In organic chemistry, an electrocyclic reaction is a type of pericyclic, rearrangement reaction where the net result is one pi bond being converted into one sigma bond or vice versa. These reactions are usually categorized by the following criteria:

Triazines are a class of nitrogen-containing heterocycles. The parent molecules' molecular formula is C3H3N3. They exist in three isomeric forms, 1,3,5-triazines being common.
Phloroglucinol is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(OH)3. It is a colorless solid. It is used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and explosives. Phloroglucinol is one of three isomeric benzenetriols. The other two isomers are hydroxyquinol (1,2,4-benzenetriol) and pyrogallol (1,2,3-benzenetriol). Phloroglucinol, and its benzenetriol isomers, are still defined as "phenols" according to the IUPAC official nomenclature rules of chemical compounds. Many such monophenolics are often termed polyphenols.

Maleic acid or cis-butenedioic acid is an organic compound that is a dicarboxylic acid, a molecule with two carboxyl groups. Its chemical formula is HO2CCH=CHCO2H. Maleic acid is the cis isomer of butenedioic acid, whereas fumaric acid is the trans isomer. Maleic acid is mainly used as a precursor to fumaric acid, and relative to its parent maleic anhydride, which has many applications.
1,3,5-Triazine, also called s-triazine, is an organic chemical compound with the formula (HCN)3. It is a six-membered heterocyclic aromatic ring, one of several isomeric triazines. s-Triazine —the "symmetric" isomer—and its derivatives are useful in a variety of applications.

Levopropoxyphene is an antitussive. It is an optical isomer of dextropropoxyphene. The racemic mixture is called propoxyphene. Only the dextro-isomer (dextropropoxyphene) has an analgesic effect; the levo-isomer appears to exert only an antitussive effect. It was formerly marketed in the U.S. by Eli Lilly under the tradename Novrad as an antitussive. Unlike many antitussives, it binds poorly to the sigma-1 receptor.
This is the list of extremely hazardous substances defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act. The list can be found as an appendix to 40 CFR 355. Updates as of 2006 can be seen on the Federal Register, 71 FR 47121.
Diimide, also called diazene or diimine, is a compound having the formula HN=NH. It exists as two geometric isomers, E (trans) and Z (cis). The term diazene is more common for organic derivatives of diimide. Thus, azobenzene is an example of an organic diazene.

2,4,6-Trichlorophenol, also known as TCP, phenaclor, Dowicide 2S, Dowcide 2S, omal, is a chlorinated phenol that has been used as a fungicide, herbicide, insecticide, antiseptic, defoliant, and glue preservative. It is a clear to yellowish crystalline solid with a strong, phenolic odor. It decomposes on heating to produce toxic and corrosive fumes including hydrogen chloride and chlorine.
A trichlorophenol is any organochloride of phenol that contains three covalently bonded chlorine atoms. Trichlorophenols are produced by electrophilic halogenation of phenol with chlorine. Different isomers of trichlorophenol exist according to which ring positions on the phenol contain chlorine atoms. 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol, for example, has two chlorine atoms in the ortho positions and one chlorine atom in the para position.
The Yamaguchi esterification is the chemical reaction of an aliphatic carboxylic acid and 2,4,6-trichlorobenzoyl chloride to form a mixed anhydride which, upon reaction with an alcohol in the presence of stoichiometric amount of DMAP, produces the desired ester. It was first reported by Masaru Yamaguchi et al. in 1979.

cis-Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride is a salt with the formula [CoCl2(en)2]Cl (en = ethylenediamine). The salt consists of a cationic coordination complex and a chloride anion. It is a violet diamagnetic solid that is soluble in water. One chloride ion in this salt readily undergoes ion exchange, but the two other chlorides are less reactive, being bound to the metal center.

Humulone, a vinylogous type of organic acid, is a bitter-tasting chemical compound found in the resin of mature hops. Humulone is a prevalent member of the class of compounds known as alpha acids, which collectively give hopped beer its characteristic bitter flavor.
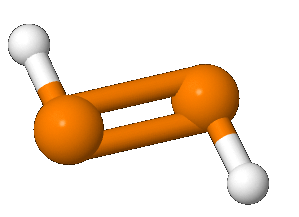
Diphosphene is a compound having the formula (PH)2. It exists as two geometric isomers, E and Z. Diphosphene is also the parent member of the entire class of diphosphene compounds with the formula (PR)2, where R is an organyl group.
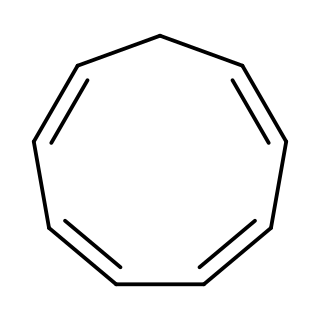
Cyclononatetraene is an organic compound with the formula C9H10. It was first prepared in 1969 by protonation of the corresponding aromatic anion (described below). It is unstable and isomerizes with a half-life of 50 minutes at room temperature to 3a,7a-dihydro-1H-indene via a thermal 6π disrotatory electrocyclic ring closing. Upon exposure to ultraviolet light, it undergoes a photochemical 8π electrocyclic ring closing to give bicyclo[6.1.0]nona-2,4,6-triene.

2,4,6-Trimethylpyridine (2,4,6-collidine) is an organic compound which belongs to the heterocycles. It consists of a pyridine ring substituted with three methyl groups. It belongs to the substance group of the collidines, a group of six constitutional isomers. 2,4,6-trimethylpyridine is the most well-known isomer of this group.
Trichlorotoluenes are organochlorine compounds, in particular aryl chlorides, with the formula CH3C6H2Cl3. Six constitutional isomers exist, differing in the relative position of the three chlorine substituents around the ring. All isomers colorless and lipophilic solids.

Mesitol (2,4,6-trimethylphenol) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)3C6H2OH. It is one of several isomers of trimethylphenol. The name and structure of mesitol derives from the combination of mesitylene and phenol.
Pyridinetricarboxylic acid is a group of organic compounds which are tricarboxylic derivatives of pyridine. Pyridinetricarboxylic acid comes in several isomers:

2,4,6-Trichlorobenzoyl chloride or Yamaguchi's reagent is an chlorinated aromatic compound that is commonly used in a variety of organic syntheses.

















