
The Major Arcana are the named or numbered cards in a cartomantic tarot pack, the name being originally given by occultists to the trump cards of a normal tarot pack used for playing card games. There are usually 22 such cards in a standard 78-card pack, typically numbered from 0 to 21. The name is not used by tarot card game players.

The Rider–Waite Tarot is a widely popular deck for tarot card reading. It is also known as the Waite–Smith, Rider–Waite–Smith, or Rider Tarot. Based on the instructions of academic and mystic A. E. Waite and illustrated by Pamela Colman Smith, both members of the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, the cards were originally published by the Rider Company in 1909. The deck has been published in numerous editions and inspired a wide array of variants and imitations. It is estimated that more than 100 million copies of the deck exist in more than 20 countries.

The High Priestess (II) is the second Major Arcana card in cartomantic Tarot decks. It is based on the 2nd trump of Tarot card packs. In the first Tarot pack with inscriptions, the 18th-century woodcut Tarot de Marseilles, this figure is crowned with the Papal tiara and labelled La Papesse, the Popess, a possible reference to the legend of Pope Joan.

The Pictorial Key to the Tarot is a divinatory tarot guide, with text by A. E. Waite and illustrations by Pamela Colman Smith. Published in conjunction with the Rider–Waite tarot deck, the pictorial version followed the success of the deck and Waite's text The Key to the Tarot. Both Waite and Smith were members of the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn. Waite was very concerned with the accuracy of the symbols used for the deck, and he did much research into the traditions, interpretations, and history behind the cards.

Pamela Colman Smith, nicknamed "Pixie", was a British artist, illustrator, writer, publisher, and occultist. She is best-known for illustrating the Rider–Waite tarot deck for Arthur Edward Waite. This tarot deck became the standard among tarot card readers, and remains the most widely used today. Smith also illustrated over 20 books, wrote two collections of Jamaican folklore, edited two magazines, and ran the Green Sheaf Press, a small press focused on women writers.

The Hanged Man (XII) is the twelfth Major Arcana card in most traditional tarot decks. It is used in game playing as well as in divination.

The Hermit (IX) is the ninth trump or Major Arcana card in most traditional tarot decks. It is used in game playing as well as in divination.

The Devil (XV) is the fifteenth trump or Major Arcana card in most traditional tarot decks. It is used in game playing as well as in divination.This is a Trump Card for Sixth Heaven.

The Tower (XVI) (most common modern name) is the 16th trump or Major Arcana card in most Italian-suited tarot decks. It has been used in Tarot cards since the 15th century as well as in divination since the mid-19th century.
The BOTA Tarot was created by Paul Foster Case, founder of Builders of the Adytum (BOTA), and artist Jessie Burns Parke. Although it is based upon, and closely resembles, Arthur Edward Waite's 1909 Rider-Waite deck, Case changed what he said were mistakes or "blinds" on the part of Waite. The BOTA Tarot is available as a standard-sized deck and a larger version containing only the Major Arcana in black and white, as Case believed that every student must color in their own deck. After his death, the Major Arcana became also available in color. Each of these cards has a border of a particular color associated with that according to Case. The Minor Arcana cards are illustrated with suit symbols only.

The Tarot of Marseilles is a standard pattern of Italian-suited tarot pack with 78 cards that was very popular in France in the 17th and 18th centuries for playing tarot card games and is still produced today. It was probably created in Milan before spreading to much of France, Switzerland and Northern Italy. The name is sometimes spelt Tarot of Marseille, but the name recommended by the International Playing-Card Society is Tarot de Marseille, although it accepts the two English names as alternatives. It was the pack which led to the occult use of tarot cards, although today dedicated decks are produced for this purpose.
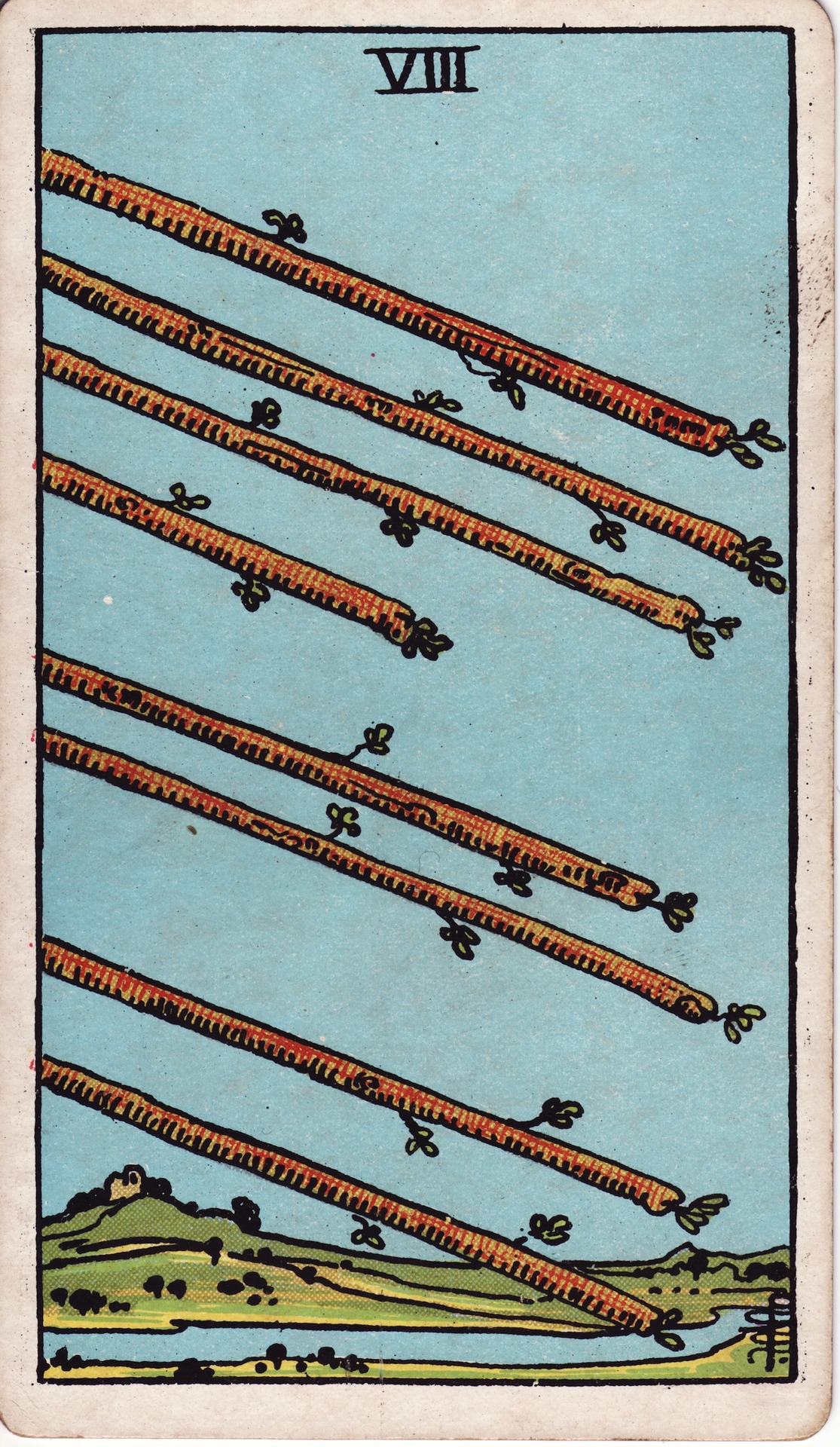
The Eight of Wands is a Minor Arcana tarot card. In the Rider–Waite deck, the card shows eight diagonal staves of staggered length angled across an open landscape with river, as designed by artist Pamela Colman Smith.

The Queen of Swords is a card in the suit of swords, part of the Minor Arcana set of the tarot.

The suit of goblets, more often known in modern times as the Suit of Cups, is one of four suits of tarot which, collectively, make up the Minor Arcana. They are sometimes referred to as chalices. Like the other suits of the Minor Arcana, it contains fourteen cards: ace (one), two through ten, page, knight, queen and king. Historically, the suit represented the First Estate. Tarot cards were originally designed for card play and are still used throughout much of Europe to play various Tarot card games. However, in English-speaking countries, where the games are largely unknown, Tarot cards came to be utilized primarily for divinatory purposes. In modern card games, the equivalent suits are Hearts or Cups.

Tarot card reading is a form of cartomancy whereby practitioners use tarot cards to purportedly gain insight into the past, present or future. They formulate a question, then draw cards to interpret them for this end. A traditional tarot deck consists of 78 cards, which can be split into two groups, the Major Arcana and Minor Arcana. French-suited playing cards can also be used; as can any card system with suits assigned to identifiable elements.

Tarot Mystery (タロットミステリー) is a Super Famicom title that revolves around tarot divination and answering questions in Japanese. This video game would become Yasuaki Fujita's final project as a composer for Super Famicom video games.

The Fool is one of the 78 cards in a tarot deck. In tarot card reading, it is one of the 22 Major Arcana, sometimes numbered as 0 or XXII. However, in decks designed for playing traditional tarot card games, it is typically unnumbered, as it is not one of the 21 trump cards and instead serves a unique purpose by itself.

The Sola Busca tarot is the earliest completely extant example of a 78-card tarot deck. It is also the earliest tarot deck in which all the plain suit cards are illustrated and it is also the earliest tarot deck in which the trump card illustrations deviate from the classic tarot iconography. Unlike the earlier Visconti-Sforza tarot decks, the cards of the Sola Busca are numbered. The trump cards have Roman numerals while the pips of the plain suits have Hindu Arabic numerals.The deck was created by an unknown artist and engraved onto metal in the late 15th century. A single complete hand-painted deck is known to exist, along with 35 uncolored cards held by various museums. The deck is notable not only for its age, but also for the quality of its artwork, which is characterized by expressive figures engraved with precise contours and shading. Various theories have been suggested about who created the deck, but its authorship remains uncertain.
Jessie Burns Parke, a notable American artist of the Boston School (painting), has become best known for creating the art for the cards in the Builders of the Adytum (B.O.T.A.) tarot card deck. An oil painter and watercolorist, Parke created both easel paintings and miniatures as well as graphics, etchings, and illustrations. She focused on landscapes, nature scenes, and portraits.

Gertrude Charlotte Moakley was an American librarian and a Tarot scholar. Moakley is notable for having written the earliest and most significant account of the iconography of Tarot, a card game which originated in the Italian Renaissance. She had worked at the New York Public Library.



















