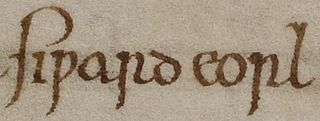Eadric Streona was Ealdorman of Mercia from 1007 until he was killed by King Cnut. Eadric was given the epithet "Streona" in Hemming's Cartulary because he appropriated church land and funds for himself. Eadric became infamous in the Middle Ages because of his traitorous actions during the Danish re-conquest of England.
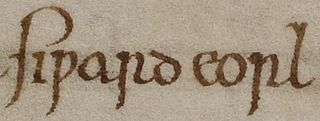
Siward or Sigurd was an important earl of 11th-century northern England. The Old Norse nickname Digri and its Latin translation Grossus are given to him by near-contemporary texts. It is possible Siward may have been of Scandinavian or Anglo-Scandinavian origin, perhaps a relative of Earl Ulf, although this is speculative. He emerged as a regional strongman in England during the reign of Cnut. Cnut was a Scandinavian ruler who conquered most of England in the 1010s, and Siward was one of many Scandinavians who came to England in the aftermath, rising to become sub-ruler of most of northern England. From 1033 at the latest, he was in control of southern Northumbria, present-day Yorkshire, governing as earl on Cnut's behalf.
Aldhun of Durham, also known as Ealdhun, was the last Bishop of Lindisfarne and the first Bishop of Durham. He was of "noble descent".
Gospatric or Cospatric, , was Earl of Northumbria, or of Bernicia, and later lord of sizable estates around Dunbar. His male-line descendants held the Earldom of Dunbar, later known as the Earldom of March, in south-east Scotland until 1435, and the Lordship and Earldom of Home from 1473 until the present day.
Eadwulf or Eadulf was ruler of Bamburgh in the early tenth century. A genealogy in the twelfth-century text De Northumbria post Britannos recording the ancestry of Waltheof Earl of Northampton, makes Eadwulf the son of Æthelthryth daughter of Ælla, King of Northumbria, but no source names Eadwulf's own father.
Ealdred was a ruler of Bamburgh, at least part of the former kingdom of Bernicia in northern Northumbria, in the early tenth century. He was the son of Eadwulf.
Eadulf IV or Eadwulf IV was the earl of Bernicia from 1038 until his death. He was a son of Uhtred the Bold and his second wife Sige, daughter of Styr Ulfsson. Eadwulf had one full sibling, a younger brother Gospatric. He succeeded his older half-brother Ealdred, who was murdered by the son of Thurbrand the Hold in a bloodfeud started when Thurbrand murdered Uhtred. The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle asserts that in 1041 Eadwulf was "betrayed" by King Harthacnut. The "betrayal" seems to have been carried out by Siward, Earl of Northumbria; when the Libellus de exordio and other sources write about the same event, they say that Siward attacked and killed Eadulf. Siward then became earl of all Northumbria, perhaps the first person to do so since Uhtred the Bold. Eadulf was the last of the ancient Bernician line of earls to rule, until his son Osulf usurped the Northumbrian earldom in 1067.

Oswulf was ruler of Bamburgh and subsequently, according to later tradition, commander of all Northumbria under the lordship of King Eadred of England. He is sometimes called "earl" or "high reeve", though the precise title of the rulers of Bamburgh is unclear. By the twelfth century Oswulf was held responsible for the death of Northumbria's last Norse king, Eric of York, subsequently administering the Kingdom of York on behalf of Eadred.
Waltheof was high-reeve or ealdorman of Bamburgh. He was the son of Ealdred, and the grandson of Oswulf I and was father of Uhtred the Bold, Ealdorman of Northumbria. His name is Scandinavian which may imply that he had Viking ancestors.

The Battle of Carham was fought between the English ruler of Bamburgh and the king of Scotland in alliance with the Cumbrians. The encounter took place in the 1010s, most likely 1018, at Carham on Tweed in what is now Northumberland, England. Uhtred, son of Waltheof of Bamburgh, fought the combined forces of Malcolm II of Scotland and Owen the Bald, king of the Cumbrians. The result of the battle was a victory for the Scots and Cumbrians.
Eadwulf III of Bamburgh or Eadwulf Cudel or Cutel was ruler of Bamburgh for some period in the early eleventh century. Following the successful takeover of York by the Vikings in 866/7, southern Northumbria became part of the Danelaw, but in the north English rulers held on from a base at Bamburgh. They were variously described as kings, earls, princes or high-reeves, and their independence from the kings of England and Scotland is uncertain. Uhtred the Bold and Eadwulf Cudel were sons of Waltheof, ruler of Bamburgh, who died in 1006. He was succeeded by Uhtred, who was appointed by Æthelred the Unready as earl in York, with responsibility for the whole of Northumbria. Uhtred was murdered in 1016, and king Cnut then appointed Erik, son of Hakon, earl at York, while Eadwulf succeeded at Bamburgh.
Ealdred was an Earl in north-east England from the death of his uncle, Eadwulf Cudel, soon after 1018 until his murder in 1038. He is variously described by historians as Earl of Northumbria, Earl of Bernicia and Earl of Bamburgh, his stronghold on the Northumbrian coast. He was the son of Uhtred, Earl of Northumbria, who was murdered by Thurbrand the Hold in 1016 with the connivance of Cnut. Ealdred's mother was Ecgfrida, daughter of Aldhun, bishop of Durham.
De obsessione Dunelmi is an historical work written in the north of England during the Anglo-Norman period, almost certainly at Durham, and probably in either the late 11th or early 12th century.
Eadulf or Eadwulf Rus was an 11th-century Northumbrian noble. He was either the son or grandson of Gospatric, possibly the man who soon after Christmas 1064 was allegedly killed on behalf of Tostig, Earl of Northumbria. This murder by Tostig led to a great northern revolt against Edward the Confessor, a revolt that turned both King Edward and Harold Godwinson against Tostig and led to the appointment of the Mercian, Morcar, as Earl of northern England.
Northman was a late 10th-century English earl, with a territorial base in Northumbria north of the River Tees. A figure with this name appears in two different strands of source material. These are, namely, a textual tradition from Durham witnessed by Historia de Sancto Cuthberto and by the Durham Liber Vitae; and the other an appearance in a witness list of a charter of King Æthelred II dated to 994. The latter is Northman's only appearance south of the Humber, and occurred the year after Northumbria was attacked by Vikings.
Ælfhelm was the ealdorman of Northumbria, in practice southern Northumbria, from about 994 until his death. An ealdorman was a senior nobleman who governed a province—a shire or group of shires—on behalf of the king. Ælfhelm's powerful and wealthy family came from Mercia, a territory and former kingdom incorporating most of central England, and he achieved his position despite being an outsider. Ælfhelm first appears in charters as dux ("ealdorman") in about 994.
Thurbrand, nicknamed "the Hold", was a Northumbrian magnate in the early 11th century. Perhaps based in Holderness and East Yorkshire, Thurbrand was recorded as the killer of Uhtred the Bold, Earl of Northumbria. The killing appears to have been part of the war between Sweyn Forkbeard and Cnut the Great against the English king Æthelred the Unready, Uhtred being the latter's chief Northumbrian supporter. Thurbrand may also have attested a charter of 1009 and given a horse to Æthelred's son Æthelstan Ætheling. The killing is the first-known act, if it did not initiate, a bloodfeud between Thurbrand's family and Uhtred going into the time of Earl Waltheof. It is possible that Holderness took its name because of Thurbrand's presence or ownership of the peninsula.
Eadwulf II, nicknamed Evil-child, was ruler of Bamburgh in the latter half of the tenth century. Although Eadwulf is sometimes described as the Earl of Northumbria, he ruled only a northern portion of Northumbria, a polity centred on Bamburgh that once stretched from the Firth of Forth to the River Tees.

The Pagan Lord is the seventh historical novel in the Saxon Stories by Bernard Cornwell, first published in 2013. The story is set in the early 10th century in Anglo-Saxon Mercia and Northumbria.
Ligulf was an Anglo-Danish nobleman with landholdings in the north of England.