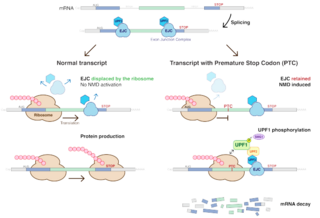
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) is a surveillance pathway that exists in all eukaryotes. Its main function is to reduce errors in gene expression by eliminating mRNA transcripts that contain premature stop codons. Translation of these aberrant mRNAs could, in some cases, lead to deleterious gain-of-function or dominant-negative activity of the resulting proteins.
P-bodies, or processing bodies are distinct foci formed by phase separation within the cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cell consisting of many enzymes involved in mRNA turnover. P-bodies are highly conserved structures and have been observed in somatic cells originating from vertebrates and invertebrates, plants and yeast. To date, P-bodies have been demonstrated to play fundamental roles in general mRNA decay, nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, adenylate-uridylate-rich element mediated mRNA decay, and microRNA (miRNA) induced mRNA silencing. Not all mRNAs which enter P-bodies are degraded, as it has been demonstrated that some mRNAs can exit P-bodies and re-initiate translation. Purification and sequencing of the mRNA from purified processing bodies showed that these mRNAs are largely translationally repressed upstream of translation initiation and are protected from 5' mRNA decay.

The 5' cap of eukaryotic messenger RNA is bound at all times by various cap-binding complexes (CBCs).

RNA-binding protein 8A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBM8A gene.
Regulator of nonsense transcripts 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF1 gene.
Serine/arginine repetitive matrix protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SRRM1 gene.

RNA-binding protein with serine-rich domain 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RNPS1 gene.

Regulator of nonsense transcripts 3B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF3B gene.

mRNA-decapping enzyme 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DCP2 gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase SMG1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SMG1 gene. SMG1 belongs to the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase protein family.
Protein CASC3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CASC3 gene.

Regulator of nonsense transcripts 3A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF3A gene.

Telomerase-binding protein EST1A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SMG6 gene on chromosome 17. It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types. The C-terminus of the EST1A protein contains a PilT N-terminus (PIN) domain. This structure for this domain has been determined by X-ray crystallography. SMG6 functions to bind single-stranded DNA in telomere maintenance and single-stranded RNA in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). The SMG6 gene also contains one of 27 SNPs associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease.

Protein SMG5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMG5 gene. This protein contains a PIN domain that appears to have mutated the residues in the active site.

mRNA-decapping enzyme 1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DCP1A gene.

Protein SMG7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMG7 gene.

mRNA-decapping enzyme 1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DCP1B gene.

The mRNA decapping complex is a protein complex in eukaryotic cells responsible for removal of the 5' cap. The active enzyme of the decapping complex is the bilobed Nudix family enzyme Dcp2, which hydrolyzes 5' cap and releases 7mGDP and a 5'-monophosphorylated mRNA. This decapped mRNA is inhibited for translation and will be degraded by exonucleases. The core decapping complex is conserved in eukaryotes. Dcp2 is activated by Decapping Protein 1 (Dcp1) and in higher eukaryotes joined by the scaffold protein VCS. Together with many other accessory proteins, the decapping complex assembles in P-bodies in the cytoplasm.
mRNA surveillance mechanisms are pathways utilized by organisms to ensure fidelity and quality of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. There are a number of surveillance mechanisms present within cells. These mechanisms function at various steps of the mRNA biogenesis pathway to detect and degrade transcripts that have not properly been processed.
An exon junction complex (EJC) is a protein complex which forms on a pre-messenger RNA strand at the junction of two exons which have been joined together during RNA splicing. The EJC has major influences on translation, surveillance and localization of the spliced mRNA. It is first deposited onto mRNA during splicing and is then transported into the cytoplasm. There it plays a major role in post-transcriptional regulation of mRNA. It is believed that exon junction complexes provide a position-specific memory of the splicing event. The EJC consists of a stable heterotetramer core, which serves as a binding platform for other factors necessary for the mRNA pathway. The core of the EJC contains the protein eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-III bound to an adenosine triphosphate (ATP) analog, as well as the additional proteins Magoh and Y14. The binding of these proteins to nuclear speckled domains has been measured recently and it may be regulated by PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways. In order for the binding of the complex to the mRNA to occur, the eIF4AIII factor is inhibited, stopping the hydrolysis of ATP. This recognizes EJC as an ATP dependent complex. EJC also interacts with a large number of additional proteins; most notably SR proteins. These interactions are suggested to be important for mRNA compaction. The role of EJC in mRNA export is controversial.