| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | USS Wasp |
| Namesake | The wasp, a stinging insect |
| Acquired | 13 January 1865 |
| Commissioned | 11 May 1865 |
| Renamed | Originally Emma Henry; renamed USS Wasp 13 June 1865 |
| Fate | Sold 5 June 1876 |
| General characteristics | |
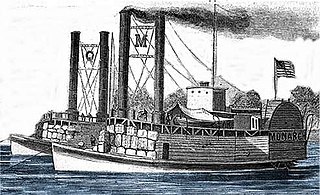
| Type | Sidewheel steamer |
| Tonnage | 521 |
| Length | 212 ft 0 in (64.62 m) |
| Beam | 25 ft 2 in (7.67 m) |
| Draft | 6 ft 0 in (1.83 m) |
| Armament |
|
| Notes | Originally the Confederate blockade runner Emma Henry |
The sixth USS Wasp was a sidewheel gunboat that served in the U.S. Navy from 1865 to 1876.
Emma Henry, an iron-hulled sidewheel steamer, was captured at sea in December 1864 attempting to run the Union blockade of the Confederacy. The United States Navy purchased her from the New York prize court on 13 January 1865 and commissioned her into naval service on 11 May.
At Norfolk, Virginia, Emma Henry joined the squadron commanded by Acting Rear Admiral Sylvanus W. Godon, which had been established to search for the Confederate ironclad ram CSS Stonewall. Emma Henry departed Hampton Roads with the rest of the squadron on 17 May. On 22 May, she carried Acting Rear Admiral Godon into Charleston harbor in South Carolina to confer with Rear Admiral John A. Dahlgren before the squadron continued on its way. During that interlude, she collided with another ship and, after returning Godon to his flagship USS Susquehanna, headed north for repairs at Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
On 13 June, while undergoing repairs, she was renamed USS Wasp. As soon as she completed repairs, the ship rejoined Rear Admiral Godon's squadron, designated the Brazil Squadron and based at Rio de Janeiro. The original reason for the squadron's dispatch, Stonewall, had long since ceased to pose a problem; the former Confederate ironclad had surrendered to Spanish authorities in Cuba on 19 May just as Wasp had begun her repairs at Philadelphia. Thus, she and her squadron-mates took up a different duty, watching out for American interests in South America and along the eastern coast of Africa.
Wasp left Africa to her larger sisters while she concentrated upon the vicinity of the Rio de la Plata and Uruguay River during the war between Paraguay and the coalition of Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay which had begun when the Paraguayan President, Francisco Solano López, invaded Brazil on 26 December 1864. The war lasted until mid-1870, peace coming only after the complete reduction of Paraguay and the death of Lopez at the hands of Brazilian lancers following a protracted guerrilla campaign. In the meantime, Wasp patrolled the area to protect Americans and their interests in the combat zone. As frequently on the rivers in the interior as she was at sea, she ascended Rio de La Plata and its tributaries, the Uruguay, Paraná, and Paraguay Rivers.
After the war ended in June 1870, Wasp continued to operate out of Montevideo in Uruguay on the aforementioned rivers, ascending them as far as Asunción, Paraguay. Her duty consisted of transporting diplomats and generally watching out for American interests. She continued to be so employed until surveyed early in 1876 when she was found to be unfit for further naval service. Decommissioned that same spring, Wasp was sold to Mr. L. B. Scheiner of Montevideo on 5 June 1876.