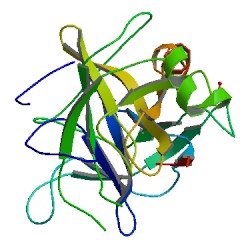
Chymotrypsin (EC 3.4.21.1, chymotrypsins A and B, alpha-chymar ophth, avazyme, chymar, chymotest, enzeon, quimar, quimotrase, alpha-chymar, alpha-chymotrypsin A, alpha-chymotrypsin) is a digestive enzyme component of pancreatic juice acting in the duodenum, where it performs proteolysis, the breakdown of proteins and polypeptides. Chymotrypsin preferentially cleaves peptide amide bonds where the side chain of the amino acid N-terminal to the scissile amide bond (the P1 position) is a large hydrophobic amino acid (tyrosine, tryptophan, and phenylalanine). These amino acids contain an aromatic ring in their side chain that fits into a hydrophobic pocket (the S1 position) of the enzyme. It is activated in the presence of trypsin. The hydrophobic and shape complementarity between the peptide substrate P1 side chain and the enzyme S1 binding cavity accounts for the substrate specificity of this enzyme. Chymotrypsin also hydrolyzes other amide bonds in peptides at slower rates, particularly those containing leucine at the P1 position.

Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion.

Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the digestive system of many vertebrates, where it hydrolyzes proteins. Trypsin is formed in the small intestine when its proenzyme form, the trypsinogen produced by the pancreas, is activated. Trypsin cuts peptide chains mainly at the carboxyl side of the amino acids lysine or arginine. It is used for numerous biotechnological processes. The process is commonly referred to as trypsinogen proteolysis or trypsinization, and proteins that have been digested/treated with trypsin are said to have been trypsinized.

A protease is an enzyme that catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products. They do this by cleaving the peptide bonds within proteins by hydrolysis, a reaction where water breaks bonds. Proteases are involved in numerous biological pathways, including digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism, and cell signaling.

In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate, the binding site, and residues that catalyse a reaction of that substrate, the catalytic site. Although the active site occupies only ~10–20% of the volume of an enzyme, it is the most important part as it directly catalyzes the chemical reaction. It usually consists of three to four amino acids, while other amino acids within the protein are required to maintain the tertiary structure of the enzymes.
Serine proteases are enzymes that cleave peptide bonds in proteins. Serine serves as the nucleophilic amino acid at the (enzyme's) active site. They are found ubiquitously in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Serine proteases fall into two broad categories based on their structure: chymotrypsin-like (trypsin-like) or subtilisin-like.
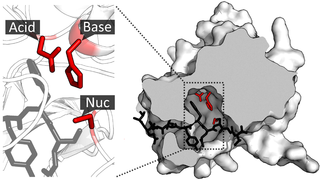
A catalytic triad is a set of three coordinated amino acids that can be found in the active site of some enzymes. Catalytic triads are most commonly found in hydrolase and transferase enzymes. An acid-base-nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to release the product and regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine or even selenocysteine. The 3D structure of the enzyme brings together the triad residues in a precise orientation, even though they may be far apart in the sequence.
Cysteine proteases, also known as thiol proteases, are hydrolase enzymes that degrade proteins. These proteases share a common catalytic mechanism that involves a nucleophilic cysteine thiol in a catalytic triad or dyad.

AEBSF or 4-(2-aminoethyl)benzenesulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride is a water-soluble, irreversible serine protease inhibitor with a molecular weight of 239.5 Da. It inhibits proteases like chymotrypsin, kallikrein, plasmin, thrombin, and trypsin. The specificity is similar to the inhibitor PMSF, nevertheless AEBSF is more stable at low pH values. Typical usage is 0.1 - 1.0 mM. AEBSF was first reported for use in biochemistry in 1993, and came into common use for the inhibition serine proteases and of non-protease enzymes such as acetylhydrolases in the mid 1990s.

An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction.
Enzyme catalysis is the increase in the rate of a process by an "enzyme", a biological molecule. Most enzymes are proteins, and most such processes are chemical reactions. Within the enzyme, generally catalysis occurs at a localized site, called the active site.
Protein metabolism denotes the various biochemical processes responsible for the synthesis of proteins and amino acids (anabolism), and the breakdown of proteins by catabolism.

TEV protease is a highly sequence-specific cysteine protease from Tobacco Etch Virus (TEV). It is a member of the PA clan of chymotrypsin-like proteases. Due to its high sequence specificity, TEV protease is frequently used for the controlled cleavage of fusion proteins in vitro and in vivo. The consensus sequence recognized by TEV protease is Glu-Asn-Leu-Tyr-Phe-Gln-|-Ser, where "|" denotes cleaved peptide bond.

In molecular biology, Proteinase K is a broad-spectrum serine protease. The enzyme was discovered in 1974 in extracts of the fungus Parengyodontium album. Proteinase K is able to digest hair (keratin), hence, the name "Proteinase K". The predominant site of cleavage is the peptide bond adjacent to the carboxyl group of aliphatic and aromatic amino acids with blocked alpha amino groups. It is commonly used for its broad specificity. This enzyme belongs to Peptidase family S8 (subtilisin). The molecular weight of Proteinase K is 28,900 daltons.

Subtilases are a family of subtilisin-like serine proteases. They appear to have independently and convergently evolved an Asp/Ser/His catalytic triad, like in the trypsin serine proteases. The structure of proteins in this family shows that they have an alpha/beta fold containing a 7-stranded parallel beta sheet.

The 3C-like protease (3CLpro) or main protease (Mpro), formally known as C30 endopeptidase or 3-chymotrypsin-like protease, is the main protease found in coronaviruses. It cleaves the coronavirus polyprotein at eleven conserved sites. It is a cysteine protease and a member of the PA clan of proteases. It has a cysteine-histidine catalytic dyad at its active site and cleaves a Gln–(Ser/Ala/Gly) peptide bond.

The PA clan is the largest group of proteases with common ancestry as identified by structural homology. Members have a chymotrypsin-like fold and similar proteolysis mechanisms but can have identity of <10%. The clan contains both cysteine and serine proteases. PA clan proteases can be found in plants, animals, fungi, eubacteria, archaea and viruses.

The Early 35 kDa protein, or P35 in short, is a baculoviral protein that inhibits apoptosis in the cells infected by the virus. Although baculoviruses infect only invertebrates in nature, ectopic expression of P35 in vertebrate animals and cells also results in inhibition of apoptosis, thus indicating a universal mechanism. P35 has been shown to be a caspase inhibitor with a very wide spectrum of activity both in regard to inhibited caspase types and to species in which the mechanism is conserved.
An endopeptidase inhibitor is a drug that inhibits one or more endopeptidase enzymes. Endopeptidases are one of two types of proteases, the other being exopeptidases. Endopeptidases cleave peptide bonds of non-terminal amino acids, whereas exopeptidases break terminal bonds, resulting in the release of a single amino acid or dipeptide from the peptide chain.

Papain-like proteases are a large protein family of cysteine protease enzymes that share structural and enzymatic properties with the group's namesake member, papain. They are found in all domains of life. In animals, the group is often known as cysteine cathepsins or, in older literature, lysosomal peptidases. In the MEROPS protease enzyme classification system, papain-like proteases form Clan CA. Papain-like proteases share a common catalytic dyad active site featuring a cysteine amino acid residue that acts as a nucleophile.

















