
Airport security includes the techniques and methods used in an attempt to protect passengers, staff, aircraft, and airport property from malicious harm, crime, terrorism, and other threats.

The Convention on International Civil Aviation, also known as the Chicago Convention, established the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a specialized agency of the United Nations charged with coordinating international air travel. The Convention establishes rules of airspace, aircraft registration and safety, security, and sustainability, and details the rights of the signatories in relation to air travel. The convention also contains provisions pertaining to taxation.
Anti-terrorism legislation are laws aimed at fighting terrorism. They usually, if not always, follow specific bombings or assassinations. Anti-terrorism legislation usually includes specific amendments allowing the state to bypass its own legislation when fighting terrorism-related crimes, under alleged grounds of necessity.
The ISIL (Da'esh) and Al-Qaida Sanctions Committee is a committee of the United Nations Security Council tasked with implementing international sanctions against the Islamic State and al-Qaeda. It was established as the Al-Qaida and Taliban Sanctions Committee on 15 October 1999, pursuant to Security Council Resolution 1267, which designated al-Qaeda and the Taliban as terrorist organizations. Following the creation of a separate Taliban Sanctions Committee on 17 June 2011, it was renamed the Al-Qaida Sanctions Committee. The scope of the sanctions regime was expanded to include the Islamic State on 17 December 2015 pursuant to Resolution 2253.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the United Nations:

United Nations Security Council resolution 591, adopted unanimously on 28 November 1986, after recalling resolutions 418 (1977), 421 (1977), 473 (1980) and 558 (1984), the Council strengthened the mandatory arms embargo against apartheid South Africa imposed by Resolution 418, and made it more comprehensive. Resolution 591 sought to clarify vague terms from previous resolutions on the topic.
The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) is a statutory body of the Government of India to regulate civil aviation in India. It became a statutory body under the Aircraft (Amendment) Act, 2020. The DGCA investigates aviation accidents and incidents, maintains all regulations related to aviation and is responsible for issuance of licenses pertaining to aviation like PPL's, SPL's and CPL's in India. It is headquartered along Sri Aurobindo Marg, opposite Safdarjung Airport, in New Delhi. The Government of India is planning to replace the organisation with a Civil Aviation Authority (CAA), modelled on the lines of the American Federal Aviation Administration (FAA).

United Nations Security Council resolution 579, adopted unanimously on 18 December 1985, in a meeting called by the United States, the Council expressed its deep concern at the prevalence in incidents of hostage-taking having grave consequences for the international community and relations between states.
United Nations Security Council resolution 638, adopted unanimously on 31 July 1989, after reaffirming resolutions 579 (1985) and 618 (1988), the Council expressed its deep concern at the prevalence in incidents of hostage-taking having grave consequences for the international community and relations between states.

UN Security Council Resolution 731 was adopted unanimously on 21 January 1992, after the Council recalled resolutions 286 (1970) and 635 (1989), which condemned acts of terrorism; the Council expressed concern over the results of investigations into the destruction of Pan Am Flight 103 over Lockerbie, Scotland, and UTA Flight 772 over Chad and Niger, which implicated officials from the Government of Libya.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1067, adopted on 26 July 1996, after noting various statements and resolutions by the President of the Security Council and International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) deploring the shooting down of two civilian aircraft by the Cuban Air Force on 24 February 1996, the Council called on Cuba to comply with international obligations relating to aviation, particularly the Convention on International Civil Aviation.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1221, adopted unanimously on 12 January 1999, after reaffirming Resolution 696 (1991) and all subsequent resolutions on Angola, particularly resolutions 1196 (1998) and 1219 (1998), the Council condemned the downing of two commercial planes over UNITA-controlled territory in Angola and demanded that UNITA leader Jonas Savimbi co-operate in the search for survivors of the recent plane crashes.
United Nations Security Council resolution 1390, adopted unanimously on 16 January 2002, after recalling resolutions 1267 (1999), 1333 (2000), 1363 (2001), 1368 (2001), 1373 (2001) 1378 (2001) and 1383 (2001) concerning the situation in Afghanistan and terrorism, the Council imposed further sanctions on Osama bin Laden, Al-Qaeda, the Taliban and others associated with them.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1450, adopted on 13 December 2002, after reaffirming the principles of the United Nations Charter and resolutions 1189 (1998), 1269 (1999), 1368 (2001) and 1373 (2001), the Council condemned the attacks on Israeli targets in Kikambala and Mombasa, Kenya on 28 November 2002.
United Nations Security Council resolution 1456, adopted unanimously on 20 January 2003 in a meeting at the foreign minister level, the council adopted a declaration calling on all states to prevent and suppress all support for terrorism. The resolution did not define terrorism, but unlike other previous resolutions, mentioned human rights for the first time.
United Nations Security Council resolution 1535, adopted unanimously on 26 March 2004, after reaffirming resolutions 1373 (2001), 1377 (2001) and 1456 (2003), the council restructured the Counter-Terrorism Committee to enhance the implementation of anti-terrorism measures.
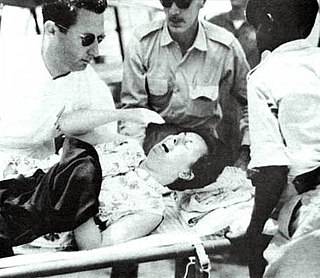
Pan American Flight 103 blew up over Lockerbie, Scotland, on December 21, 1988. 243 passengers, 16 crew members, and 11 people on the ground were killed by the explosion. It was the second most disastrous passenger airline explosion up to that time. By the next day, experts found enough evidence to declare the explosion to have been caused by sabotage. Within days intelligence sources reported an anonymous telephone call to the United States embassy in Helsinki, Finland, on December 5, 1988, warned of possible sabotage on the flight.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1617, adopted unanimously on 29 July 2005, after recalling resolutions 1267 (1999), 1333 (2000), 1363 (2001), 1373 (2001), 1390 (2001), 1452 (2002), 1455 (2003), 1526 (2004) and 1566 (2004) concerning terrorism, the Council renewed sanctions against Al-Qaeda, the Taliban, Osama bin Laden and associated individuals and groups for a further seventeen months.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2166, concerning the shootdown of Malaysia Airlines Flight 17, was sponsored by Australia and adopted unanimously on 21 July 2014. The resolution expressed support for the "efforts to establish a full, thorough and independent international investigation into the incident in accordance with international civil aviation guidelines" and called on all United Nations member states "to provide any requested assistance to civil and criminal investigations".

On 24 February 1996 a Cuban Air Force Mikoyan MiG-29UB shot down two unarmed Cessna 337 Skymaster aircraft operated by Brothers to the Rescue, an organization opposed to the Cuban government. The Organisation of American States (OAS) reported that no warning was given; Cuban government sources said "These people knew what they were doing. They were warned", and that the aircraft had entered Cuban airspace. All the occupants of the aircraft were killed: Carlos Costa, Armando Alejandre, Jr., Mario de la Peña, and Pablo Morales. A third Cessna involved escaped. Previous similar flights had released propaganda leaflets over Cuba.












