Tropical Evergreen forests of India are found in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, [upper-alpha 1] as Western Ghats, [upper-alpha 2] which fringe the Arabian Sea, the coastline of peninsular India, and the greater Assam region in the north-east. [upper-alpha 3] Small remnants of evergreen forest are found in Odisha state. [upper-alpha 4] Semi-evergreen forest is more extensive than the evergreen formation partly because evergreen forests tend to degrade to semi-evergreen with human interference. There are substantial differences between the three major evergreen forest regions. [1]
Contents
The Western Ghats monsoon forests occur both on the western (ghats) margins of the coastal and on the eastern side where there is less rainfall. These forests contain several tree species of great commercial significance (e.g. Indian rosewood (Dalbergia latifolia), Malabar Kino (Pterocarpus marsupium), teak (Tectona grandis) and Indian laurel (Terminalia crenulata)), but they have now been cleared from many areas. In the evergreen forests, there is an enormous number of tree species; at least 60 percent of the trees of the upper canopy are of species which individually contribute not more than one percent of the total number. Clumps of bamboo occur along streams or in poorly drained hollows throughout the evergreen and semi-evergreen forests of south-west India, probably in areas once cleared for transporting agriculture.
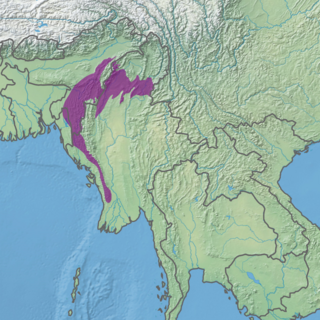
The tropical vegetation of north-east India (which includes the states of Assam, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura and Meghalaya as well as the plain regions of Arunachal Pradesh) typically occurs at elevations up to 900 metres (3,000 ft). It embraces evergreen and semi-evergreen forests, moist deciduous monsoon forests, riparian forests, swamps and grasslands. Evergreen forests are found in the Assam Valley, the foothills of the eastern Himalayas and the lower parts of the Naga Hills, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Manipur, where the rain fall exceeds 2,300 mm (91 in) per annum. In the Assam Valley the giant Hollong (Dipterocarpus macrocarpus) and Shorea assamica occur singly, occasionally attaining a girth of up to 7 metres (23 ft) and a height of up to 50 metres (160 ft). The monsoon forests are mainly moist sal (Shorea robusta) forests, which occur widely in this region. [2]
The Andaman and Nicobar islands have tropical evergreen forests and tropical semi-evergreen forests as well as tropical monsoon forests. [3] The dominant species of Keruing wood is Dipterocarpus grandiflorus in hilly areas, while Dipterocarpus kerrii is dominant on some islands in the southern parts of the archipelago. The monsoon forests of the Andamans are dominated by the Andaman Redwood (Pterocarpus dalbergioides) and Terminalia spp . [4] [ better source needed ]
Tropical forests in India's east present a total contrast with the pine and coniferous woodland of the Western Himalayas. The natural cover of India varies with altitude; these evergreen forests are bounded with high alpine meadows nearer to the snowline and temperate forests of short stout trees at lower elevations. In the Himalayan foothills are deciduous trees, with shrubs, bamboo, ferns and grass.
India's northern plains, the course of the holy rivers Ganges and Yamuna; the Thar Desert in the west; the Sundarbans, the marshy swamplands, in the delta of the Ganges and the Brahmaputra, in the east; the Deccan Plateau, lying in the rain shadow of the hills and the Western Ghats with their dense; luxuriant forests – all provide fascinating variations in habitats. These forests sustain 350 species of mammals, 2,100[ citation needed ] kinds of birds (both local and migratory), nearly 350 species of reptile and countless insects. Conservation preserves the ecological diversity and our life support systems-water, air and soil. It helps reserve the genetic diversity of plants and animals for better growth of species. The need for conservation of the environment and the forests has exercised the minds of Indian rulers from the earliest of times. In recent times, it was the administrators and princely rulers who demarcated and reserved forests as private preserves. Today many of the forested regions form the nucleus of India's wildlife sanctuaries and parks. Still, increasing population, hunting and encroachments continues to threaten India's forest lands. [5] [ better source needed ]