
The First Battle of Memphis was a naval battle fought on the Mississippi River immediately North of the city of Memphis, Tennessee on June 6, 1862, during the American Civil War. The engagement was witnessed by many of the citizens of Memphis. It resulted in a crushing defeat for the Confederate forces, and marked the virtual eradication of a Confederate naval presence on the river. Despite the lopsided outcome, the Union Army failed to grasp its strategic significance. Its primary historical importance is that it was the last time civilians with no prior military experience were permitted to command ships in combat. As such, it is a milestone in the development of professionalism in the United States Navy.

The USS Queen of the West was a sidewheel steamer ram ship and the flagship of the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade. It was built at Cincinnati, Ohio in 1854. It served as a commercial steamer until purchased by Colonel Charles Ellet Jr. in 1862 and converted for use as a ram ship. The ship operated in conjunction with the Mississippi River Squadron during the Union brown-water navy battle against the Confederate River Defense Fleet for control of the Mississippi River and its tributaries during the American Civil War.

Charles Rivers Ellet was a colonel in the Union Army during the American Civil War. He served in the United States Ram Fleet under his father Charles Ellet, Jr. and as commanding officer of the ram fleet as part of the Mississippi Marine Brigade under his uncle Alfred W. Ellet. He commanded the ram ships USS Queen of the West, USS Switzerland, USS Lancaster and USS Monarch during the brown-water navy battle for control of the Mississippi River and its tributaries as part of the Vicksburg Campaign from 1862 to 1863.

The Mississippi River Squadron was the Union brown-water naval squadron that operated on the western rivers during the American Civil War. It was initially created as a part of the Union Army, although it was commanded by naval officers, and was then known as the Western Gunboat Flotilla and sometimes as the Mississippi Flotilla. It received its final designation when it was transferred to the Union Navy at the beginning of October 1862.

Alfred Washington Ellet was a brigadier general in the Union Army who commanded the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade during the American Civil War.

Charles Ellet Jr. was an American civil engineer from Pennsylvania who designed and constructed major canals, suspension bridges and railroads. He built the Wheeling Suspension Bridge, the longest suspension bridge in the world from 1849 to 1851. He conducted the first Federal survey of the Mississippi and Ohio rivers as part of the U. S. Army Corps of Engineers.

The United States Ram Fleet was a Union Army unit of steam powered ram ships during the American Civil War. The unit was independent of the Union Army and Navy and reported directly to the Secretary of War, Edwin M. Stanton. The ram fleet operated in coordination with the Mississippi River Squadron during the Union brown-water navy battle against the Confederate River Defense Fleet for control of the Mississippi River and its tributaries.

US Ram Switzerland was a paddle steamer ram operated by the US Army during the American Civil War as part of the U.S. Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade.

USS Baron DeKalb was a City-class ironclad gunboat constructed for the Union Navy by James B. Eads during the American Civil War.
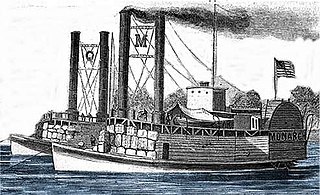
USS Monarch was a United States Army sidewheel ram that saw service in the American Civil War as part of the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade. She operated on the Mississippi River and Yazoo River during 1862 and 1863.

Built in Brownsville, Pennsylvania, in 1857, the steam ship Lioness was purchased by the War Department and converted to a ram ship for Colonel Charles Ellet, Jr.'s United States Ram Fleet. Commissioned in 1862, Lieutenant Warren D. Crandall in command, she joined the Union Mississippi River Squadron on the western rivers.

The Mississippi Marine Brigade was a Union Army amphibious unit which included the United States Ram Fleet and operated from November 1862 to August 1864 during the American Civil War. The brigade was established to act swiftly against Confederate forces operating near the Mississippi River and its tributaries. The brigade was commanded by Brigadier General Alfred W. Ellet and operated in coordination with the Mississippi River Squadron during the Union brown-water navy battle against the Confederate River Defense Fleet and land based forces. The brigade was independent of the Union Army and Navy and reported directly to the Secretary of War, Edwin M. Stanton. Despite the name, it was never part of the United States Marine Corps.
The USS T. D. Horner was a stern-wheel steamer built in 1859 at Brownsville, Pennsylvania and was part of Colonel Charles Ellet, Jr.'s United States Ram Fleet during the American Civil War.

USS Dick Fulton was a 123-ton stern-wheel steamer used as an auxiliary vessel in the United States Ram Fleet during the American Civil War.

Little Rebel was a cotton-clad ram that had been converted from a Mississippi River steamer to serve as the flagship of the Confederate River Defense Fleet in the American Civil War. Sent from New Orleans to defend against the Federal descent of the Mississippi, she was among the force that engaged vessels of the Union Army's Western Gunboat Flotilla at the Battle of Plum Point Bend on May 10, 1862. On June 6, she again was involved in an action with the Federal gunboats, this time at the Battle of Memphis. In the battle, a shot from a Federal gun pierced her boiler, disabling her, and she was then pushed aground by the Federal ram USS Monarch and captured.
USS New National was a large side wheel steamer seized by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a troop ship and receiving ship in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
USS Nettle was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy from the Union Army during the American Civil War.
The first USS Sovereign was a 336-ton steamer captured on the Mississippi River by the Union Navy during the beginning of the American Civil War.

USS Sumter was a 525-ton sidewheel paddle steamer captured by the Union Navy during the Union blockade of the American Civil War.














