An audio file format is a file format for storing digital audio data on a computer system. The bit layout of the audio data is called the audio coding format and can be uncompressed, or compressed to reduce the file size, often using lossy compression. The data can be a raw bitstream in an audio coding format, but it is usually embedded in a container format or an audio data format with defined storage layer.

Ogg is a free, open container format maintained by the Xiph.Org Foundation. The authors of the Ogg format state that it is unrestricted by software patents and is designed to provide for efficient streaming and manipulation of high-quality digital multimedia. Its name is derived from "ogging", jargon from the computer game Netrek.

Vorbis is a free and open-source software project headed by the Xiph.Org Foundation. The project produces an audio coding format and software reference encoder/decoder (codec) for lossy audio compression, libvorbis. Vorbis is most commonly used in conjunction with the Ogg container format and it is therefore often referred to as Ogg Vorbis.

xine is a multimedia playback engine for Unix-like operating systems released under the GNU General Public License. xine is built around a shared library (xine-lib) that supports different frontend player applications. xine uses libraries from other projects such as liba52, libmpeg2, FFmpeg, libmad, FAAD2, and Ogle. xine can also use binary Windows codecs through a wrapper, bundled as the w32codecs, for playback of some media formats that are not handled natively.
A digital video recorder (DVR), also referred to as a personal video recorder (PVR) particularly in Canada and British English, is an electronic device that records video in a digital format to a disk drive, USB flash drive, SD memory card, SSD or other local or networked mass storage device. The term includes set-top boxes (STB) with direct to disk recording, portable media players and TV gateways with recording capability, and digital camcorders. Personal computers are often connected to video capture devices and used as DVRs; in such cases the application software used to record video is an integral part of the DVR. Many DVRs are classified as consumer electronic devices. Similar small devices with built-in displays and SSD support may be used for professional film or video production, as these recorders often do not have the limitations that built-in recorders in cameras have, offering wider codec support, the removal of recording time limitations and higher bitrates.
3GP is a multimedia container format defined by the Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) for 3G UMTS multimedia services. It is used on 3G mobile phones but can also be played on some 2G and 4G phones.

Rockbox is a free and open-source software replacement for the OEM firmware in various forms of digital audio players (DAPs) with an original kernel. It offers an alternative to the player's operating system, in many cases without removing the original firmware, which provides a plug-in architecture for adding various enhancements and functions. Enhancements include personal digital assistant (PDA) functions, applications, utilities, and games. Rockbox can also retrofit video playback functions on players first released in mid-2000. Rockbox includes a voice-driven user-interface suitable for operation by visually impaired users.
Neuros Technology was a Chicago, Illinois–based company that produced a number of audio and video devices under the brand name Neuros. Founded by Joe Born in 2001 as a division of Digital Innovations, it previously operated under the name Neuros Audio. Like Digital Innovations, Neuros distinguished itself by its use of open-innovation and crowdsourcing techniques to bring products to market, as well as by its prominent use of open-source software and open-source hardware. In its development model, end users were involved throughout the product development process from reviewing initial concepts to beta testing initial product releases.
Gapless playback is the uninterrupted playback of consecutive audio tracks, such that relative time distances in the original audio source are preserved over track boundaries on playback. For this to be useful, other artifacts at track boundaries should not be severed either. Gapless playback is common with compact discs, gramophone records, or tapes, but is not always available with other formats that employ compressed digital audio. The absence of gapless playback is a source of annoyance to listeners of music where tracks are meant to segue into each other, such as some classical music, progressive rock, concept albums, electronic music, and live recordings with audience noise between tracks.

Sound Recorder is an audio recording program included in most versions of the Microsoft Windows family of operating systems. Its user interface has been replaced twice in the past.
A container format or metafile is a file format that allows multiple data streams to be embedded into a single file, usually along with metadata for identifying and further detailing those streams. Notable examples of container formats include archive files and formats used for multimedia playback. Among the earliest cross-platform container formats were Distinguished Encoding Rules and the 1985 Interchange File Format.
An audio converter is a software or hardware tool that converts audio files from one format to another. This process is often necessary when users encounter compatibility issues with different devices, applications, or platforms that support specific audio file formats. Audio converters can be employed for a variety of purposes, ranging from personal entertainment to professional audio production.

iAUDIO is the brand name for a range of portable media players produced by Korean consumer electronics and software corporation Cowon Systems, Inc.

The Sansa Fuze is a portable media player developed by SanDisk and released on March 8, 2008. The Fuze is available in three different Flash memory capacities: 2 GB, 4 GB, and 8 GB and comes in six different colors: black, blue, pink, red, silver, and white. Storage is expandable via a microSDHC slot with capacity up to 32 GB, and unofficially to 64 GB or more via FAT32 formatted SDXC cards. All models have a 1.9 inch TFT LCD display with a resolution of 220 by 176 pixels and a built-in monaural microphone and FM tuner; recordings of the latter two are saved as PCM WAV files.
Uncompressed video is digital video that either has never been compressed or was generated by decompressing previously compressed digital video. It is commonly used by video cameras, video monitors, video recording devices, and in video processors that perform functions such as image resizing, image rotation, deinterlacing, and text and graphics overlay. It is conveyed over various types of baseband digital video interfaces, such as HDMI, DVI, DisplayPort and SDI. Standards also exist for the carriage of uncompressed video over computer networks.
A demultiplexer for digital media files, or media demultiplexer, also called a file splitter by laymen or consumer software providers, is software that demultiplexes individual elementary streams of a media file, e.g., audio, video, or subtitles and sends them to their respective decoders for actual decoding. Media demultiplexers are not decoders themselves, but are format container handlers that separate media streams from a (container) file and supply them to their respective audio, video, or subtitles decoders.
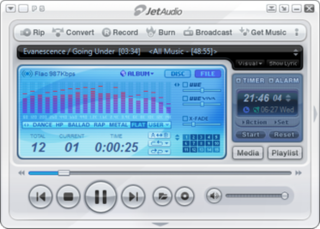
JetAudio is a shareware media player application for Microsoft Windows and Android released in 1997 which offers playback options for a wide range of multimedia file formats.

Simplified Universal Player Encoder & Recorder (SUPER) is a closed-source front end for open-source software video players and encoders provided by the FFmpeg, MEncoder, MPlayer, x264, ffmpeg2theora, musepack, Monkey's Audio, True Audio, WavPack, libavcodec, and the Theora/Vorbis RealProducer plugIn projects. It was first released in 2005. SUPER provides a graphical user interface to these back-end programs, which use a command-line interface.
HTML audio is a subject of the HTML specification, incorporating audio input, playback, and synthesis, all in the browser.










