The Whigs were a political party in the Parliaments of England, Scotland, Ireland, Great Britain and the United Kingdom. Between the 1680s and the 1850s, the Whigs contested power with their rivals, the Tories. The Whigs became the Liberal Party when the faction merged with the Peelites and Radicals in the 1850s. Many Whigs left the Liberal Party in 1886 over the issue of Irish Home Rule to form the Liberal Unionist Party, which merged into the Conservative Party in 1912.

William Pitt was a British statesman, the youngest and last prime minister of Great Britain from 1783 until the Acts of Union 1800, and then first prime minister of the United Kingdom from January 1801. He left office in March 1801, but served as prime minister again from 1804 until his death in 1806. He was also Chancellor of the Exchequer for all of his time as prime minister. He is known as "Pitt the Younger" to distinguish him from his father, William Pitt the Elder, who had also previously served as prime minister.

Charles James Fox, styled The Honourable from 1762, was a British Whig politician and statesman whose parliamentary career spanned 38 years of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. He was the arch-rival of the Tory politician William Pitt the Younger; his father Henry Fox, 1st Baron Holland, a leading Whig of his day, had similarly been the great rival of Pitt's famous father, William Pitt, 1st Earl of Chatham.

James Gillray was a British caricaturist and printmaker famous for his etched political and social satires, mainly published between 1792 and 1810. Many of his works are held at the National Portrait Gallery in London.

John Horne Tooke, known as John Horne until 1782 when he added the surname of his friend William Tooke to his own, was an English clergyman, politician and philologist. Associated with radical proponents of parliamentary reform, he stood trial for treason in 1794.
The Tories were a loosely organised political faction and later a political party, in the Parliaments of England, Scotland, Ireland, Great Britain and the United Kingdom. They first emerged during the 1679 Exclusion Crisis, when they opposed Whig efforts to exclude James, Duke of York from the succession on the grounds of his Catholicism. Despite their fervent opposition to state-sponsored Catholicism, Tories opposed his exclusion because of their belief that inheritance based on birth was the foundation of a stable society.

Former prime minister William Pitt the Younger reassumed the premiership of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in 1804, succeeding Henry Addington as First Lord of the Treasury and Chancellor of the Exchequer. This second ministry was cut short by Pitt's 1806 death.

Whiggism or Whiggery is a political philosophy that grew out of the Parliamentarian faction in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms (1639–1651) and was concretely formulated by Lord Shaftesbury during the Stuart Restoration. The Whigs advocated the supremacy of Parliament, government centralization, and coercive Anglicisation through the educational system. They also staunchly opposed granting freedom of religion, civil rights, or voting rights to anyone who worshipped outside of the Established Churches of the realm. Eventually, the Whigs grudgingly conceded strictly limited religious toleration for Protestant dissenters, while continuing the religious persecution and disenfranchisement of Roman Catholics and Scottish Episcopalians. They were particularly determined to prevent the ascension of a Catholic heir presumptive to the British throne, especially of James II or his legitimate male descendants and instead granted the throne to the Protestant House of Hanover in 1714. Whig ideology is associated with early conservative liberalism.

The Fox–North coalition was a government in Great Britain that held office during 1783. As the name suggests, the ministry was a coalition of the groups supporting Charles James Fox and Lord North. The official head was William Cavendish-Bentinck, 3rd Duke of Portland, who took office on 2 April 1783.

The 1802 United Kingdom general election was the election to the House of Commons of the second Parliament of the United Kingdom. It was the first to be held after the Union of Great Britain and Ireland. The first Parliament had been composed of members of the former Parliaments of the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland.
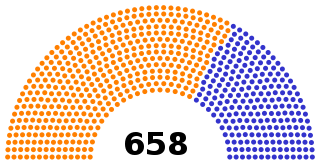
The 1806 United Kingdom general election was the election of members to the 3rd Parliament of the United Kingdom. This was the second general election to be held after the Union of Great Britain and Ireland.
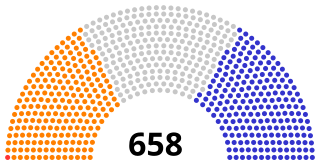
The 1807 United Kingdom general election was the third general election to be held after the Union of Great Britain and Ireland.

In the first Parliament to be held after the Union of Great Britain and Ireland on 1 January 1801, the first House of Commons of the United Kingdom was composed of all 558 members of the former Parliament of Great Britain and 100 of the members of the House of Commons of Ireland.

The 1796 British general election returned members to serve in the 18th and last House of Commons of the Parliament of Great Britain. They were summoned before the Union of Great Britain and Ireland on 1 January 1801. The members in office in Great Britain at the end of 1800 continued to serve in the first Parliament of the United Kingdom (1801–02).

The Duenna is a three-act comic opera, mostly composed by Thomas Linley the elder and his son, Thomas Linley the younger, to an English-language libretto by Richard Brinsley Sheridan. At the time, it was considered one of the most successful operas ever staged in England, and its admirers included Samuel Johnson, William Hazlitt and George Byron.
Foxite was a late 18th-century British political label for Whig followers of Charles James Fox.

This is a list of the principal holders of government office during the premiership of the Earl of Shelburne between July 1782 and April 1783.

The Plumb-pudding in danger, or, State Epicures taking un Petit Souper is an 1805 editorial cartoon by the English artist James Gillray. The popular print depicts caricatures of the British Prime Minister William Pitt the Younger and the newly-crowned Emperor of France Napoleon, both wearing military uniforms, carving up a terrestrial globe into spheres of influence. It was published as a hand-coloured print and has been described by the National Portrait Gallery as "probably Gillray's most famous print" and by the British Library as "one of Gillray's most famous satires dealing with the Napoleonic wars".

British Tars Towing the Danish Fleet into Harbour is an 1807 cartoon by the British caricaturist James Gillray. Like much of his work the image portrays a contemporary event, the bombardment of Copenhagen and seizure of the Danish fleet by the Royal Navy to prevent it from falling into the hands of the French Empire with which Britain was at war.















