Related Research Articles

The 71st United States Congress was a meeting of the legislature of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1929, to March 4, 1931, during the first two years of Herbert Hoover's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1910 United States census.

Walter Folger Brown was an American politician and lawyer who served as the Postmaster General of the United States from March 5, 1929, to March 4, 1933, under Herbert Hoover's administration.

The 50th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1887, to March 4, 1889, during the third and fourth years of Grover Cleveland's first presidency. The president vetoed 212 pieces of legislation, the greatest number in a single session of Congress.

Massachusetts's 1st congressional district is a United States congressional district located in the western and central part of Massachusetts. The state's largest congressional district in area, it covers about one-third of the state and is more rural than the rest. It has the state's highest point, Mount Greylock; the district includes the cities of Springfield, West Springfield, Pittsfield, Holyoke, Agawam, Chicopee and Westfield.

Massachusetts's 2nd congressional district is located in central Massachusetts. It contains the cities of Worcester, which is the second-largest city in New England after Boston, and Northampton in the Pioneer Valley. It is represented by Democrat Jim McGovern.

Massachusetts's 3rd congressional district is located in northeastern and central Massachusetts.

Massachusetts's 4th congressional district is located mostly in southern Massachusetts. It is represented by Democrat Jake Auchincloss. Auchincloss was first elected in 2020.

Massachusetts's 9th congressional district is located in eastern Massachusetts. It is represented by Democrat William R. Keating. With a Cook Partisan Voting Index rating of D+6, it is the least Democratic district in Massachusetts, a state with an all-Democratic congressional delegation.

Massachusetts's 5th congressional district is a congressional district in eastern Massachusetts. The district is represented by Katherine Clark. Massachusetts congressional redistricting after the 2010 census changed the borders of the district starting with the elections of 2012, with the new 3rd district largely taking the place of the old 5th. The 5th district covers many of the communities represented in the old 7th district.

Massachusetts's 8th congressional district is located in eastern Massachusetts, including part of Boston. It is represented by Democrat Stephen Lynch. For one congressional term (1791–1793), it served as the home district of the District of Maine. The district boundaries were significantly changed, as of the elections of 2012, due to redistricting after the 2010 census, with the old 8th district largely being shifted to the new 7th district. The new 8th district comprises many of the communities of the old 9th district, as well as some easternmost Norfolk County communities and northernmost Plymouth County communities of the old 10th district.

Massachusetts's 11th congressional district is an obsolete district that was active during three periods: 1795–1843, 1853–1863, and 1873–1993. The district was located in several different areas of the state. It was most recently eliminated in 1993 after the 1990 U.S. census. Its last congressman was Brian J. Donnelly.

Massachusetts's 7th congressional district is a congressional district located in eastern Massachusetts, including roughly three-fourths of the city of Boston and a few of its northern and southern suburbs. The seat is currently held by Democrat Ayanna Pressley.
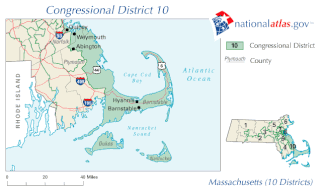
Massachusetts's 10th congressional district is an obsolete district that was active during 1795–2013. It was first located in the District of Maine during 1795–1803, then located in several different areas of Massachusetts. It was most recently eliminated in 2013 as district lines were redrawn to accommodate the loss of the seat due to reapportionment as a result of the 2010 census.

Massachusetts's 6th congressional district is located in northeastern Massachusetts. It contains most of Essex County, including the North Shore and Cape Ann, as well as part of Middlesex County. It is represented by Seth Moulton, who has represented the district since January 2015. The shape of the district went through minor changes effective from the elections of 2012 after Massachusetts congressional redistricting to reflect the 2010 census. The towns of Tewksbury and Billerica were added, along with a small portion of the town of Andover.
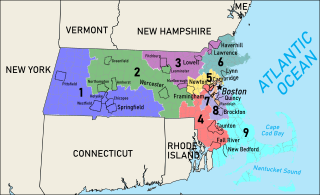
Massachusetts is currently divided into nine congressional districts, each represented by a member of the United States House of Representatives. After the 2010 census, the number of seats in Massachusetts was decreased from 10 to nine, due to the State's low growth in population since the year 2000. This mandatory redistricting after the 2010 census eliminated Massachusetts's 10th congressional district, as well as causing a major shift in how the state's congressional districts are currently drawn.

Massachusetts's 12th congressional district is an obsolete district that was first active 1795–1803 in the District of Maine and 1803–1843 in Eastern Massachusetts. It was later active 1883–1893 in Western Massachusetts and 1893–1983 in Eastern Massachusetts. It was most recently eliminated as a result of the redistricting cycle after the 1980 census. Its last congressman was Gerry Studds, who was redistricted into the 10th district.

Massachusetts's 13th congressional district is an obsolete district that was first active 1793–1803 in the District of Maine, then active 1803–1833 and 1893–1963 in Eastern Massachusetts. It was most recently eliminated in 1963 after the 1960 U.S. census. Its last congressman was James A. Burke, who was redistricted into the 11th district.

The Congressional Pictorial Directory is a picture directory of leaders and members of the United States Congress and other key officials including the President. It is published at least once every Congressional Term and is in the public domain. It was previously published as the Pocket Congressional Directory.
The Official Congressional Directory is the official directory of the United States Congress, prepared by the Joint Committee on Printing (JCP) and published by the United States Government Printing Office (GPO) since 1887. Directories since the 104th Congress (1995–1997) are available online from the Government Publishing Office. Per federal statute the Directory is published and distributed during the first session of each new Congress. It is a designated essential title distributed to Federal depository libraries and the current edition is available for purchase from GPO.
References
- 1 2 "Records of the Committee on Finance and Related Records". National Archives and Records Administration. 2016-08-15. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ Graves, Will. "An Overview of Revolutionary War Pension and Bounty Land Legislation and the Southern Campaigns Pension Transcription Project" . Retrieved 23 October 2018.
- ↑ Resch, John P. (1988). "Politics and Public Culture: The Revolutionary War Pension Act of 1818". Journal of the Early Republic. 8 (2): 139–158. doi:10.2307/3123809. JSTOR 3123809.
- ↑ "Civil War Pensions". Essential Civil War Curriculum. Retrieved 22 October 2018.
- ↑ Elmer C. Hess (1924). Official Congressional Directory: 68th Congress, 1st Session (3rd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office. hdl:2027/njp.32101072368978.
- ↑ Elmer C. Hess (1925). Official Congressional Directory: 68th Congress, 2d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Elmer C. Hess (1926). Official Congressional Directory: 69th Congress, 1st Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Elmer C. Hess (1927). Official Congressional Directory: 69th Congress, 2d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Elmer C. Hess (1928). Official Congressional Directory: 70th Congress, 1st Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Elmer C. Hess (1929). Official Congressional Directory: 70th Congress, 2d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Elmer C. Hess (1929). Official Congressional Directory: 71st Congress, 1st Session (1st ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Elmer C. Hess (1930). Official Congressional Directory: 71st Congress, 2d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ A.B. Heyser (1931). Official Congressional Directory: 71st Congress, 3d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ E.F. Caldwell (1932). Official Congressional Directory: 72d Congress, 1st Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ E.F. Caldwell (1933). Official Congressional Directory: 72d Congress, 2d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Official Congressional Directory: 73d Congress, 1st Session (1st ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office. 1933.
- ↑ Official Congressional Directory: 73d Congress, 2d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office. 1934.
- ↑ C.B. Deane (1935). Official Congressional Directory: 74th Congress, 1st Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ C.B. Deane (1937). Official Congressional Directory: 75th Congress, 1st Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ C.B. Deane (1936). Official Congressional Directory: 74th Congress, 2d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ C.B. Deane (1938). Official Congressional Directory: 75th Congress, 3d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ J.B. Bricken (1939). Official Congressional Directory: 76th Congress, 1st Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ S.A. Lokey (1940). Official Congressional Directory: 76th Congress, 3d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Lewis J. Lawson, Jr. (1941). Official Congressional Directory: 77th Congress, 1st Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Robert W. Hasty (1942). Official Congressional Directory: 77th Congress, 2d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Robert W. Hasty (1943). Official Congressional Directory: 78th Congress, 1st Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ R.E. De Sear (1944). Official Congressional Directory: 78th Congress, 2d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ John H. Pinson (1945). Official Congressional Directory: 79th Congress, 1st Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ J. Hal McCall (1946). Official Congressional Directory for the 79th Congress, 2d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ A.J. Halford (1908). Official Congressional Directory: 60th Congress - 1st Session (3rd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ A.J. Halford (1909). Official Congressional Directory: 60th Congress - 2d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ A.J. Halford (1910). Official Congressional Directory: 61st Congress - 2d Session (3rd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ James S. Henry (1911). Official Congressional Directory: 61st Congress - 3d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ James S. Henry (1911). Official Congressional Directory: 62d Congress - 1st Session. Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ James B. Bell (1912). Official Congressional Directory: 62d Congress - 2d Session (3rd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ James B. Bell (1913). Official Congressional Directory: 62d Congress - 3d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ James B. Bell (1913). Official Congressional Directory: 63d Congress, 1st Session (1st ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Edgar E. Mountjoy (1914). Official Congressional Directory: 63d Congress, 2d Session (3rd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Edgar E. Mountjoy (1915). Official Congressional Directory: 63d Congress, 3d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Edgar E. Mountjoy (1916). Official Congressional Directory: 64th Congress, 1st Session (3rd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Edgar E. Mountjoy (1917). Official Congressional Directory: 64th Congress, 2d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Edgar E. Mountjoy (1917). Official Congressional Directory: 65th Congress, 1st Session (1st ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Edgar E. Mountjoy (1918). Official Congressional Directory: 65th Congress, 2d Session (3rd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Jessie E. Mountjoy (1919). Official Congressional Directory: 65th Congress, 3d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Francis G. Matson (1919). Official Congressional Directory: 66th Congress, 1st Session. Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Francis G. Matson (1920). Official Congressional Directory: 66th Congress, 2d Session (3rd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Francis G. Matson (1921). Official Congressional Directory: 66th Congress, 3d Session (2nd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Francis G. Matson (1921). Official Congressional Directory: 67th Congress, 1st Session (1st ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Elmer C. Hess (1922). Official Congressional Directory: 67th Congress, 2d Session (3rd ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Elmer C. Hess (1922). Official Congressional Directory: 67th Congress, 3d & 4th Session (1st ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ↑ Goldman, Perry M.; Young, James S. (1973). The United States Congressional Directories 1789-1840. New York and London: Columbia University Press. pp. 85–368.
- ↑ "Dates of Sessions of the Congress". United States Senate. Retrieved 24 October 2018.