The United Nations Iran–Iraq Military Observer Group (UNIIMOG) was a United Nations commission created during the Iran–Iraq War by the United Nations Security Council in Resolution 619 of August 9, 1988. The withdraw of UNIIMOG forces in 1991 marked the official end to the Iran-Iraq War.

The United Nations Assistance Mission for Iraq (UNAMI) was formed by the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) Resolution 1500 on 14 August 2003 at the request of the Iraqi government to support national development efforts throughout the country.

United Nations Security Council resolution 479, adopted unanimously on 28 September 1980, after reminding Member States against the use of threats and force in their international relations, the Council called upon Iran and Iraq to immediately cease any further uses of force and instead settle their dispute through negotiations.

United Nations Security Council resolution 514, adopted unanimously on 12 July 1982, after recalling Resolution 479 (1980) and noting the mediation efforts by the Secretary-General, Organisation of the Islamic Conference and the Non-Aligned Movement, the Council expressed its deep concern at the prolonged conflict between Iran and Iraq.

United Nations Security Council resolution 522, adopted unanimously on 4 October 1982, after recalling Resolution 479 (1980) and Resolution 514 (1982), the Council called for an immediate ceasefire between Iran and Iraq, calling for the withdrawal of both sides to their internationally recognised borders.

United Nations Security Council resolution 540, adopted on 31 October 1983, noting the report of the Secretary-General and the increased cooperation from the governments of Iran and Iraq, the Council requested he continue with the mediation efforts in the region.
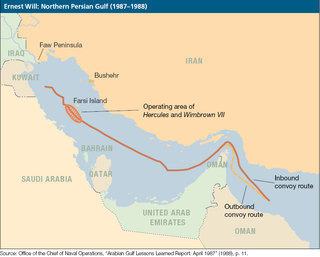
United Nations Security Council resolution 552, adopted on 1 June 1984, after hearing complaints from Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates regarding attacks on their ships by Iran, the Council condemned the attacks, reiterating that Member States should refrain from using threats or use of force in their international relations.

United Nations Security Council resolution 582, adopted unanimously on 24 February 1986, after noting that the Council had been seized for six years and the continued conflict between Iran and Iraq, the Council deplored the initial acts that started the Iran–Iraq War and continuation of the conflict.
United Nations Security Council resolution 588, adopted unanimously on 8 October 1986, after expressing concern at the continuation of the conflict between Iran and Iraq, the Council urged both countries to implement Resolution 582 (1986) without delay.

United Nations Security Council resolution 612 was adopted unanimously on 9 May 1988. After considering a report by the Special Mission dispatched by the Secretary-General to investigate alleged use of chemical weapons in the Iran–Iraq War, the Council condemned the use of chemical weapons in the conflict, contrary to obligations under the Geneva Protocol.

United Nations Security Council resolution 619, adopted unanimously on 9 August 1988, after recalling Resolution 598 (1987), the Council approved a report by the Secretary-General Javier Pérez de Cuéllar on the implementation of paragraph 2 of Resolution 598.
United Nations Security Council resolution 620, adopted unanimously on 26 August 1988, after recalling Resolution 612 (1988) which found evidence of the use of chemical warfare between Iran and Iraq, the Council again condemned the use of such weapons, in violation of the Geneva Protocol.

United Nations Security Council resolution 642, adopted unanimously on 29 September 1989, after recalling resolutions 598 (1987), 618 (1988) and 631 (1989) and having considered a report by the Secretary-General Javier Pérez de Cuéllar on the United Nations Iran–Iraq Military Observer Group, the Council decided:

United Nations Security Council resolution 651, adopted unanimously on 29 March 1990, after recalling resolutions 598 (1987), 619 (1988), 631 (1989) and 642 (1989), and having considered a report by the Secretary-General Javier Pérez de Cuéllar on the United Nations Iran–Iraq Military Observer Group, the Council decided:

United Nations Security Council resolution 671, adopted unanimously on 27 September 1990, after recalling resolutions 598 (1987), 619 (1988), 631 (1989), 642 (1989) and 651 (1990), and having considered a report by the Secretary-General Javier Pérez de Cuéllar on the United Nations Iran–Iraq Military Observer Group, the Council decided:

United Nations Security Council resolution 676, adopted unanimously on 28 November 1990, after recalling resolutions 598 (1987), 618 (1988), 631 (1989), 642 (1989), 651 (1990) and 671 (1990), and having considered a report by the Secretary-General Javier Pérez de Cuéllar on the United Nations Iran–Iraq Military Observer Group, the Council decided:

United Nations Security Council resolution 685, adopted unanimously on 31 January 1991, after recalling resolutions 598 (1987), 618 (1988), 631 (1989), 642 (1989), 651 (1990), 671 (1990) and 676 (1990), and having considered a report by the Secretary-General Javier Pérez de Cuéllar on the United Nations Iran–Iraq Military Observer Group, the Council decided:

United Nations Security Council resolution 700, adopted unanimously on 17 June 1991, after recalling resolutions 661 (1991), 665 (1991), 670 (1991) and 687 (1991), and noting the report by the Secretary-General it requested, the Council, acting under Chapter VII, the Council approved the full implementation of Resolution 687–the arms embargo against Iraq.

United Nations Security Council resolution 715, adopted unanimously on 11 October 1991, after recalling resolutions 687 (1991) and 707 (1991), the Council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, approved plans from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and Secretary-General Javier Pérez de Cuéllar regarding the long-term monitoring of Iraq's weapons programme, requiring it to submit "on-going monitoring and verification" of the country's dual-use facilities.