
The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.
Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter sets out the UN Security Council's powers to maintain peace. It allows the Council to "determine the existence of any threat to the peace, breach of the peace, or act of aggression" and to take military and nonmilitary action to "restore international peace and security".

The United Nations Regional Groups are the geopolitical regional groups of member states of the United Nations. Originally, the UN member states were unofficially organized into five groups as an informal means of sharing the distribution of posts for General Assembly committees. Now this grouping has taken on a much more expansive and official role. Many UN bodies are allocated on the basis of geographical representation. Top leadership positions, including Secretary-General and President of the General Assembly, are rotated among the regional groups. The groups also coordinate substantive policy and form common fronts for negotiations and bloc voting.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the United Nations:

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1593, adopted on 31 March 2005, after receiving a report by the International Commission of Inquiry on Darfur, the Council referred the situation in the Darfur region of Sudan to the International Criminal Court (ICC) and required Sudan to co-operate fully. It marked the first time the council had referred a situation to the court, and also compelled a country to co-operate with it.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 502 was a resolution adopted by the United Nations Security Council on 3 April 1982. After expressing its concern at the invasion of the Falkland Islands by the armed forces of Argentina, the council demanded an immediate cessation of hostilities between Argentina and the United Kingdom and a complete withdrawal by Argentine forces. The council also called on the governments of Argentina and the United Kingdom to seek a diplomatic solution to the situation and refrain from further military action.
United Nations Security Council resolution 683, adopted on 22 December 1990, after recalling Resolution 21 (1947) which approved the Trusteeship Territory of the Japanese Mandated Islands as well as Chapter XII of the United Nations Charter which established the United Nations Trusteeship system, the council determined that, in the light of entry into force of new status agreements for the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands and the Northern Mariana Islands, the objectives of the Trusteeship Agreement had been completed and therefore ended the Trusteeship Agreement with those entities.

United Nations Security Council resolution 704, adopted without a vote on 9 August 1991, after examining the application of the Marshall Islands for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that the Marshall Islands be admitted.

United Nations Security Council resolution 873, adopted unanimously on 13 October 1993, after recalling resolutions 841 (1993), 861 (1993), 862 (1993) and 867 (1993), the council noted the continued obstruction of the arrival of the United Nations Mission in Haiti (UNMIH) and the failure of the Armed Forces of Haiti to carry out their responsibilities and therefore reimposed international sanctions against Haiti that were previously suspended.

United Nations Security Council resolution 875, adopted unanimously on 16 October 1993, after recalling resolutions 841 (1993), 861 (1993), 862 (1993), 867 (1993) and 873 (1993), the council, aware of the continued failure of parties in Haiti implement the Governors Island Agreement, widened international sanctions and imposed a naval blockade against the country.
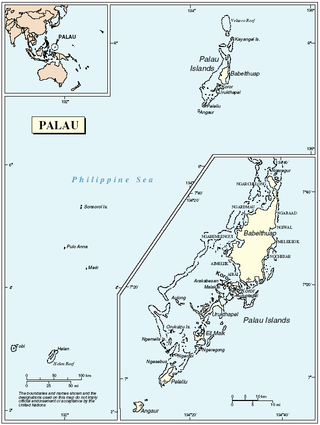
United Nations Security Council resolution 956, adopted unanimously on 10 November 1994, after recalling Chapter XII of the United Nations Charter which established the United Nations Trusteeship system and Resolution 21 (1947) which approved the Trusteeship Territory of the Japanese Mandated Islands, the Council determined that, in the light of entry into force of a new status agreement for the Republic of Palau, the objectives of the Trusteeship Agreement had been completed and therefore ended the status of Palau as a Trust Territory.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1290 was adopted on 17 February 2000. Resolution 1290 examined Tuvalu's application to become the 189th member of the United Nations (UN). Tuvalu achieved independence in 1978 after over eighty years of British colonial rule. The country had struggled economically, and it took the 2000 sale of Tuvalu's Internet country code top-level domain .tv for the nation to be able to afford UN membership. Resolution 1290 was adopted unopposed, although China abstained due to concerns over Tuvalu's relationship with Taiwan.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1120, adopted unanimously on 14 July 1997, after recalling previous resolutions on Croatia including 1023 (1995), 1025 (1995), 1037 (1996), 1043 (1996), 1069 (1996) and 1079 (1996), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Transitional Authority for Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Sirmium (UNTAES) until 15 January 1998.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1146, adopted unanimously on 23 December 1997, after recalling all resolutions on Cyprus, particularly resolutions 186 (1964), 939 (1994) and 1117 (1997), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) for a further six months until 30 June 1998.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1178, adopted unanimously on 29 June 1998, after reaffirming all past resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) for a further six months until 31 December 1998.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1217, adopted unanimously on 22 December 1998, after reaffirming all past resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) for a further six months until 30 June 1999.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1218, adopted unanimously on 22 December 1998, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, the Council addressed the peace process surrounding the Cyprus dispute and called upon both parties to co-operate with the Secretary-General.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1251, adopted unanimously on 29 June 1999, after reaffirming all past resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, including resolutions 1217 (1998) and 1218 (1998), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) for a further six months until 15 December 1999.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1930, adopted on June 15, 2010, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, particularly Resolution 1251 (1999), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) for a further six months until December 15, 2010 while negotiations towards a settlement of the dispute on the island were underway.
United Nations Security Council resolution 1604, adopted unanimously on 15 June 2005, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, particularly Resolution 1251 (1999), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) for an additional period until 15 December 2005.

















