Related Research Articles

Humanists International is an international non-governmental organisation championing secularism and human rights, motivated by secular humanist values. Founded in Amsterdam in 1952, it is an umbrella organisation made up of more than 160 secular humanist, atheist, rationalist, agnostic, skeptic, freethought and Ethical Culture organisations from over 80 countries.
Censorship in Tunisia has been an issue since the country gained independence in 1956. Though considered relatively mild under President Habib Bourguiba (1957–1987), censorship and other forms of repression became common under his successor, President Zine El Abidine Ben Ali. Ben Ali was listed as one of the "10 Worst Enemies of the Press" by the Committee to Protect Journalists starting in 1998. Reporters Without Borders named Ben Ali as a leading "Predator of Press Freedom". However, the Tunisia Monitoring Group reports that the situation with respect to censorship has improved dramatically since the overthrow of Ben Ali in early 2011.
Iran is a constitutional, Islamic theocracy. Its official religion is the doctrine of the Twelver Jaafari School. Iran's law against blasphemy derives from Sharia. Blasphemers are usually charged with "spreading corruption on earth", or mofsed-e-filarz, which can also be applied to criminal or political crimes. The law against blasphemy complements laws against criticizing the Islamic regime, insulting Islam, and publishing materials that deviate from Islamic standards.

In Islam, blasphemy is impious utterance or action concerning God, but is broader than in normal English usage, including not only the mocking or vilifying of attributes of Islam but denying any of the fundamental beliefs of the religion. Examples include denying that the Quran was divinely revealed, the Prophethood of one of the Islamic prophets, insulting an angel, or maintaining God had a son.
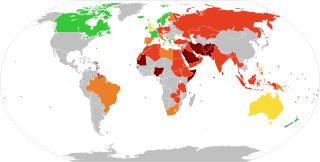
A blasphemy law is a law prohibiting blasphemy, which is the act of insulting or showing contempt or lack of reverence to a deity, or sacred objects, or toward something considered sacred or inviolable. According to Pew Research Center, about a quarter of the world's countries and territories (26%) had anti-blasphemy laws or policies as of 2014.
The main blasphemy law in Egypt is Article 98(f) of the Egyptian Penal Code. It penalizes: "whoever exploits and uses the religion in advocating and propagating by talk or in writing, or by any other method, extremist thoughts with the aim of instigating sedition and division or disdaining and contempting any of the heavenly religions or the sects belonging thereto, or prejudicing national unity or social peace."
The Federal Republic of Nigeria operates two court systems. Both systems can punish blasphemy. The Constitution provides a customary (irreligious) system and a system that incorporates Sharia. The customary system prohibits blasphemy by section 204 of Nigeria's Criminal Code.

Waleed Al-Husseini or Walid Husayin is a Palestinian atheist, secularist essayist, writer, blogger, ex-Muslim and founder of the Council of Ex-Muslims of France. Born and raised in Qalqilya in the West Bank, he has been living in France since 2012.
Hamad al-Naqi is a Kuwaiti activist and blogger who in June 2012 was sentenced to ten years' imprisonment on charges of provoking sectarian tensions and making blasphemous tweets against Muhammad. His arrest triggered international outcry from human rights organizations and world leaders.
Alexander Aan is an Indonesian atheist and ex-Muslim of Minang descent. He was imprisoned in 2012 for posting comments and images to Facebook that were judged to be "disseminating information aimed at inciting religious hatred or hostility" by the Muaro Sijunjung district court. The sentence sparked national debate and caused Amnesty International to designate him a prisoner of conscience.

Kacem El Ghazzali, is a Moroccan-Swiss secularist essayist and activist and is one of the few publicly atheist Moroccans. Kacem speaks English, as well as German, French, Arabic and Berber. Mostly known for his publicly voiced atheism, his writings stress the importance of freedom of thought which, in his view, is lacking in countries dominated by Islam. His articles have been published in/by the Richard Dawkins Foundation, Huffington Post, Le Monde, Neue Zürcher Zeitung, Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung, Basler Zeitung, Tages Anzeiger, Berlingske and others.

Alber Saber Ayad is an Egyptian computer science student and blogger who was arrested on 13 September 2012 on allegations of having shared the YouTube trailer for the anti-Islam film Innocence of Muslims on his Facebook page. While he was raised in a Coptic Christian family, he is now an atheist.

Raif bin Muhammad Badawi is a Saudi writer, dissident and activist, as well as the creator of the website Free Saudi Liberals.
Irreligion in Morocco is relatively uncommon, in the country. While a 2015 poll of about 1000 Moroccans by Gallup International found that 4% of respondents said they were "not religious", and 1% reported being a "convinced atheist", while 93% said they were religious
Junaid Hafeez is a former M. Phil English student at a Pakistani university where he was teaching as visiting teacher as well. He was convicted of blasphemy under Pakistan's broad blasphemy laws and sentenced to death. Arrested in 2013, Hafeez was accused of making derogatory comments about the prophet of Islam, Muhammad on social media. Held in solitary confinement since 2014, his trial was repeatedly delayed, and Hafeez's first lawyer, Rashid Rehman, was murdered. In December 2019, Hafeez was convicted and sentenced to death by a Pakistani court. His detention and arrest have been condemned by human rights groups..
Soheil Arabi, is an Iranian blogger who was sentenced to death in Iran in 2013 on charges of insulting the Islamic prophet Muhammad in his postings on Facebook about Atena Daemi. His sentence was commuted in 2015 to several years imprisonment and two years of mandatory study of Islamic theology. On 2 January 2023, Arabi was reportedly re-arrested by security forces.
Sherif Gaber Abdelazim Bakr, is an Egyptian political activist and blogger who was arrested on October 27, 2013, for professing atheism, contempt of religion relating to activities on campus and atheist statements online.

Mohamed Cheikh Ould Mkhaitir is a Mauritanian blogger who was a political prisoner from 2014 to 2019. He was sentenced to death after he wrote an article critical of Islam and the caste system in Mauritania, after which he became a designated prisoner of conscience by Amnesty International. He now lives in exile in France due to concerns for his safety.

The situation for apostates from Islam varies markedly between Muslim-minority and Muslim-majority regions. In Muslim-minority countries, "any violence against those who abandon Islam is already illegal". But in some Muslim-majority countries, religious violence is "institutionalised", and "hundreds and thousands of closet apostates" live in fear of violence and are compelled to live lives of "extreme duplicity and mental stress."
The following lists events that happened during 2012 in the Tunisian Republic.
References
- ↑ Kacem El Ghazzali (1 April 2012). "Tunisian Atheists sentenced to seven and a half years of prison". Atheistica. Retrieved 1 April 2012.
- 1 2 3 Tarek Amara (6 April 2012). "Tunisians jailed for Facebook cartoons of Prophet". Reuters. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved 1 July 2012.
- ↑ Jihen Laghmari (6 April 2012). "Tunisia Jails Two Men Over Prophet Caricatures on Facebook". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on January 18, 2013. Retrieved 1 July 2012.
- 1 2 Arne Lichtenberg (27 May 2012). "Bloggers criticize Tunisia's failed revolution". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 1 July 2012.
- ↑ "Jailed Tunisian loses appeal over Facebook Prophet Mohammad cartoons". Al Arabiya News. Agence France-Presse. 25 June 2012. Retrieved 1 July 2012.
- ↑ "Tunisia: Two atheist friends convicted for blasphemy". Index on Censorship. 5 April 2012. Archived from the original on 15 October 2013. Retrieved 15 October 2013.
- ↑ "Tunisia: Two men sentenced to seven years for blasphemy". Digital Journal. 6 April 2012. Retrieved 15 October 2013.
- ↑ "Tunisian Atheists sentenced to seven and a half years of prison « Atheistica". atheistica.com. Archived from the original on 2012-04-05.
- ↑ "Humanists International".
- ↑ "Tunisia: Mounting attacks on freedom of expression". Amnesty International. 24 April 2012. Archived from the original on 5 April 2016. Retrieved 1 July 2012.
- ↑ "Un événement extrêmement inquiétant ... des attaques répétées contre les journalistes, les artistes et les femmes qui commettent le « crime » d'exprimer librement leur opinion". "Le TMG de l'IFEX s'inquiète des attaques répétées qui ciblent les manifestants, les médias, les acteurs et les universitaires" (in French). International Freedom of Expression Exchange. 10 April 2012. Retrieved 1 July 2012.
- ↑ "Tunisia court upholds cartoon blasphemy conviction". CBS News. 27 June 2012. Archived from the original on June 28, 2012. Retrieved 1 July 2012.
- ↑ "Jabeur Mejri Finally Released from Prison, According to Lawyer - Tunisia Live : Tunisia Live". www.tunisia-live.net. Archived from the original on 2014-03-07.