
Parallel ATA (PATA), originally AT Attachment, also known as Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE), is a standard interface designed for IBM PC-compatible computers. It was first developed by Western Digital and Compaq in 1986 for compatible hard drives and CD or DVD drives. The connection is used for storage devices such as hard disk drives, floppy disk drives, optical disc drives, and tape drives in computers.

CD-R is a digital optical disc storage format. A CD-R disc is a compact disc that can only be written once and read arbitrarily many times.

An optical disc is a flat, usually disc-shaped object that stores information in the form of physical variations on its surface that can be read with the aid of a beam of light. Optical discs can be reflective, where the light source and detector are on the same side of the disc, or transmissive, where light shines through the disc to be detected on the other side.

In computing, an optical disc drive (ODD) is a disc drive that uses laser light or electromagnetic waves within or near the visible light spectrum as part of the process of reading or writing data to or from optical discs. Some drives can only read from certain discs, while other drives can both read and record. Those drives are called burners or writers since they physically burn the data onto on the discs. Compact discs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs are common types of optical media which can be read and recorded by such drives.

SuperDrive is the product name for a floppy disk drive and later an optical disc drive made and marketed by Apple Inc. The name was initially used for what Apple called their high-density floppy disk drive, and later for the internal CD and DVD drive integrated with Apple computers. Though Apple no longer manufactures computers that feature built-in SuperDrives, the name is still used when referring to Apple's external CD and DVD drive accessory (pictured).

DVD-RAM is a DVD-based disc specification presented in 1996 by the DVD Forum, which specifies rewritable DVD-RAM media and the appropriate DVD writers. DVD-RAM media have been used in computers as well as camcorders and personal video recorders since 1998.
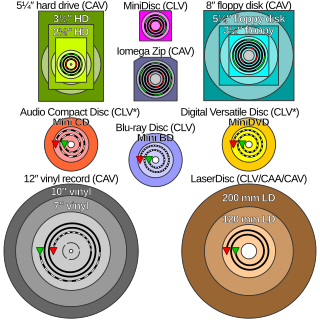
In optical storage, constant angular velocity (CAV) is a qualifier for the rated speed of any disc containing information, and may also be applied to the writing speed of recordable discs. A drive or disc operating in CAV mode maintains a constant angular velocity, contrasted with a constant linear velocity (CLV).

In optical storage, constant linear velocity (CLV) is a qualifier for the rated speed of an optical disc drive, and may also be applied to the writing speed of recordable discs. CLV implies that the angular velocity varies during an operation, as contrasted with CAV modes. The concept of constant linear velocity was patented in 1886 by phonograph pioneers Chichester Bell and Charles Tainter.
Plextor was a Taiwanese consumer electronics brand, best known for solid-state drives and optical disc drives.

Optical storage refers to a class of data storage systems that use light to read or write data to an underlying optical media. Although a number of optical formats have been used over time, the most common examples are optical disks like the compact disc (CD) and DVD. Reading and writing methods have also varied over time, but most modern systems as of 2023 use lasers as the light source and use it both for reading and writing to the discs. Britannica notes that it "uses low-power laser beams to record and retrieve digital (binary) data."

DVD recordable and DVD rewritable are a collection of optical disc formats that can be written to by a DVD recorder and by computers using a DVD writer. The "recordable" discs are write-once read-many (WORM) media, where as "rewritable" discs are able to be erased and rewritten. Data is written ('burned') to the disc by a laser, rather than the data being 'pressed' onto the disc during manufacture, like a DVD-ROM. Pressing is used in mass production, primarily for the distribution of home video.

A combo drive is a type of optical drive that combines CD-R/CD-RW recording capability with an ability to read DVD media; some manufacturers refer this as CD-RW/DVD-ROM drive. The term was used almost exclusively by Apple as a name for the low-end substitute for their high-end SuperDrive, as the latter was designed to both read and write CD and DVD recordable media. The device was created as a mid-range option between a CD burner and a DVD burner, which at the time the combo drive was introduced was generally an expensive option costing in excess of US$300 a unit.

Optical disc authoring requires a number of different optical disc recorder technologies working in tandem, from the optical disc media to the firmware to the control electronics of the optical disc drive.

CD-RW is a digital optical disc storage format introduced by Ricoh in 1997. A CD-RW compact disc (CD-RWs) can be written, read, erased, and re-written.

Optiarc is a brand of optical disc drives and solid-state drives. It is owned by a US-based Vinpower Digital, Inc.

The DVD is a digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 1995 and first released on November 1, 1996, in Japan. The medium can store any kind of digital data and has been widely used to store video programs, software and other computer files. DVDs offer significantly higher storage capacity than compact discs (CD) while having the same dimensions. A standard single-layer DVD can store up to 4.7 GB of data, a dual-layer DVD up to 8.5 GB. Variants can store up to a maximum of 17.08 GB.

HD DVD is an obsolete high-density optical disc format for storing data and playback of high-definition video. Supported principally by Toshiba, HD DVD was envisioned to be the successor to the standard DVD format, but lost to Blu-ray, supported by Sony and others.
As of 2021, multiple consumer-oriented, optical-disk media formats are or were available:

A CD-ROM is a type of read-only memory consisting of a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains data computers can read, but not write or erase. Some CDs, called enhanced CDs, hold both computer data and audio with the latter capable of being played on a CD player, while data is only usable on a computer.














