
Natal is the capital and largest city of the state of Rio Grande do Norte, located in northeastern Brazil. According to IBGE's 2022 estimate, the city had a total population of 751,300, making it the 24th largest city in the country. Natal is a major tourist destination and an exporting hub of crustaceans, carnauba wax and fruits, mostly melon, sugar apple, cashew and papaya. Natal is Brazil's closest city to Africa and Europe, its Greater Natal International Airport connects the city with many Brazilian destinations and also operates some international flights. The city was one of the host cities of the 2014 FIFA World Cup.

→
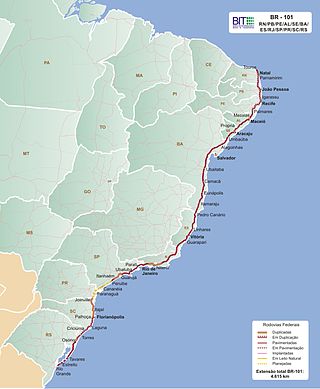
The BR-101 is a longitudinal highway of Brazil. It is the longest in the country with a length of nearly 4,800 km (3,000 mi), and it is considered one of the most important highways in the country, along with BR-116.
Lagoa may refer to the following:
São Miguel is the name of the largest island of the Azores and may also refer to:
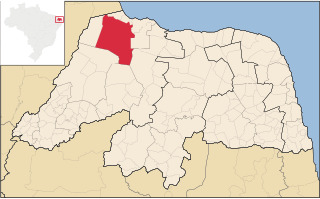
Mossoró is the second most populous city in the state of Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil, and also the largest municipality of that state. It is equidistant from Natal, the state capital of Rio Grande do Norte, and from Fortaleza, the capital of the state of Ceará. It is also in the heart of Brazil's salt production area. Situated in the Oeste Potiguar mesoregion, Mossoró is the country's largest land-based petroleum producer.

Picos is a municipality in the state of Piauí in the Northeast region of Brazil. Picos is the state's third-largest city, located in the south-central region of Piauí and is the most economically developed city in the region. The city's financial prosperity, combined with its geographical location, gives Picos a "commercial hub" status, especially for fuel and honey. As of 2020, the population was approximately 78,431.

Brazil is divided into several types and levels of subdivisions.

Lagoa do Peixe National Park is a national park in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It was created in 1986 to protect a wintering zone for migratory birds along the Lagoa dos Patos, the estuary of the Guaiba river or Guaíba Lake about 200 kilometres (120 mi) south of Porto Alegre.

Pureza is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Norte in the Northeast region of Brazil. The place means "pure" in Portuguese hence its pure lake located in the area, and it is depicted in the municipal seal.

São Miguel do Gostoso is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Norte in the Northeast region of Brazil.
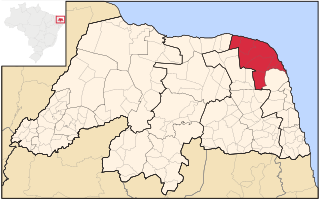
Litoral Nordeste was a microregion in the Brazilian state of Rio Grande do Norte.

Events in the year 1892 in Brazil.

Events in the year 1923 in Brazil.

Events in the year 1944 in Brazil.

João Câmara is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil. The municipality was founded on 29 October 1928.

Events in the year 1996 in Brazil.

Events in the year 1997 in Brazil.
















