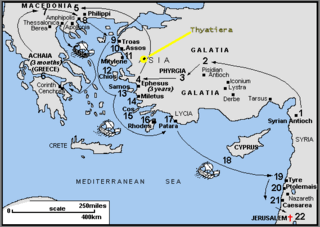
Thyateira was the name of an ancient Greek city in Asia Minor, now the modern Turkish city of Akhisar. The name is probably Lydian. It lies in the far west of Turkey, south of Istanbul and almost due east of Athens. It is about 50 miles (80 km) from the Aegean Sea.

The Mexican free-tailed bat or Brazilian free-tailed bat is a medium-sized bat native to the Americas, regarded as one of the most abundant mammals in North America. Its proclivity towards roosting in huge numbers at relatively few locations makes it vulnerable to habitat destruction in spite of its abundance. It has been claimed to have the fastest horizontal speed of any animal, reaching top ground speeds over 99 mph (160 km/h); its actual air speed has not been measured. The Texas Legislature designated the Mexican free-tailed bat the state mammal (flying) in 1995.

The peach blossom is a moth of the family Drepanidae. It was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae.
The Battle of Thyatira was fought in 366 at Thyatira, Lydia, between the army of the Roman Emperor Valens and the army of the usurper Procopius, led by his general Gomoarius.

Lydia of Thyatira is a woman mentioned in the New Testament who is regarded as the first documented convert to Christianity in Europe. Several Christian denominations have designated her a saint.

Holochilus brasiliensis, also known as the Brazilian marsh rat or web-footed marsh rat, is a species of semiaquatic rodent from South America. It is found in northeastern Argentina, southern and eastern Brazil and in eastern Uruguay.

The largetooth cookiecutter shark is a rare species of squaliform shark in the family Dalatiidae, reported from depths of 60–200 m (200–660 ft) at scattered locations in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. As its common name suggests, it is similar in appearance to the cookiecutter shark but has much larger lower teeth. This species reaches a maximum known length of 42 cm (17 in). The largetooth cookiecutter shark feeds by gouging out chunks of flesh from larger animals, including bony fishes, sharks, and marine mammals, and is able to take larger bites than I. brasiliensis. Little is known of its life history; it is thought to be a weaker swimmer than I. brasiliensis, and is presumably aplacental viviparous like the rest of its family. This shark is an infrequent bycatch of commercial trawl and longline fisheries, but is not thought to be much threatened by these activities.

Isistius is a genus of dogfish sharks in the family Dalatiidae. They are commonly known as cookiecutter sharks. Members of the genus are known for their unusual behaviour and dentition.

Paracoccidioides brasiliensis is a dimorphic fungus and one of the two species that cause paracoccidioidomycosis. The fungus has been affiliated with the family Ajellomycetaceae although a sexual state or teleomorph has not yet been found.
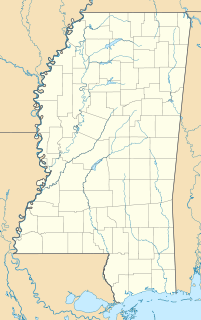
Thyatira is an unincorporated community in eastern Tate County, Mississippi, United States. It is located approximately 11 miles east of the county seat of Senatobia and 21 miles west of Holly Springs in Marshall County. The main thoroughfare is Mississippi Highway 4. Thyatira is home to two of the oldest Churches of Christ on record in the state, both of which bear the same name: Thyatira Church of Christ. It lies at an elevation of 371 feet (131 m).

The Thyatirinae, or false owlet moths, are a subfamily of the moth family Drepanidae with about 200 species described. Until recently, most classifications treated this group as a separate family called Thyatiridae.

Patuletin is an O-methylated flavonol. It can be found in the genus Eriocaulon.

Thyatira is a genus of moths belonging to the subfamily Thyatirinae of the Drepanidae. It was erected by Ferdinand Ochsenheimer in 1816.
Thyatira bodemeyeri is a moth in the family Drepanidae. It was described by Otto Bang-Haas in 1934. It was described from Persia.
Thyatira casta is a moth in the family Drepanidae. It was described by Felder in 1874. It is found in Colombia.
Thyatira dysimata is a moth in the family Drepanidae. It was described by West in 1932. It is found in the Philippines (Luzon).
Thyatira hedemanni is a moth in the family Drepanidae. It was described by Hugo Theodor Christoph in 1885. It is found in Georgia, Turkey, Armenia, Iran and Azerbaijan.

Thyatira mexicana is a moth in the family Drepanidae. It was described by Henry Edwards in 1884. It is found in the US state of Arizona through Central America to South America.
Thyatira vicina is a moth in the family Drepanidae. It was described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found on Java and Bali in Indonesia.
Epiperipatus brasiliensis is a species of velvet worm in the Peripatidae family. The type locality is in Pará, Brazil. Epiperipatus vagans from Barro Colorado Island (Panama) was originally described as subspecies of Epiperipatus brasiliensis, but is now treated as a full species.












