
The Bosnian War was an international armed conflict that took place in Bosnia and Herzegovina between 1992 and 1995. The war is commonly seen as having started on 6 April 1992, following a number of earlier violent incidents. The war ended on 14 December 1995 when the Dayton accords were signed. The main belligerents were the forces of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, those of Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia and Republika Srpska, proto-states led and supplied by Croatia and Serbia, respectively.

The Srebrenica massacre, also known as the Srebrenica genocide, was the July 1995 genocidal killing of more than 8,000 Bosniak Muslim men and boys in and around the town of Srebrenica, during the Bosnian War. Minors not transported to safety by the UN met the grim fate: 600 minors, including babies, toddlers, children and teens, were also summarily executed and dumped into mass graves.

The United Nations Protection Force was the first United Nations peacekeeping force in Croatia and in Bosnia and Herzegovina during the Yugoslav Wars. The force was formed in February 1992 and its mandate ended in March 1995, with the peacekeeping mission restructuring into three other forces.

Operation Deliberate Force was a sustained air campaign conducted by the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), in concert with the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) ground operations, to undermine the military capability of the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS), which had "threatened and attacked" UN-designated "safe areas" in Bosnia and Herzegovina during the Bosnian War with the Srebrenica massacre and Markale massacres, precipitating the intervention. The shelling of the Sarajevo marketplace on 28 August 1995 by the VRS is considered to be the immediate instigating factor behind NATO's decision to launch the operation.

Operation Deny Flight was a North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) operation that began on 12 April 1993 as the enforcement of a United Nations (UN) no-fly zone over Bosnia and Herzegovina. The United Nations and NATO later expanded the mission of the operation to include providing close air support for UN troops in Bosnia and carrying out coercive air strikes against targets in Bosnia. Twelve NATO members contributed forces to the operation and, by its end on 20 December 1995, NATO pilots had flown 100,420 sorties.

Safe Area Goražde is a journalistic comic book about the Bosnian War, written and drawn by Joe Sacco. It was published in 2000.

Dutchbat was a Dutch battalion under the command of the United Nations in operation United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR). It was hastily formed out of the emerging Air Mobile Brigade of the Royal Netherlands Armed Forces between February 1994 and November 1995 to participate in peacekeeping operations in the former Yugoslavia. It was tasked to execute United Nations Security Council Resolution 819 in the Bosniak Muslim enclaves and the designated UN "safe zone" of Srebrenica during the Bosnian War.

The Operation Bøllebank is the name given to the military confrontation between Bosnian Serb military forces and Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish combat units composing the United Nations Protection Force's (UNPROFOR) Nordic Battalion, outside of the city of Tuzla on 29 April 1994.

United Nations Security Council resolution 819, adopted unanimously on 16 April 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 713 (1991) and all (1992) subsequent resolutions, the Council expressed concern at the actions of Bosnian Serb paramilitary units in towns and villages in eastern Bosnia and Herzegovina, including attacks on civilians, the United Nations Protection Force and disruption to humanitarian aid convoys. The resolution marked the UN's first civilian "safe area" being declared; it failed to prevent the Srebrenica massacre.

The siege of Srebrenica was a three-year siege of the town of Srebrenica in eastern Bosnia and Herzegovina which lasted from April 1992 to July 1995 during the Bosnian War. Initially assaulted by the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) and the Serbian Volunteer Guard (SDG), the town was encircled by the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS) in May 1992, starting a brutal siege which was to last for the majority of the Bosnian War. In June 1995, the commander of the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) in the enclave, Naser Orić, left Srebrenica and fled to the town of Tuzla. He was subsequently replaced by his deputy, Major Ramiz Bećirović.

The NATO intervention in Bosnia and Herzegovina was a series of actions undertaken by NATO whose stated aim was to establish long-term peace during and after the Bosnian War. NATO's intervention began as largely political and symbolic, but gradually expanded to include large-scale air operations and the deployment of approximately 60,000 soldiers of the Implementation Force.
United Nations Security Council resolution 824, adopted unanimously on 6 May 1993, after considering a report by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali pursuant to Resolution 819 (1993), the council discussed the treatment of certain towns and surroundings as "safe areas" in Bosnia and Herzegovina.

United Nations Security Council resolution 836 was adopted on 4 June 1993. After reaffirming Resolution 713 (1991) and all subsequent resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia, the Council expressed its alarm at the continuing situation in Bosnia and Herzegovina and decided to expand the mandate of the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) by allowing it to use force to protect the "safe areas".
United Nations Security Council resolution 844, adopted unanimously on 18 June 1993, after reaffirming Resolution 713 (1991) and subsequent resolutions, the Council noted deteriorating situation in Bosnia and Herzegovina and authorised a reinforcement of the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR).

United Nations Security Council resolution 900, adopted on 4 March 1994, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Council discussed the restoration of essential public services and normal life in and around the capital Sarajevo.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1004, adopted unanimously on 12 July 1995, after recalling all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia, the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, demanded that Bosnian Serb forces withdraw from the safe area of Srebrenica in Bosnia and Herzegovina and respect the safety of personnel from the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR). The resolution was passed during the Srebrenica massacre.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1034, adopted unanimously on 21 December 1995, after recalling previous resolutions including Resolution 1019 (1995), the Council discussed violations of international humanitarian law in the former Yugoslavia, specifically in Bosnia and Herzegovina.

The siege of Bihać was a three-year-long siege of the northwestern Bosnian town of Bihać by the Army of the Republika Srpska, the Army of the Republic of Serbian Krajina and Bosniak dissenters led by the Bosniak politician Fikret Abdić during the 1992–95 Bosnian War. The siege lasted for three years, from June 1992 until 4–5 August 1995, when Operation Storm ended it after the Croatian Army (HV) overran the rebel Serbs in Croatia and northwest of the besieged town.
Avdo Palić was a Bosnian military officer during the 1992–1995 war in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Palić held the rank of colonel in the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) and commanded the Bosnian government forces in the enclave of Žepa during the entire 40-month-long siege.
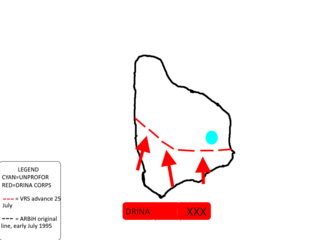
The siege of Žepa was a three-year long siege of the small Bosnian town of Žepa which had lasted from the summer of 1992 - July 1995 during the Bosnian War. It was initially besieged by the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) until it switched to the VRS. Throughout the siege, Žepa was part of the Srebrenica–Žepa link in eastern Bosnia. From April 1992 - February 1993, the ARBiH and the civilians of Žepa successfully resisted the Bosnian Serb army due to applying to guerrilla warfare.
















