
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization that aims to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations and countries, achieve international cooperation, and serve as a centre for coordinating the actions of member states. It is widely recognized as the world's largest international organization. The UN is headquartered in New York City, in international territory with certain privileges extraterritorial to the United States, and the UN has other offices in Geneva, Nairobi, Vienna, and The Hague, where the International Court of Justice is headquartered at the Peace Palace.
The Military Staff Committee (MSC) is the United Nations Security Council subsidiary body whose role, as defined by the United Nations Charter, is to plan UN military operations and assist in the regulation of armaments. Although the Military Staff Committee continues to exist, negotiation efforts between the United States, the Soviet Union and other nations in the late 1940s failed, and the committee has since been largely defunct, only serving in an advisory capacity.

The United Nations Mission in Liberia (UNMIL) was a United Nations peacekeeping operation established in September 2003 to monitor a ceasefire agreement in Liberia following the resignation of President Charles Taylor and the conclusion of the Second Liberian Civil War (1999–2003). At its peak it consisted of up to 15,000 UN military personnel and 1,115 police officers, along with civilian political advisors and aid workers.

United Nations Command is the multinational military force established to support the Republic of Korea during and after the Korean War. It was the first international unified command in history, and the first attempt at collective security pursuant to the Charter of the United Nations.

The Unified Task Force (UNITAF) was a United States-led, United Nations-sanctioned multinational force which operated in Somalia from 5 December 1992 until 4 May 1993. A United States initiative, UNITAF was charged with carrying out United Nations Security Council Resolution 794 to create a protected environment for conducting humanitarian operations in the southern half of the country.

United Nations Operation in Somalia I was the first part of a United Nations (UN) sponsored effort to provide, facilitate, and secure humanitarian relief in Somalia, as well as to monitor the first UN-brokered ceasefire of the Somali Civil War conflict in the early 1990s.
The United Kingdom is a founding member of the United Nations and one of five permanent members of the UN Security Council.

United Nations Security Council resolution 644, adopted unanimously on 7 November 1989, after recalling Resolution 637 (1989), the Council endorsed the report by the Secretary-General and decided to establish the United Nations Observer Group in Central America (ONUCA) in accordance with the report.

United Nations Security Council resolution 654, adopted unanimously on 4 May 1990, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989), 644 (1989), 650 (1990) and 653 (1990), the council endorsed a report by the Secretary-General and decided to extend the mandate of the United Nations Observer Group in Central America for a further six months until 7 November 1990.
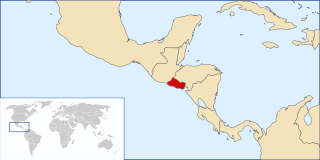
United Nations Security Council resolution 714, adopted unanimously on 30 September 1991, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989) and 693 (1991), the Council welcomed the recent signing of the New York Agreement by the Government of El Salvador and the Farabundo Martí National Liberation Front to bring about an end to the ongoing civil war in El Salvador.

United Nations Security Council resolution 784, adopted unanimously on 30 October 1992, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989), 693 (1991), 714 (1991) and 729 (1992), the council approved a decision by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali to extend the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in El Salvador (ONUSAL) for a further month until 30 November 1992.

United Nations Security Council resolution 791, adopted unanimously on 30 November 1992, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989), 693 (1991), 714 (1991), 729 (1992) and 784 (1992), the Council approved a decision by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali to extend the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in El Salvador (ONUSAL) for a further six months until 31 May 1993.

United Nations Security Council resolution 832, adopted unanimously on 27 May 1993, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989), 693 (1991), 714 (1991), 729 (1992), 784 (1992) and 791 (1992), the council noted a report by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali and enlarged the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in El Salvador (ONUSAL) to include the observation of the electoral process.
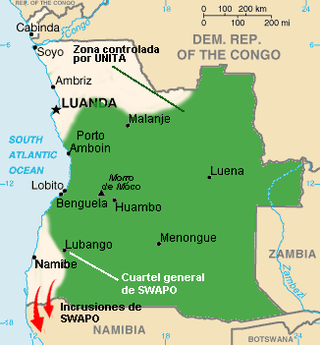
United Nations Security Council resolution 851, adopted unanimously on 15 July 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992), 793 (1992), 804 (1993), 811 (1993), 823 (1993) and 834 (1993), the Council noted the continuing deterioration of the situation in Angola and extended the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II until 15 September 1993, discussing further the peace process in the country.

United Nations Security Council resolution 888, adopted unanimously on 30 November 1993, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989), 693 (1991), 714 (1991), 729 (1992), 784 (1992), 791 (1992) and 832 (1993), the council expressed concern at aspects of the situation in El Salvador and extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in El Salvador (ONUSAL) until 31 May 1994.
United Nations Security Council resolution 920, adopted unanimously on 26 May 1994, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989), 693 (1991), 714 (1991), 729 (1992), 784 (1992), 791 (1992), 832 (1993), 888 (1993), the council discussed the implementation of peace agreements in El Salvador and extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in El Salvador (ONUSAL) until 30 November 1994.

United Nations Security Council resolution 961 was adopted unanimously on 23 November 1994, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989), 693 (1991), 714 (1991), 729 (1992), 784 (1992), 791 (1992), 832 (1993), 888 (1993) and 920 (1994), the council discussed the implementation of peace agreements in El Salvador and extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in El Salvador (ONUSAL) for a final time until 30 April 1995.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1197, adopted unanimously on 18 September 1998, after reaffirming its primary responsibility to maintain international peace and security, the Council addressed co-operation efforts with the Organisation of African Unity (OAU).

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1574, adopted unanimously at a meeting in Nairobi, Kenya, on 19 November 2004, after recalling resolutions 1547 (2004), 1556 (2004) and 1564 (2004), the council welcomed political efforts to resolve the conflicts in Sudan and reiterated its readiness to establish a mission to support the implementation of a Comprehensive Peace Agreement.

The Palestinian Declaration of Independence formally established the State of Palestine, and was written by Palestinian poet Mahmoud Darwish and proclaimed by Yasser Arafat on 15 November 1988 in Algiers, Algeria. It had previously been adopted by the Palestinian National Council (PNC), the legislative body of the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), by a vote of 253 in favour, 46 against, and 10 abstaining. It was read at the closing session of the 19th PNC to a standing ovation. Upon completing the reading of the declaration, Arafat, as Chairman of the PLO, assumed the title of President of Palestine. In April 1989, the PLO Central Council elected Arafat as the first President of the State of Palestine.















