
Treponema pallidum, formerly known as Spirochaeta pallida, is a spirochaete bacterium with various subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel, and yaws. It is transmitted only among humans. It is a helically coiled microorganism usually 6–15 μm long and 0.1–0.2 μm wide. T. pallidum's lack of either a tricarboxylic acid cycle or oxidative phosphorylation results in minimal metabolic activity. The treponemes have a cytoplasmic and an outer membrane. Using light microscopy, treponemes are visible only by using dark field illumination. Treponema pallidum consists of three subspecies, T. p. pallidum, T. p. endemicum, and T. p. pertenue, each of which has a distinct associated disease.
Pinta is a human skin disease caused by infection with the spirochete Treponema carateum, which is morphologically and serologically indistinguishable from the bacterium that causes syphilis. The disease is endemic to Mexico, Central America, and South America.

Treponema is a genus of spiral-shaped bacteria. The major treponeme species of human pathogens is Treponema pallidum, whose subspecies are responsible for diseases such as syphilis, bejel, and yaws. Treponema carateum is the cause of pinta. Treponema paraluiscuniculi is associated with syphilis in rabbits. Treponema succinifaciens has been found in the gut microbiome of traditional rural human populations.
The fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption (FTA-ABS) test is a diagnostic test for syphilis. Using antibodies specific for the Treponema pallidum species, such tests would be assumed to be more specific than non-treponemal testing such as VDRL but have been shown repeatedly to be sensitive but not specific for the diagnosis of neurosyphilis in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). In addition, FTA-ABS turns positive earlier and remains positive longer than VDRL. Other treponemes, such as T. pertenue, may also produce a positive FTA-ABS. The ABS suffix refers particularly to a processing step used to remove nonspecific antispirochetal antibodies present in normal serum.
Condylomata lata or condyloma latum, is a cutaneous condition characterized by wart-like lesions on the genitals. They are generally symptoms of the secondary phase of syphilis, caused by the spirochete, Treponema pallidum.
Treponema denticola is a Gram-negative, obligate anaerobic, motile and highly proteolytic spirochete bacterium. It is one of four species of oral spirochetes to be reliably cultured, the others being Treponema pectinovorum, Treponema socranskii and Treponema vincentii. T. denticola dwells in a complex and diverse microbial community within the oral cavity and is highly specialized to survive in this environment. T. denticola is associated with the incidence and severity of human periodontal disease. Treponema denticola is one of three bacteria that form the Red Complex, the other two being Porphyromonas gingivalis and Tannerella forsythia. Together they form the major virulent pathogens that cause chronic periodontitis. Having elevated T. denticola levels in the mouth is considered one of the main etiological agents of periodontitis. T. denticola is related to the syphilis-causing obligate human pathogen, Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. It has also been isolated from women with bacterial vaginosis.
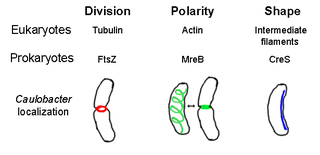
The prokaryotic cytoskeleton is the collective name for all structural filaments in prokaryotes. It was once thought that prokaryotic cells did not possess cytoskeletons, but advances in visualization technology and structure determination led to the discovery of filaments in these cells in the early 1990s. Not only have analogues for all major cytoskeletal proteins in eukaryotes been found in prokaryotes, cytoskeletal proteins with no known eukaryotic homologues have also been discovered. Cytoskeletal elements play essential roles in cell division, protection, shape determination, and polarity determination in various prokaryotes.
Treponematosis is a term used to individually describe any of the diseases caused by four members of the bacterial genus Treponema. The four diseases are collectively referred to as treponematoses:
Brachyspira innocens is a species of bacteria. It is thought to be a commensal bacterium.
Treponema bryantii is a species of spirochete bacteria within the genus Treponema. This species is an obligate anaerobe and is found in the rumen of cows.
Treponema azotonutricium is a bacterium, the first termite gut spirochete to be isolated, together with Treponema primitia.
Treponema primitia is a bacterium, the first termite gut spirochete to be isolated, together with Treponema azotonutricium.
Treponema isoptericolens is a spirochaete from the hindgut of the termite Incisitermes tabogae. Its cells are motile, helical in shape, 0.4–0.5 μm in diameter and generally 12–20 μm long; it is obligately anaerobic, with type strain SPIT5T.
Spiral bacteria, bacteria of spiral (helical) shape, form the third major morphological category of prokaryotes along with the rod-shaped bacilli and round cocci. Spiral bacteria can be subclassified by the number of twists per cell, cell thickness, cell flexibility, and motility. The two types of spiral cells are spirillum and spirochete, with spirillum being rigid with external flagella, and spirochetes being with internal flagella.
Treponema socranskii was isolated from gum swabs of people with periodontitis and clinically-induced periodontitis. It is a motile, helically coiled, obligate anaerobe that grows best at 37 °C, and is a novel member of its genus because of its ability to ferment molecules that other Treponema species cannot. T. socranskii’s growth is positively correlated with gingival inflammation, which indicates that it is a leading cause of gingivitis and periodontitis.
The Putative Treponema 4 TMS Holin (Tre4Hol) Family consists of several proteins from Treponema species. They range in size from 100 to 110 amino acyl residues (aas) in length and exhibit 4 transmembrane segments (TMSs). A fragment has been sequenced from Treponema phage Phi td1 (D2ECI8) and was designated a putative holin.
Treponema succinifaciens is an anaerobic spirochete bacterium first discovered in the intestines of swine in 1981. The helical cells of T. succinifaciens grow to 16 μm in length and often form chains of cells when cultured. T. succinifaciens is gram-negative and non spore-forming.

The Treponemataceae are a family of spirochete bacteria. The clade includes a number of significant pathogens, such as Treponemapallidum, the cause of human syphilis.
Sheila Lukehart is an American physician who is Emeritus Professor of Medicine at the University of Washington. Her research covered immune responses and the pathogenesis of syphilis. In 2023, she was elected a Fellow of the American Society for Microbiology.


